What is ICD 10 for poorly controlled diabetes?
ICD-10. ICD-10-CM Codes. Factors influencing health status and contact with health services. Persons encountering health services for examinations. Encounter for screening for other diseases and disorders (Z13) Encounter for screening for …
What are the criteria for diagnosis of diabetes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Z13.1 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . POA Exempt. Z13.1 is exempt from POA reporting ( Present On Admission).
What is considered prediabetes A1C ICD 10?
Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus Code Edits Present on Admission (POA) Convert Z13.1 to ICD-9 Code
How to code diabetes correctly?
Z13.1 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Documentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. Clinically undetermined.

What is the ICD-10 code for screening for diabetes?
You would assign ICD-10 code Z13. 1, Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus. This code can be found under “Screening” in the Alphabetical Index of the ICD-10 book.
What is the ICD-10 code for screening?
Z13.9ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for screening, unspecified Z13. 9.
What is the CPT code for diabetes screening?
Medicare Diabetes Screening guideline – CPT 82947, 82950 , 82951.
What ICD-10 code covers hemoglobin A1c screening?
1.
What is an encounter for screening?
Encounter for screening for other diseases and disorders Screening is the testing for disease or disease precursors in asymptomatic individuals so that early detection and treatment can be provided for those who test positive for the disease.
What is the ICD 10 code for screening mammogram?
Z12. 31, Encounter for screening mammogram for malignant neoplasm of breast, is the primary diagnosis code assigned for a screening mammogram. If the mammogram is diagnostic, the ICD-10-CM code assigned is the reason the diagnostic mammogram was performed.Mar 13, 2019
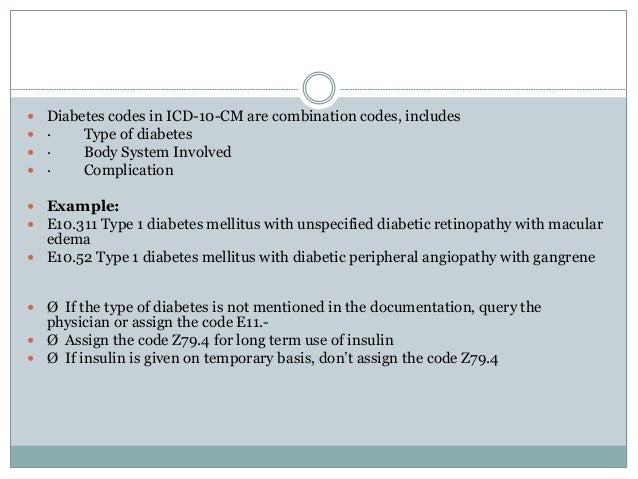
What are the ICD-10 codes for diabetes?
Common Diabetes ICD-10 Diagnosis Codes.E10.22/E11.22 Diabetes, Renal Complication.PLUS.Diabetes, Circulatory/Vascular Complication.Diabetes, Neurological Complication.E10.9. Type 1 Diabetes, w/o complication. E11.9. ... Diabetes, with other Spec. Complications.Type 1 Diabetes with Hypoglycemia.More items...
What is diabetes diagnosis code?
ICD-Code E11* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250. Code I10 is the diagnosis code used for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for new onset diabetes?
E11. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What diagnosis covers hemoglobin A1C?
The measurement of hemoglobin A1c is recommended for diabetes management, including screening, diagnosis, and monitoring for diabetes and prediabetes. hyperglycemia (Skyler et al., 2017).Apr 1, 2019
What diagnosis can be used for hemoglobin A1C?
The A1C test is a blood test that provides information about your average levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, over the past 3 months. The A1C test can be used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.
What diagnosis covers HbA1c?
HbA1c is widely accepted as medically necessary for the management and control of patients with diabetes. It is also valuable to assess hyperglycemia, a history of hyperglycemia or dangerous hypoglycemia.Feb 8, 2016
What is the Z13.1 code?
Z13.1 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus. The code Z13.1 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.#N#The code Z13.1 describes a circumstance which influences the patient's health status but not a current illness or injury. The code is unacceptable as a principal diagnosis.
What is a screening test?
Also called: Screening tests. Screenings are tests that look for diseases before you have symptoms. Screening tests can find diseases early, when they're easier to treat. You can get some screenings in your doctor's office. Others need special equipment, so you may need to go to a different office or clinic.
Where does glucose come from?
Glucose comes from the foods you eat . Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. With type 2 diabetes, the more common type, your body does not make or use insulin well.
Can too much glucose cause heart disease?
Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes. Blood tests can show if you have diabetes.
Can a pregnant woman get diabetes?
Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes. Blood tests can show if you have diabetes. One type of test, the A1C, can also check on how you are managing your diabetes. Exercise, weight control and sticking to your meal plan can help control your diabetes.
Is Z13.1 a POA?
