What is mild tertiary contractions of the esophagus?
Tertiary contractions of esophagus and dysmotility are ways of saying that the tube that runs from the throat to the stomach called the esophagus is not working like it should. The esophagus is not pushing food down in a coordinated efficient manner. This can cause trouble with swallowing, heart burn, food getting stuck and chest pain.
What are the possible complications of esophageal dilation?
They include:
- Peptic stricture. This is caused by reflux esophagitis. With this problem, the esophagus is irritated by acid reflux. ...
- Schatzki's ring. This is an abnormal ring of tissue. It forms where the esophagus meets the stomach. ...
- Achalasia. This problem prevents food and liquids from moving into the stomach from the esophagus. ...
What is the diagnosis for esophageal cancer?
- Barium swallow, also called an esophagram. ...
- Upper endoscopy, also called esophagus-gastric-duodenoscopy, or EGD. ...
- Endoscopic ultrasound. ...
- Bronchoscopy. ...
- Biopsy. ...
- Biomarker testing of the tumor. ...
- PD-L1 and microsatellite instability (MSI) testing. ...
- HER2 testing. ...
- Computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan. ...
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). ...
What is the diagnosis code for esophageal cancer?
• Metastasis to esophagus typically from breast or lung. Esophageal cancer is classified to ICD-9-CM category 150. The fourth digit identifies the site of the cancer as follows: • 150.0, Cervical esophagus; • 150.1, Thoracic esophagus; • 150.2, Abdominal esophagus; • 150.3, Upper third of esophagus, proximal third of esophagus;
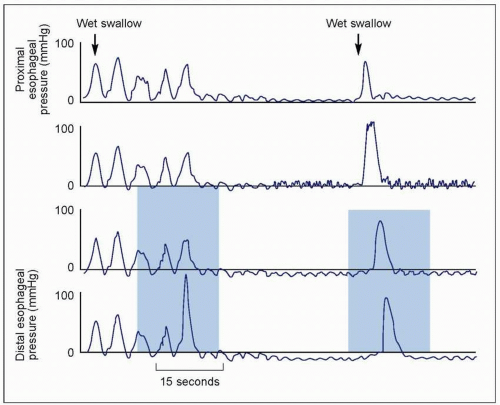
What is esophageal motility?
Esophageal motility refers to contractions occurring in the esophagus, which propel the food bolus forward toward the stomach. When contractions in the esophagus become irregular, unsynchronized or absent, the patient is said to have esophageal dysmotility. Furthermore, what is Presbyesophagus?
What is the shape of the esophagus called?
Presbyesophagus is a term used to describe an abnormal shape of the swallowing tube (esophagus) that occurs in some individuals. In this situation, the esophagus appears wavier than a typically straight esophagus. This change may impact esophageal movement (motility).
What is the esophagus?
Your esophagus is the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (gerd) happens when a muscle at the end of your esophagus does not close properly. This allows stomach contents to leak back, or reflux, into the esophagus and irritate it. You may feel a burning in the chest or throat called heartburn. Sometimes, you can taste stomach fluid in the back of the mouth. This is acid indigestion. If you have these symptoms more than twice a week, you may have gerd. Anyone, including infants and children, can have gerd. If not treated, it can lead to more serious health problems. In some cases, you might need medicines or surgery. However, many people can improve their symptoms by#N#avoiding alcohol and spicy, fatty or acidic foods that trigger heartburn#N#eating smaller meals#N#not eating close to bedtime#N#losing weight if needed#N#wearing loose-fitting clothes 1 avoiding alcohol and spicy, fatty or acidic foods that trigger heartburn 2 eating smaller meals 3 not eating close to bedtime 4 losing weight if needed 5 wearing loose-fitting clothes
What is reflux in the esophagus?
A chronic disorder characterized by reflux of the gastric and/or duodenal contents into the distal esophagus. It is usually caused by incompetence of the lower esophageal sphincter. Symptoms include heartburn and acid indigestion. It may cause injury to the esophageal mucosa.
What are the symptoms of a bile syringe in the esophagus?
Symptoms include heartburn and acid indigestion. Retrograde flow of gastric juice (gastric acid) and/or duodenal contents (bile acids; pancreatic juice) into the distal esophagus, commonly due to incompetence of the lower esophageal sphincter.
The ICD code K224 is used to code Diffuse esophageal spasm
Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) is a condition characterized by uncoordinated contractions of the esophagus, which may cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or regurgitation. In some cases, it may causes symptoms such as chest pain, similar to heart disease. The cause of DES remains unknown.
Coding Notes for K22.4 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #391-392 - Esophagitis, gastroent and misc digest disorders with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K22.4 - Dyskinesia of esophagus'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K22.4. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 530.5 was previously used, K22.4 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd code for osa
- 2. icd 10 code for elvated bnp
- 3. icd 10 code for knee pain and swelling
- 4. 2015 icd 10 code for severe atrophic kidney
- 5. icd 10 code for i50.33
- 6. icd 10 code for volar plate collateral ligaments
- 7. icd 10 code for family hx of uterine cancer
- 8. icd 10 code for fall out of car
- 9. icd 10 code for selfharm
- 10. icd 10 code for left middle finger pip dislocation