What is the ICD 10 code for tonsillitis?
diphtheritic tonsillitis (A36.0); herpesviral pharyngotonsillitis (B00.2); streptococcal tonsillitis (J03.0); tuberculous tonsillitis (A15.8); Vincent's tonsillitis (A69.1); code (B95-B97) to identify infectious agent. code ( B95-B97) to identify infectious agent.
What is acute exudative tonsillitis?
Acute exudative tonsillitis is one of the common diseases among children in pediatric emergency services. Exudative tonsillitis is commonly associated with adenovirus, Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), and Group A streptococcus (GAS), though influenza virus, parainfluenza virus (PIV), or enterovirus (EV) has been reported.
What are the treatment options for tonsillitis?
Treatment for tonsillitis depends on the cause. If the cause is a virus, there is no medicine to treat it. If the cause is a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, your child will need to take antibiotics. It is important for your child to finish the antibiotics even if he or she feels better.
What are the signs and symptoms of tonsillitis?
An acute inflammation of the tonsils caused by viruses or bacteria. Signs and symptoms include fever, enlargement of the tonsils, difficulty swallowing, and enlargement of the regional lymph nodes.
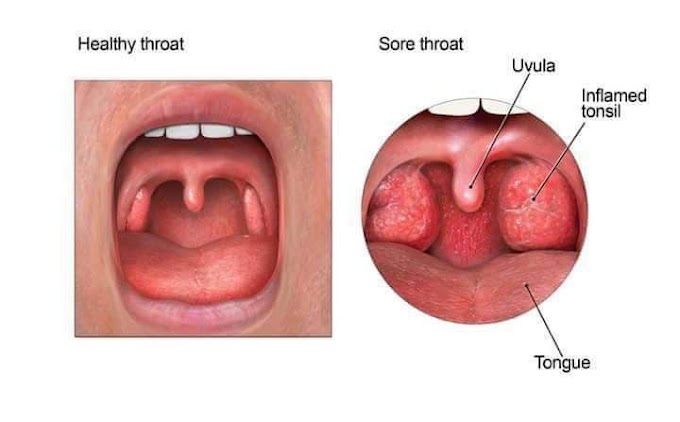
What is exudative tonsillitis?
Tonsillar exudate is a fluid secreted by the tonsils in response to infection or inflammation. Various types of bacterial infections and viral infections cause tonsillitis, or the inflammation of the tonsils, which then results in secretion of tonsillar exudate.
What is the ICD-10 code for exudative pharyngitis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J02 J02.
What causes exudative tonsillitis?
Exudative tonsillitis is commonly associated with adenovirus, Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), and Group A streptococcus (GAS), though influenza virus, parainfluenza virus (PIV), or enterovirus (EV) has been reported.
What are the three types of tonsillitis?
There are three types:Acute tonsillitis. These symptoms usually last 3 or 4 days but can last up to 2 weeks.Recurrent tonsillitis. This is when you get tonsillitis several times in a year.Chronic tonsillitis. This is when you have a long-term tonsil infection.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code R50 9?
ICD-10 | Fever, unspecified (R50. 9)
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
Does exudate on tonsils always mean strep?
Many parents believe that “pus on the tonsils”, or “white pus pockets”, is a sign of strep throat. This is NOT true. While pharyngitis caused by GAS can sometimes cause what Page 2 doctors refer to as “exudate”, in MOST cases of strep throat no exudate is present.
What causes exudate?
Exudates are the result of either increased vascular permeability secondary to inflammation or vessel injury/leakage (hemorrhagic effusion, chylous effusion). An exudative fluid usually contains both increased protein and an increased nucleated cell count.
How do you get exudative pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis is most commonly caused by viral infections such as the common cold, influenza, or mononucleosis. Viral infections don't respond to antibiotics, and treatment is only necessary to help relieve symptoms. Less commonly, pharyngitis is caused by a bacterial infection. Bacterial infections require antibiotics.
What are the 2 types of tonsillitis?
The two types of tonsillitis are:Viral tonsillitis: Most cases (up to 70 percent) of tonsillitis are caused by a virus such as cold or flu (influenza).Bacterial tonsillitis (strep throat): Other cases of tonsillitis are caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria. Bacterial tonsillitis is commonly called strep throat.
What are the classification of tonsillitis?
It can be classified as acute, recurrent and chronic tonsillitis.
What are the 5 tonsils?
TonsilsPalatine tonsils.Lingual tonsils.Tubal tonsils.Pharyngeal tonsils/adenoids.
What does a doctor look for in a child's throat?
The provider will look at your child's throat and neck, checking for things such as redness or white spots on the tonsils and swollen lymph nodes. Your child will probably also have one or more tests to check for strep throat, since it can cause tonsillitis and it requires treatment.
How long does it take to get a rapid strep test?
With the rapid strep test, testing is done in the office, and you get the results within minutes. The throat culture is done in a lab, and it usually takes a few days to get the results.
How common is tonsillitis in children?
Tonsillitis is most common in children over age two. Almost every child in the United States gets it at least once. Tonsillitis caused by bacteria is more common in kids ages 5-15. Tonsillitis caused by a virus is more common in younger children. Adults can get tonsillitis, but it is not very common.
How do tonsils work?
The lymphatic system clears away infection and keeps body fluids in balance. Tonsils and adenoids work by trapping the germs coming in through the mouth and nose.
What is the J03.90 code?
J03.90 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of acute tonsillitis, unspecified. The code J03.90 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. Unspecified diagnosis codes like J03.90 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown ...
How long does it take for a child to recover from tonsil surgery?
Very young children and people who have complications may need to stay in the hospital overnight. It can take a week or two before your child completely recovers from the surgery.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code J03.90 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
The ICD code J03 is used to code Upper respiratory tract infection
Upper respiratory tract infections (URI or URTI) are illnesses caused by an acute infection which involves the upper respiratory tract including the nose, sinuses, pharynx or larynx. This commonly includes tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, and the common cold.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'J03.90 - Acute tonsillitis, unspecified'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code J03.90. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code J03.90 and a single ICD9 code, 463 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the name of the infection that causes the nose to swell?
Upper respiratory tract infections (URI or URTI) are illnesses caused by an acute infection which involves the upper respiratory tract including the nose, sinuses, pharynx or larynx. This commonly includes tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, and the common cold.
What is an additional code note?
Use Additional Code note means a second code must be used in conjunction with this code. Codes with this note are Etiology codes and must be followed by a Manifestation code or codes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for psoriatic arthritis.
- 2. icd 10 code for degenerative joint disease c spine
- 3. icd 10 code for depressive disorder billable
- 4. icd 10 code for acute cholecystitis with cholelithiasis
- 5. icd 10 code for granulomatosis with polyangiitis (gpa)
- 6. icd 9 code for dilated ascending aorta
- 7. icd 10 code for heat exhaustion unspecified
- 8. icd 10 code for rule out uti
- 9. icd 10 code for abdominal wall mass
- 10. icd 10 code for small cell carcinoma of the right lower lobe of the lung