Z13.1 is exempt from POA reporting - The Present on Admission (POA) indicator is used for diagnosis codes included in claims involving inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals. POA indicators must be reported to CMS on each claim to facilitate the grouping of diagnoses codes into the proper Diagnostic Related Groups (DRG).
Can you have diabetes if you have high blood sugar?
You can also have prediabetes. This means that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Having prediabetes puts you at a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'Z13.1 - Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code Z13.1. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code V77.1 was previously used, Z13.1 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetes?
Icd-10 Diagnosis Code Z13.1. The code Z13.1 is exempt from POA reporting. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy.
What are the symptoms of diabetes mellitus?
[6] Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss. [3] Symptoms may also include increased hunger, feeling tired, and sores that do not heal. [3] Often symptoms come on slowly. [6] Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, strokes, diabetic retinopathy which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the limbs which may lead to amputations. [1] The sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. [4] [5] Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. [1] Some people are more genetically at risk than others. [6] Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primarily to diabetes mellitus type 1 and gestational diabetes. [1] In diabetes mellitus type 1 there is a lower total level of insulin to control blood glucose, due to an autoimmune induced loss of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. [12] [13] Diagnosis of diabetes is by blood tests such as fasting plasma glucose, oral glucose tolerance test, or glycated hemoglobin (A1C). [3] Type 2 diabetes is partly preventable by staying a normal weight, exercising regularly, and eating properly. [1] Treatment involves exercise and dietary changes. [1] If blood sugar levels are not adequately lowered, the medication metformin is typically recommended. [7] [14] Many people may eventually also require insulin injections. [9] In those on insulin, routinely checking blood sugar levels is advised; however, this may not be needed in those taking pills. [15] Bariatri Continue reading >>
What is a type 1 exclude note?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as Z13. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. encounter for diagnostic examination-code to sign or symptom Z13 Encounter for screening for other diseases and disorders Z13.0 Encounter for screening for diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism Z13.1 Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus Z13.2 Encounter for screening for nutritional, metabolic and other endocrine disorders Z13.21 Encounter for screening for nutritional disorder Z13.22 Encounter for screening for metabolic disorder Z13.220 Encounter for screening for lipoid disorders Z13.228 Encounter for screening for other metabolic disorders Z13.29 Encounter for screening for other suspected endocrine disorder Z13.4 Encounter for screening for certain developmental disorders in childhood Z13.5 Encounter for screening for eye and ear disorders Z13.6 Encounter for screening for cardiovascular disorders Z13.7 Encounter for screening for genetic and chromosomal anomalies Z13.71 Encounter for nonprocreative screening for genetic disease carrier status Z13.79 Encounter for other screening for genetic and Continue reading >>
What is AAPC coder complete?
AAPC Coder Complete provides all the coding and reimbursement tools needed for inpatient coders, outpatient coders and CDI experts. Quickly view the OPPS fee schedules for freestanding ASCs and hospital based outpatient services in one place. For each CPT code, you can identify the applicable modifiers, status indicators and payment indicators. For procedures that require devices, you can view if there is a credit adjustment policy for the device. Avoid bundling and determine proper modifier use by using the Medicare OPPS CCI checker for up to 25 codes at one time. The cross-reference tools allow you to forward and backward map CPT to ICD-9-CM Volume 1 and 3, ICD-9-CM Volume 1 to ICD-10-CM and ICD-9-CM Volume 1 to the appropriate DRG options. Easily identity the DRG options, including CC and MCC, for each ICD-9-CM Volume 1 code. APC look up provides necessary detail on one page including long descriptor, payment and coverage info and more. CPT Assistant is the official word from the AMA on proper CPT code usage. AAPC Coder's Code Connect add-on allows you to search all CPT Assistant articles from 1990 to present by CPT code to narrow the options to only related articles for quick coding guidance. The HCPCS Coding Clinic delivers the official guidance published quarterly by the American Hospital Association (AHA) Central Office on correct HCPCS level II code usage. Each issue offers consistent and accurate advice for the proper use of HCPCS and includes information on HCPCS reporting for hospitals HCPCS Level 1 (CPT) and Level II codes, the latest code assignments from emerging technologies, and real examples. Continue reading >>
Can diabetes cause heart disease?
Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes. Blood tests can show if you have diabetes. One type of test, the A1C, can also check on how you are managing your diabetes.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10-cm code for cavernoma
- 2. icd-10 code for large breasts
- 3. icd 10 code for onychocryptosis of left great toe
- 4. icd 10 code for nicotine dependence in remission
- 5. icd 10 code for failed outpatient treatment
- 6. icd 10 code for status post bilateral knee replacement
- 7. icd 10 code for ddd cervical
- 8. icd 10 cm code for swelling to her r frontal scalp
- 9. icd 10 code for otitis externa bilateral
- 10. icd 10 cm code for coronary atherosclerosis