What is the ICD 10 code for basement membrane dystrophy?
Jun 16, 2015 · Question: What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for Cogan’s corneal dystrophy or epithelial basement membrane dystrophy? Answer: Cogan's dystrophy is H16.321 right eye, H16.322 left eye, or H16.323. Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy is H18.59 only. There is no laterality with this code.
What is the classification of epithelial basement membrane dystrophy?
Corneal epithelial dystrophy; Epithelial corneal dystrophy; Juvenile epithelial corneal dystrophy; Meesman's corneal dystrophy. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.52. Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 - Converted to Parent Code 2022 Non …
What is the ICD 10 code for Cogan’s dystrophy?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.52 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.52 Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 - Converted to Parent Code 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code H18.52 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What is the CPT code for epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy?
Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy, unspecified eye. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H18.529. Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy, unspecified eye. 2021 - New Code 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H73.90 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified disorder of tympanic membrane, unspecified ear.
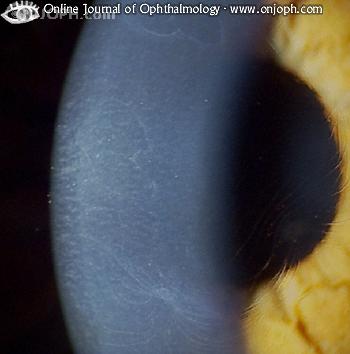
What is epithelial basement membrane dystrophy?
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) is a disease that affects the anterior cornea, causing characteristic slit lamp findings which may result in decreased vision and/or recurrent corneal erosions.12 Jan 2022
Where is the epithelial basement membrane?
The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and endothelium, and the underlying connective tissue.
What is the basement membrane of corneal epithelium?
The corneal epithelial basement membrane is secreted by the overlying epithelia and is comprised of sheets of extracellular matrix constituents, including type IV collagen, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, and various glycoproteins (laminin, entactin, nidogen, and fibronectin) and growth factors that mediate cellular ...1 Aug 2009
What is anterior basement membrane dystrophy of the cornea?
Anterior Basement Membrane Dystrophy (ABMD) is an inherited disorder of the cornea that may present with a variety of symptoms, including recurrent corneal erosions and/or blurred vision. ABMD is a type of corneal dystrophy that affects the thin outside layer of the cornea.
What is an epithelial membrane?
Epithelial membranes consist of epithelial tissue and the connective tissue to which it is attached. The two main types of epithelial membranes are the mucous membranes and serous membranes.
What does basement membrane signify?
: a thin membranous layer of connective tissue that separates a layer of epithelial cells from the underlying lamina propia.
Where is basement membrane of cornea?
The corneal epithelial basement membrane (BM) is positioned between basal epithelial cells and the stroma.27 Sept 2013
What causes anterior basement membrane dystrophy?
There are generally two conditions which cause basement membrane dysfunction – one inherited, and one acquired by a deep corneal abrasion (scratch) which damages the basement membrane. This condition is common, treatable, and rarely leads to significant vision loss.
What is lattice dystrophy?
Lattice corneal dystrophy is a rare inherited condition characterized by amyloid deposition in the corneal stroma. It is a bilateral, slowly progressive disease that results in recurrent corneal erosions and decreased vision due to opacification of the cornea.4 Jun 2019
What causes epithelial dystrophy?
EBMD usually is not inherited , occurring randomly in people with no family history of EBMD. However, familial cases with autosomal dominant inheritance have been reported. In some people with EBMD, a mutation in the TGFBI gene has been identified as the cause. However in most cases, the cause remains unknown.
Is epithelial basement membrane dystrophy rare?
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy is a common form of corneal dystrophy and is also known as map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy and Cogan microcystic dystrophy. This extremely rare form of corneal dystrophy affects the epithelial layer of the cornea.
What is epithelial juvenile corneal dystrophy?
Disease definition. Meesmann corneal dystrophy (MECD) is a rare form of superficial corneal dystrophy characterized by distinct tiny bubble-like, round-to-oval punctate bilateral opacities in the central corneal epithelium, and to a lesser extent in the peripheral cornea, with little impact on vision.
What is the ICd 10 code for corneal dystrophy?
Non-specific codes like H18.52 require more digits to indicate the appropriate level of specificity. Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy: 1 BILLABLE CODE - Use H18.521 for Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy, right eye 2 BILLABLE CODE - Use H18.522 for Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy, left eye 3 BILLABLE CODE - Use H18.523 for Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy, bilateral 4 BILLABLE CODE - Use H18.529 for Epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy, unspecified eye
What is H18.52?
