What is the ICD 10 code for neoplasm of the larynx?
Personal history of malignant neoplasm of larynx. Z85.21 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for family history of neoplasm?
Z80.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Family history of malignant neoplasm of organs or systems The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z80.8 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for malignant neoplasm?
Z80.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z80.8 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z80.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z80.8 may differ. C02 Malignant neoplasm of other and unspecif...
What is the ICD 10 code for Lynch syndrome?
Z80.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z80.0 became effective on October 1, 2020. ... Family history of lynch syndrome (inherited condition causes high risk of colon cancer)

What is the ICD-10 code for history of laryngeal cancer?
ICD-10 code Z85. 21 for Personal history of malignant neoplasm of larynx is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for laryngeal cancer?
C32. 9 - Malignant neoplasm of larynx, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
What is diagnosis code R90 82?
ICD-10 code R90. 82 for White matter disease, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Can Z80 0 be a primary diagnosis?
Correct Coding Guidelines states to use Z12. 11 as primary diagnosis and Z80. 0 as secondary for family histories.
What is laryngeal carcinoma?
Laryngeal cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the larynx. Use of tobacco products and drinking too much alcohol can affect the risk of laryngeal cancer. Signs and symptoms of laryngeal cancer include a sore throat and ear pain.
What does Transglottic mean?
trans·glot·tic (trans-glot'ik), Vertical crossing of the glottis, as in the spread of carcinoma from the supraglottic to the infraglottic area.
What is diagnosis code R42?
Dizziness and GiddinessCode R42 is the diagnosis code used for Dizziness and Giddiness. It is a disorder characterized by a sensation as if the external world were revolving around the patient (objective vertigo) or as if he himself were revolving in space (subjective vertigo).
What is white matter disease?
White matter disease is an umbrella term for damage to your brain's white matter caused by reduced blood flow to the tissue. It can cause issues with memory, balance and mobility. People who have risk factors for cardiovascular disease also have a greater risk of developing white matter disease.
What is ischemic white matter disease?
White matter disease is a disease that affects the nerves that link various parts of the brain to each other and to the spinal cord. These nerves are also called white matter. White matter disease causes these areas to decline in their functionality. This disease is also referred to as leukoaraiosis.
Can Z86 010 be a primary diagnosis?
If you are receiving denials for ICD-10-CM diagnosis code Z86. 010 as "not a primary diagnosis", try submitting the claim with Z09 as primary, followed by Z86. 010. Per ICD-10 guidelines, code first any follow-up examination after completed treatment (Z09).
Can Z12 11 be a primary diagnosis?
If the patient presents for a screening colonoscopy and a polyp or any other lesion/diagnosis is found, the primary diagnosis is still going to be Z12. 11, Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of colon. The coder should also report the polyp or findings as additional diagnosis codes.
What is the difference between 45378 and 45380?
A family of CPT codes applies to colonoscopy. For example, code 45378 applies to a colonoscopy in which no polyp is detected, while codes 45380-45385 apply to colonoscopy that involves an intervention (e.g., 45385 is the code for colonoscopy with polypectomy.)
What are white matter lesions?
White matter lesions (WMLs) are areas of abnormal myelination in the brain. These lesions are best visualized as hyperintensities on T2 weighted and FLAIR (Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery) sequences of magnetic resonance imaging. They are considered a marker of small vessel disease.
What are white matter changes in the brain?
White matter disease is the wearing away of tissue in the largest and deepest part of your brain that has a number of causes, including aging. This tissue contains millions of nerve fibers, or axons, that connect other parts of the brain and spinal cord and signal your nerves to talk to one another.
What is white matter hyperintensities?
White matter hyperintensities (WMHs) are lesions in the brain that show up as areas of increased brightness when visualised by T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). WMH's are also referred to as Leukoaraiosis and are often found in CT or MRI's of older patients.
What does white matter do in the brain?
