What can cause facial paralysis?
Possible causes of facial paralysis include:
- Middle and inner ear infections
- Trauma to the head
- Endocrine disorders (hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, Cushing's disease)
- Toxins, including botulism, which is used to synthesize Botox and which dogs can get from eating raw meat, according to Wag!
- Tumors, especially growths that invade or compress cranial nerve VII or the brainstem
What are the signs of facial paralysis?
The symptoms might include:
- headaches
- seizures
- difficulty articulating
- difficulty speaking
- loss of balance
- personality changes
- weakness or paralysis in one part or side of the body
- vision changes
- facial numbness
- confusion
What causes paralyzation face?
- Monoplegia is a kind of generalized paralysis that affects just one limb.
- Diplegia affects the same area on both sides, like both arms, both legs, or both sides of your face.
- Hemiplegia affects just one side of your body and is usually caused by a stroke, which damages one side of your brain.
What causes facial nerve paralysis?
The Causes of Facial Paralysis
- Congenital facial paralysis may result from positioning or trauma during pregnancy or be present at birth. ...
- Inflammation is responsible for Bell’s palsy, the most common type of facial paralysis. ...
- Trauma, such as a facial fracture or a deep cut on the face, can damage facial nerves and muscles.
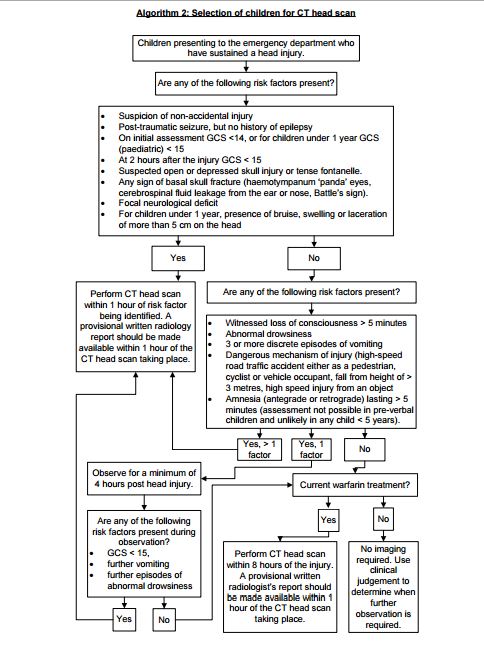
What is the medical term for facial paralysis?
Bell's palsy is an unexplained episode of facial muscle weakness or paralysis. It begins suddenly and worsens over 48 hours. This condition results from damage to the facial nerve (the 7th cranial nerve). Pain and discomfort usually occur on one side of the face or head. Bell's palsy can strike anyone at any age.
What is unilateral facial paralysis?
Overview. Bell's palsy is a condition that causes sudden weakness in the muscles on one side of the face. In most cases, the weakness is temporary and significantly improves over weeks. The weakness makes half of the face appear to droop. Smiles are one-sided, and the eye on the affected side resists closing.
What is the difference between facial nerve palsy and Bell's palsy?
In Bell's palsy there is inflammation around the facial nerve and this pressure causes facial paralysis on the affected side. Facial nerve palsy is the most common acute condition involving only one nerve, with Bell's palsy being the most common cause of acute facial paralysis.
What is the ICD-10 code for left facial droop?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I69. 392 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I69.
What is the difference between paresis and Plegia?
Paresis is a reduction in muscle strength with a limited range of voluntary movement. Paralysis (-plegia) is a complete inability to perform any movement.
How can you differentiate bilateral UMN and LMN facial palsy?
The most important factor when considering the differential diagnosis of facial nerve palsy is whether the lesion is LMN or UMN. Due to bilateral cortical innervation of the muscles of the upper face, only LMN lesions will result in complete facial paralysis, although this is not always the case.
What is the difference between Bell's palsy and Ramsay Hunt?
Compared with Bell's palsy (facial paralysis without rash), patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome often have more severe paralysis at onset and are less likely to recover completely.
Is there a difference between palsy and paralysis?
Whereas the term "palsy" includes both entities, the term "paralysis" should only be used to describe total loss of nerve function. Patients with incomplete acute Bell's palsy (paresis) should start to improve their facial function early (1-2 wk after onset) and are expected to recover completely within 3 months.