H18.52 is a non-specific and non-billable diagnosis code code, consider using a code with a higher level of specificity for a diagnosis of epithelial (juvenile) corneal dystrophy. The code is not specific and is NOT valid for the year 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. Category or Header define the heading of a category of codes that may be further subdivided by the use of 4th, 5th, 6th or 7th characters.
What is the purpose of the corneal barrier?
This part of the cornea acts as a barrier to help prevent foreign materials, such as dust and bacteria, from entering the eye. In people with Meesmann corneal dystrophy, cysts can appear as early as the first year of life. They usually affect both eyes and increase in number over time.
What is the medical term for corneal ulcers?
Corneal ulcers and infections (Medical Encyclopedia) Fuchs dystrophy (Medical Encyclopedia) Keratoconus (Medical Encyclopedia) Meesmann corneal dystrophy Meesmann corneal dystrophy is an eye disease that affects the cornea, which is the clear front covering of the eye.
What is the term for a condition in which parts of the cornea lose clarity due to a buildup of cloud
Dystrophies - conditions in which parts of the cornea lose clarity due to a buildup of cloudy material. Treatments of corneal disorders include medicines, corneal transplantation, and corneal laser surgery. NIH: National Eye Institute.
What is the outermost layer of the eye?
Your cornea is the outermost layer of your eye. It is clear and shaped like a dome. The cornea helps to shield the rest of the eye from germs, dust, and other harmful matter. It also helps your eye to focus. If you wear contact lenses, they float on top of your corneas.
What are the symptoms of a swollen eyelid?
The resulting symptoms typically include increased sensitivity to light (photophobia), twitching of the eyelids (blepharospasm), increased tear production, the sensation of having a foreign object in the eye, and an inability to tolerate wearing contact lenses.
Corneal Dystrophy: H18.5-
As previously, the fifth character of corneal dystrophy’s ICD-10 code (H18.5-) represents the type of dystrophy:
Corneal Transplant: T86.84-
As previously, the sixth character of the ICD-10 code for a corneal transplant (T86.84-) indicates type of transplant:
Other Changes
Further changes that might be relevant to your practice include the following.
Payer Readiness
While federal payers implemented these codes on Oct. 1 (apart from the two U07 codes, which were implemented earlier), others may be slower to adopt them. You should therefore:
What is EBMD in medical terms?
Epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) is characterized by abnormal quantities of basement membrane and cytoplasmic debris that are misdirected into the corneal epithelium. Clinically, the abnormal deposits in EBMD appear as dot-like opacities, map-like patterns, or whorled fingerprint-like lines in the corneal epithelium. In many patients, the epithelial lesions change in appearance, location and number over time.
What is a corneal bleb?
Corneal blebs are a less common manifestation of map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy. They are localized areas of fibrillogranular material or thickened basement membrane and vary in size from 0.05 millimeters to 0.2 millimeters in diameter. Blebs are best visualized with retroillumination.
What is the anterior layer of the cornea?
The anterior layer of the cornea is composed of the corneal epithelium and its underlying basement membrane. The basal cells of the corneal epithelium produce and adhere to the basement membrane via hemidesmosomes and basement membrane complexes.
What are the dots on a map?
The dots are gray-white opacities which can be round, comma-shaped or irregularly shaped.
Can EBMD cause symptoms?
Patient symptoms vary depending on the severity of the disease and mild conditions may produce no symptoms. Patients with EBMD may present with any of the following abnormal clinical signs and symptoms:
Does EBMD cause vision problems?
In most patients, the disease causes no significant structural deficit to the cornea, no symptoms and no functional vision problems. In patients with clinically significant EBMD, the abnormal deposits of basement membrane can result in the loss of hemidesmosomes between Bowman’s layer and the basal epithelial cells.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for history of pancreatic cancer
- 2. billable icd 10 code for gi bleed
- 3. icd 9 code for left hemiplegia
- 4. icd 10 code for benign neoplasm of hepatic flexure
- 5. icd 10 code for bartons open fracture of left radius
- 6. icd 10 code for bloody nipple discharge
- 7. 2015 icd 10 code for bilateral lower extremity edema
- 8. icd 9 code for hand median nerve compression
- 9. icd 10 code for pulled muscle of foot
- 10. icd 10 code for bronchitis with asthma, subacute