What is the ICD 10 code for Epstein-Barr virus mono?
Oct 01, 2021 · Epstein barr virus disease; Infectious mononucleosis; Infectious mononucleosis (mono) ICD-10-CM B27.90 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 39.0): 865 Viral illness with mcc; 866 Viral illness without mcc; Convert B27.90 to ICD-9-CM. Code History. 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM)
What is the serologic response to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D82.3. Immunodeficiency following hereditary defective response to Epstein-Barr virus. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B27.0.
What does EBV stand for?
The following ICD-10-CM codes support medical necessity and provide coverage for CPT codes: 87428, 87631, 87636, 87637, 0240U, 0241U when used in the outpatient setting as outlined in the related LCD. Group 1 Codes
What is the ICD 10 code for viral mononucleosis?
Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) Viral Capsid Antibody, IgM (8000100257) Test Mnemonic: ... CPT 4 Code: 86665. Note: IgM antibodies to VCA are normally present during acute EBV infection, and generally absent in convalescence. ... The diagnostic information must substantiate all tests ordered and must be in the form of an ICD-10 code or its verbal ...
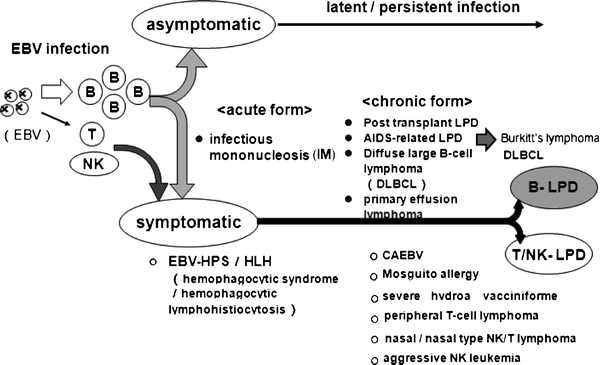
What is the diagnosis code for Epstein-Barr infectious mononucleosis?
ICD-10-CM Code for Infectious mononucleosis, unspecified without complication B27. 90.
Is Epstein-Barr Syndrome the same as mononucleosis?
Epstein-Barr is the virus that causes mononucleosis. You might know this disease better by its nickname, "mono." It's also called the "kissing disease" because of one way you can spread it to someone else. Even though Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) isn't a household name, you've probably been infected without knowing it.Jul 28, 2021
What is Epstein-Barr virus infection?
Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV, is one of the most common human viruses in the world. It spreads primarily through saliva. EBV can cause infectious mononucleosis, also called mono, and other illnesses. Most people will get infected with EBV in their lifetime and will not have any symptoms.
Why is it called Epstein-Barr virus?
In March 1964 The Lancet medical journal published a remarkable piece of research from three scientists called Anthony Epstein, Yvonne Barr, and Burt Achong. They had discovered the first human virus that can cause cancer, which later came to bear two of their names: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV).Mar 26, 2014
Is Epstein-Barr an autoimmune disorder?
Epstein-Barr infects B cells—a type of white blood cell in the immune system. This may explain the association between Epstein-Barr and the EBNA2 disorders: All seven are autoimmune diseases, conditions involving an abnormal immune response to a normal body part.Apr 18, 2018
Can you get Epstein-Barr twice?
Once you're infected with EBV, you carry the virus — usually in a dormant state — for the rest of your life. Sometimes, however, the virus may reactivate. When this happens, you're not likely to become ill. Rarely, reactivated EBV may cause illness in people who have weak immune systems, such as those who have AIDS.Dec 29, 2020
Is Epstein-Barr a precursor to MS?
The researchers say that the association between EBV and MS risk was too strong to be explained by any other known MS risk factors. The findings strongly suggest that EBV is part of the chain of events that leads to most cases of MS.Feb 1, 2022
What is the connection between Epstein-Barr and MS?