How can you tell the difference between Bell's palsy and a stroke?
According to a recent study in the Annals of Emergency Medicine, if a patient cannot move his forehead, then the diagnosis is likely Bell's Palsy. However, a patient who can move his forehead, despite partial paralysis of the face, is significantly more likely to be experiencing a stroke.
What is the ICD-10 code for left sided weakness?
Hemiplegia, unspecified affecting left dominant side The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G81. 92 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G81.
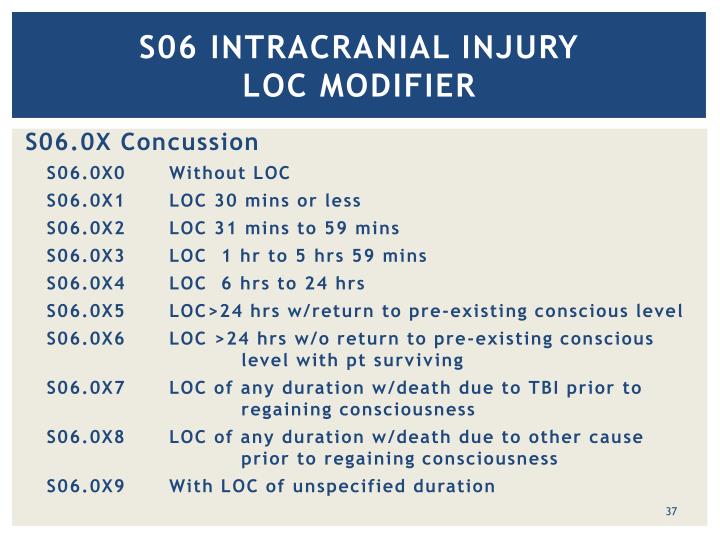
What is the ICD-10 code for Bell's palsy?
ICD-10 code G51. 0 for Bell's palsy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is the ICD-10 for CVA?
I63. 9 - Cerebral infarction, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What is unilateral facial paralysis?
A syndrome characterized by the acute onset of unilateral facial paralysis which progresses over a 2-5 day period. Weakness of the orbicularis oculi muscle and resulting incomplete eye closure may be associated with corneal injury. Pain behind the ear often precedes the onset of paralysis.
How long does it take for Bell's Palsy to show symptoms?
Symptoms are usually worst about 48 hours after they start. Scientists think that a viral infection makes the facial nerve swell or become inflamed. You are most likely to get bell's palsy if you are pregnant, diabetic or sick with a cold or flu.three in four patients improve without treatment.
What is right facial nerve disorder?
Right facial nerve disorder. Clinical Information. A disorder characterized by involvement of the facial nerve (seventh cranial nerve). A non-neoplastic or neoplastic disorder affecting the facial nerve (seventh cranial nerve). Diseases of the facial nerve or nuclei. Pontine disorders may affect the facial nuclei or nerve fascicle.
What causes facial nerves to be affected?
Diseases of the facial nerve or nuclei. Pontine disorders may affect the facial nuclei or nerve fascicle. The nerve may be involved intracranially, along its course through the petrous portion of the temporal bone, or along its extracranial course.
What is an orofacial anomaly?
The presence of hypertelorism may indicate aneuploidy. A congenital birth defect characterized by incomplete development or absence of face structures, usually affecting one side of the face.
What is a rare congenital malformation characterized by micrognathia, posterior retraction of the
A rare congenital malformation characterized by micrognathia, posterior retraction of the tongue, and cleft palate. A rare syndrome that is inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive pattern and caused by mutations in the myh3 gene. It is a severe form of arthrogryposis.
What is a congenital malformation characterized by?
Congenital malformation characterized by micrognathia, glossoptosis and cleft palate.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for extrapyramidal symptoms
- 2. billable icd 10 code for femoral nailing closed reduction
- 3. icd 10 code for hx of ptsd
- 4. icd-10-cm code for patient was stabbed in the arm with a knife during a fight
- 5. 2018 icd 10 code for portal hypertension with gastropathy
- 6. icd 10 code for post surgery complications
- 7. icd 10 code for bifascicular block. quizlet
- 8. icd 10 code for anti diabetes type 2
- 9. icd-10 code for z83.42
- 10. 2015 icd 9 code for myelonisis