In the most general sense, the gray matter of the brain facilitates information processing, and the white matter facilitates information transfer; both are critical for efficient operation of the neural networks responsible for a specific mental domain.
What is the family history of lynch syndrome?
Family history of lynch syndrome (inherited condition causes high risk of colon cancer) Family history of malignant neoplasm of biliary tract. Family history of malignant neoplasm of colon in first degree relative under age 60. Family history of malignant neoplasm of colon in two or more first degree relatives.
When will the ICD-10 Z80.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z80.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a Z77-Z99?
Z77-Z99 Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status
When will the ICD-10 Z80.49 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z80.49 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a Z77-Z99?
Z77-Z99 Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status
When will the ICd 10 Z85.21 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z85.21 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a Z77-Z99?
Z77-Z99 Persons with potential health hazards related to family and personal history and certain conditions influencing health status
What is the ICd code for malignant neoplasm of the larynx?
Z85.21 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of personal history of malignant neoplasm of larynx. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is DRG 826-830?
DRG Group #826-830 - Myeloprolif disord or poorly differentiated neoplasms with other operating room procedure without CC or MCC.
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) requires medical coders to indicate whether or not a condition was present at the time of admission, in order to properly assign MS-DRG codes.
What is DRG group 011-013?
DRG Group #011-013 - Tracheostomy for face, mouth and neck diagnoses without CC or MCC.
What is the ICd 10 code for malignant neoplasm of the larynx?
V10.21 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of personal history of malignant neoplasm of larynx. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
What are the symptoms of head and neck cancer?
Symptoms include. A lump or sore that does not heal. A sore throat that does not go away. Trouble swallowing. A change or hoarseness in the voice.
What is a code also note?
Code also note - A "code also" note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction.