Now, a study led by Stanford Medicine researchers has proved that the Epstein-Barr virus, a common type of herpes virus, triggers multiple sclerosis by priming the immune system to attack the body's own nervous system.Jan 24, 2022
What is EBV VCA IgG positive?
EBV-VCA, IgG is an antibody (protein) that is produced by the body in an immune response to an Epstein-Barr virus antigen. EBV stands for Epstein-Barr virus. Epstein-Barr virus is a virus that typically causes a mild to moderate illness.
When was Epstein-Barr identified?
Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) was first discovered in 1964, and was the first known human tumor virus now shown to be associated with a vast number of human diseases. Numerous studies have been conducted to understand infection, propagation, and transformation in various cell types linked to human diseases.Oct 25, 2016
Is Epstein-Barr virus lytic or lysogenic?
Abstract. Epstein-Barr virus, which mainly infects B cells and epithelial cells, has two modes of infection: latent and lytic. Epstein-Barr virus infection is predominantly latent; however, lytic infection is detected in healthy seropositive individuals and becomes more prominent in certain pathological conditions.
How many types of EBV are there?
Two major EBV types have been detected in humans: EBV-1 and EBV-2 (also known as types A and B). EBV-1 and EBV-2 differ in the sequence of the genes that code for the EBV nuclear antigens (EBNA-2, EBNA-3A/3, EBNA-3B/4, and EBNA-3C/6) (Sample et al., 1990).
Document Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2020 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
CMS National Coverage Policy
Title XVIII of the Social Security Act, §1862 (a) (1) (A) allows coverage and payment for only those services that are considered to be reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of illness or injury or to improve the functioning of a malformed body member.#N#Title XVIII of the Social Security Act, §1861 (t) (2) (B) Drugs and Biologicals#N#Title XVIII of the Social Security Act, §1862 (a) (1) (D) Investigational or Experimental#N#CMS Internet-Only Manual, Pub 100-02, Medicare Benefit Policy Manual, Chapter 15, §§50, 50.1, 50.4.1, 50.4.2, 50.4.3, and 50.4.5 Drugs and Biologicals.
Coverage Guidance
Rituximab is a genetically engineered chimeric murine/human monoclonal IgG1 kappa antibody directed against the CD20 antigen." Rituximab binds specifically to the antigen CD20 (human B-lymphocyte-restricted differentiation antigen, Bp35), a hydrophobic transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of approximately 35 kD located on pre-B and mature B lymphocytes.
What is the Epstein-Barr virus?
Epstein-Barr (EB) virus is a herpes group virus that is ubiquitous. It is the cause of classic infectious mononucleosis and is causally implicated in the pathogenesis of Burkitt lymphoma, some nasopharyngeal carcinomas, and rare hereditary lymphoproliferative disorders. The serologic response to EB virus includes antibody to early antigen, ...
What is EBV serology?
The most controversial use of EBV serology is in chronic fatigue syndrome, a complaint predominantly (but not exclusively) of young to middle-aged women, characterized by long persistent debilitating fatigue and a panoply of usually mild somatic complaints.
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Causes for Rejection
Frozen blood; heparin tube; improper labeling; gross specimen contamination; improper storage or transport; specimen too old; leaking or broken tube
Use
This test is intended to be used for the quantitative detection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA and as an aid in the diagnosis and management of EBV infections.
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Causes for Rejection
Hemolysis; lipemia; grossly icteric; visible particulate matter; gross bacterial contamination

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for strabismus left
- 2. icd 10 code for history of b cell lymphoma
- 3. icd 10 code for stage 4 kidney disease
- 4. icd 10 code for infrapatellar tendon tear (arthrofibrosis)
- 5. icd-10 code for anemia of chronic kidney disease
- 6. icd 10 code for endometrial lesion
- 7. icd 10 code for dental radiograph
- 8. icd 10 code for stage iv nsclc
- 9. icd 10 code for elevated blood pressure reading in pregnancy
- 10. what is the icd 10 cm code for hyperthyroidism