What is the ICD 10 code for Intraretinal microvascular abnormalities?
Other intraretinal microvascular abnormalities 1 H35.09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H35.09 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H35.09 - other international versions of ICD-10 H35.09 may differ.
What is the CPT code for removal of epiretinal membrane?
The remaining two codes were regarded as being used for removal of epiretinal membrane (67041) and removal of internal limiting membrane for repair of macular hole and diabetic macular edema (67042).
What is the pathophysiology of epiretinal membrane?
Epiretinal membrane is a slowly progressive disease that develops as a result of the formation of a thin film in the vitreous cavity. Clinical symptoms are represented by a decrease in visual acuity, the appearance of “fog” and distortion of the image in front of the eyes, diplopia.
What are the signs and symptoms of epiretinal membrane disease?
A specific symptom of the disease is diplopia, which persists even when the eyelids of one eye are closed. A complication of the epiretinal membrane is traction swelling of the macula, which occurs when the pathological formation or vitreomacular traction is reduced.

How do you code an epiretinal membrane?
371-373 Macular Pucker. Macular pucker occurs when a contracting epiretinal membrane distorts the underlying retina.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for epiretinal membrane left eye?
379.
What is epiretinal membrane of the eye?
Epiretinal membrane is a delicate tissue-like scar or membrane that forms on top of the retina. When it forms over the macula, it can cause distortion and blurring in your central vision.
Is epiretinal membrane the same as macular degeneration?
Epiretinal membranes are not related to macular degeneration. Epiretinal membranes can but often do not usually affect the other eye. They are quite common and affect up to 10% of people in later years (60 years or older).
What is H25 13 code?
H25. 13 Age-related nuclear cataract, bilateral - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What causes ERM?
Causes. The cause of ERMs is due to a defect in the surface layer of the retina where a type of cell, called glial cells, can migrate through and start to grow in a membranous sheet on the retinal surface.
Where is epiretinal membrane?
An epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a fibrocellular tissue found on the inner surface of the retina. It is semi-translucent and proliferates on the surface of the internal limiting membrane.
How serious is an epiretinal membrane?
ERMs usually cause a few mild symptoms. They are generally watched and not treated. In some instances, ERMs cause loss of vision and visual distortion. The only treatment for an ERM is a surgical procedure called a vitrectomy.
Can epiretinal membrane be caused by cataract surgery?
Patients with ERM are at higher risk for developing inflammatory changes after cataract surgery such as cystoid macular edema, neurosensory detachment and alterations of the inner-outer segment layer. However, these are not associated with any worsening of the BCVA within the first month.
Is epiretinal membrane and macular pucker the same thing?
Macular Pucker, also known as an Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) is an eye condition that affects the macula, the sweet spot of center vision. The back of your eye is lined by the retina, the light seeing layer in the back of the eye.
Can glasses correct epiretinal membrane?
Only surgical treatment can improve vision and remove distortions caused by epiretinal membranes. Nonsurgical treatments can't help — not even glasses, eye drops, medications or vitamins.
Is epiretinal membrane progressive?
Studies have shown that most epiretinal membranes do not grow or cause progressive blurring or distortion of vision.
How do you treat epiretinal membrane?
Epiretinal Membrane Surgery Vitrectomy is carried out to treat Epiretinal Membrane. In this surgery, local or general anesthetics are administered. The surgeon makes tiny cuts and removes the clouded vitreous gel from inside. If needed, the doctor gently peels away the membrane from the retina.
Can glasses correct epiretinal membrane?
Only surgical treatment can improve vision and remove distortions caused by epiretinal membranes. Nonsurgical treatments can't help — not even glasses, eye drops, medications or vitamins.
What is the success rate of epiretinal membrane surgery?
Purpose: Surgery has been successful in removing epiretinal membranes (ERM) from the macula, allowing some improvement in vision in 80-90% of patients; however, complications are relatively frequent.
How long does it take to recover from epiretinal membrane?
Full visual recovery may not be achieved until 3-6 months after your surgery and in some cases up to a year later. Your vision will never return to how it used to be before the problem started. You can eat and drink on the day of your operation and you will spend 4-6 hours in hospital.
What is the ICd 10 code for retinal vein occlusion?
Tributary (branch) retinal vein occlusion, right eye, with macular edema 1 H34.8310 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Trib rtnl vein occlusion, right eye, with macular edema 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H34.8310 became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H34.8310 - other international versions of ICD-10 H34.8310 may differ.
When will the ICD-10-CM H34.8310 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H34.8310 became effective on October 1, 2021.
When will the ICD-10-CM E11.359 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11.359 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can E11.359 be used for reimbursement?
E11.359 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. Short description: Type 2 diabetes w prolif diabetic rtnop w/o macular edema.
What is the CPT code for membrane peeling?
The complex repair code mandates use of membrane peeling. Without it, CPT code 67113 cannot be used.
What is CPT code 67041?