How do you know if you have esophageal cancer?
Signs and Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer. Trouble swallowing. The most common symptom of esophageal cancer is a problem swallowing, with a feeling like the food is stuck in the throat or chest, or even choking on food. Chest pain. Sometimes, people have pain or discomfort in the middle part of their chest. Weight loss
How is esophageal cancer treated?
Techniques for this vary, but two standard approaches are the trans-thoracic approach, where the surgery is done through the opened chest cage, and the trans-hiatal approach, where surgery is done through the abdominal cavity from below . A common approach is the removal of the esophagus (called “esophagectomy”) and replacement of it by the left half of the transverse colon. The mortality rate of this procedure in the hands of an experienced cancer surgeon is about 7%.
Can esophageal cancer be caused by gastrin?
Most esophage al cancers arise after years of chronic reflux. Long term exposure to gastri
Does the literature cite the exact location of cancer?
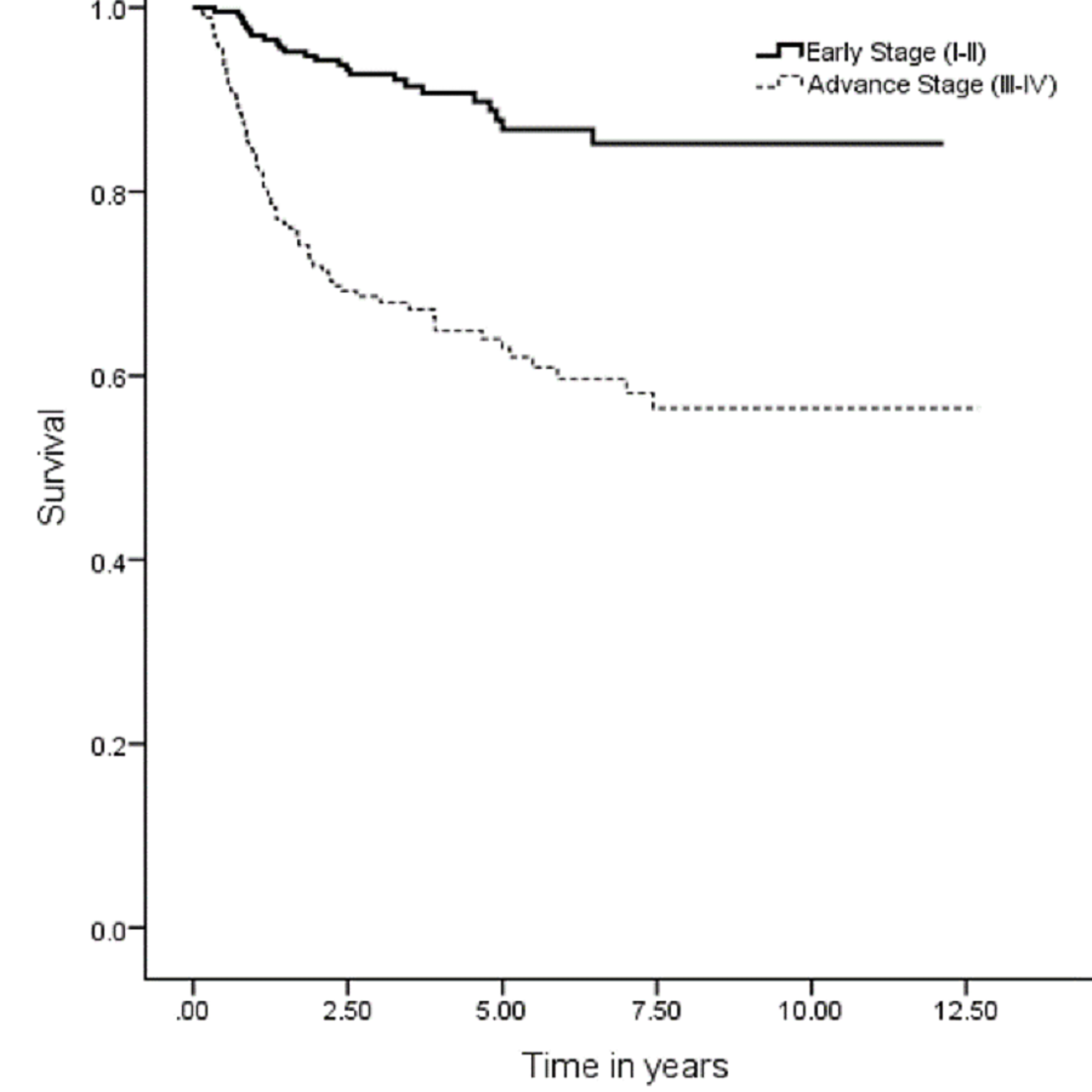
Most of the literature, however, does not cite the exact location of the cancer and therefore we only get general survival data. There are similar problems with cancer staging as some authors are very precise, even citing the TNM system on top of the stage I to IV nomenclature, but others only report about a “group that was seen in their clinic”.
Can GERD cause cancer?
Most people with GERD will not develop the cancer.
Is stage 1 esophageal cancer better than stage 2?
There seems to be a consensus that for stage I esophageal cancer surgery alone would be the treatment of choice, although better survival rates may still be achieved with with additional radiotherapy or chemotherapy. No clinical trials, however, have been done to prove this. With stage II esophageal cancer, as can be seen from the above table, the results are better by about 20 % if radiation therapy is given first followed by surgery ( 24.5 % versus 45 % ).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for influenza vaccination
- 2. icd 10 code for arthrocentesis of ganglion cyst of toe joint, both injection and aspiration
- 3. icd 10 code for intra-abdominal abscess
- 4. icd-10 code for distal interphalangeal joint osteoarthritis
- 5. icd-1- code for elevated bloodpressure
- 6. icd 10 code for pap smear screen
- 7. icd-10 code for vancomycin trough
- 8. 2019 icd 10 code for spur on knee
- 9. icd 10 cm code for febrile illness.
- 10. icd 10 code for injury left thigh