The remaining two codes were regarded as being used for removal of epiretinal membrane (67041) and removal of internal limiting membrane for repair of macular hole and diabetic macular edema (67042). Because the phrases “epiretinal membrane” and “preretinal cellular membrane/macular pucker” appeared in both codes (67038 and 67041, respectively), it was widely interpreted that use of the complex code for retinal detachment repair consisted of the combination of retinal detachment repair with epiretinal membrane peeling. This became the standard replacement for 67108 + 67038. It is important to note that both CPT codes 67041 and 67042, as well as 67043, were to be considered as replacements for 67038.
What is 67113?
67113 - Repair of complex retinal detachment (e.g., proliferative vitreoretinopathy, stage C-1 or greater, diabetic traction retinal detachment, retinopathy of prematurity, retinal tear of greater than 90 degrees), with vitrectomy and membrane peeling, may include air, gas, or silicone oil tamponade, cryotherapy, endolaser photocoagulation, drainage of subretinal fluid, scleral buckling, and/or removal of lens
When did the new CPT code for vitrectomy come into effect?
In 2008, new vitrectomy codes were established in CPT and a new code for complex retinal detachment repair was initi- ated. Here is the new code description that went into effect Jan. 1, 2008, and has since remained unchanged:
What is Pars Plana vitrectomy?
67042 - Pars plana vitrectomy; with removal of internal limiting membrane of retina (e.g., for repair of macular hole, diabetic macular edema ), includes, if performed, intraocular tamponade (i.e., air, gas or silicone oil)
Why is CPT code 67043 obsolete?
CPT code 67043 was fairly obsolete by the time the code was issued due to the development and use of various anti-VEGF drugs administered by intravitreal injection. The CPT system was slower in getting codes into the system, and codes issued in 2008 would have started their development in 2005 — about the time that Rosenfeld et al. published the first proposal for using bevacizumab (Avastin, Genentech) for treating wet AMD (preceded by the use of Macugen [pegaptanib sodium injection, Bausch + Lomb]). 1-3
What is T85.698A?
T85.698A - Other mechanical complication of other specified internal prosthetic devices, implants, and grafts
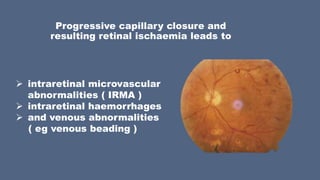
General Information
- The epiretinal membrane is a thin fibrocellular structure devoid of its own blood supply, which is located in the thickness of the vitreous body near the macula. The disease was first described in 1955 by scientist H. Kleinert. Epiretinal membrane is almost twice as often diagnosed in patients after 60 years. In patients under 60 years of age, path...
Causes
- In most cases, the etiology of the epiretinal membrane is associated with involutional changes in the fundus. Specialists in the field of ophthalmology have described cases of the disease against the background of diabetic retinopathy, traumatic injuries, myopia, vitreous detachment or retinal detachment. If the cause of its formation cannot be established, we are talking about the idiopat…
Pathogenesis
- Synthesis of this structure occurs due to glial cells, the leading role among which is assigned to fibrous astrocytes. These cells appear in the vitreous body due to damage to the retina or the posterior parts of the gelatinous substance. The role of retinal pigmentocytes, monocytes and macrophages in the formation of the epiretinal membrane has been proved. Pronounced prolifer…
Symptoms of Epiretinal Membrane
- The disease is characterized by a slowly progressive course. One eye is more often affected. In the case of binocular development, the morphological picture is asymmetric. From a clinical point of view, there are primary and secondary forms. Often, the disease has a latent course for a long time. The first symptoms of pathology are a decrease in central vision, the appearance of “fog” i…
Complications
- A complication of the epiretinal membrane is traction swelling of the macula, which occurs when the pathological formation or vitreomacular traction is reduced. It is possible to eliminate the manifestations of complications only surgically.
Diagnostics
- Diagnosis of the disease is based on the results of ophthalmoscopy, ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound), visometry, tonometry, optical coherence tomography (OCT), fluorescent angiography. 1. During ophthalmoscopy, the epiretinal membrane has a brilliant shade, which is why many authors describe it as “cellophane retinopathy”. At stage Ia, a small yellowish formation appears …
Treatment of Epiretinal Membrane
- Due to the pronounced toxic effect on the organ of vision of medications that were previously used for treatment, preference is now given to surgical tactics. Indications for surgical intervention are a strong decrease in visual acuity, a high risk of macular damage. At the first stage of the operation, a vitrectomy is performed. In this case, the posterior and central parts of …
Prognosis and Prevention
- No specific prevention measures have been developed. Non-specific preventive measures are aimed at pathogenetic mechanisms of development and are reduced to the control of hormonal status, prevention of thrombosis and embolism, compliance with safety rules at work. Patients with an established diagnosis of “epiretinal membrane”, as well as after surgery, should be exam…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for odynophagia
- 2. icd 10 code for myopathy con
- 3. icd 10 code for multiple skin lesions
- 4. icd 10 code for intramural hematoma of thoracic aorta
- 5. www. libraries.ahima.org/ icd-10-cm pcs code for cystourethroscopy with bladder fulguration ??
- 6. icd 9 code for influenza vaccine
- 7. icd code for hypertriglyceridemia
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for blood in stool
- 9. icd 10 code for louti
- 10. icd 10 code for left shoulder avulsion fracture