What should be the normal fasting blood glucose?
The results of a fasting test with respect to glucose levels in the body are as follows:
- Normal: 3.9 to 5.4 mmols/l (70 to 99 mg/dl)
- Prediabetes or Impaired Glucose Tolerance: 5.5 to 6.9 mmol/l (100 to 125 mg/dl)
- Diagnosis of diabetes: 7.0 mmol/l (126 mg/dl) or above [361]
What does abnormal fasting glucose mean?
This measures your blood sugar after an overnight fast (not eating). A fasting blood sugar level of 99 mg/dL or lower is normal, 100 to 125 mg/dL indicates you have prediabetes, and 126 mg/dL or higher indicates you have diabetes. This measures your blood sugar before and after you drink a liquid that contains glucose.
What is a normal non fasting glucose level?
What Is Normal Non-Fasting Glucose? Normal non-fasting blood sugar levels should be less than 180 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for those with diabetes, according to the ADA. For those without diabetes, it's less than 140 mg/dL, according to Virginia Mason Diabetes Care.
Is 171 blood sugar after eating normal?
Normally, when fasting, the blood sugar level should be less than 110 mg/dl. One or two hours after a meal, levels up to 180 mg/dl are considered normal. But, having blood sugar level more than 180 m/dl, even after a meal means that you have diabetes.
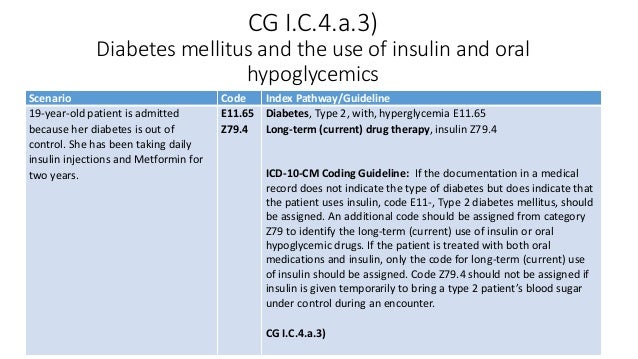
What is the ICD-10 code R73 09?
The ICD-10 code for prediabetes is R73. 09.
What is the diagnosis code for glucose?
ICD-10 Code for Other abnormal glucose- R73. 09- Codify by AAPC.
What diagnosis code covers hgb1c?
09: Other abnormal glucose.
What is meaning of impaired fasting glucose?
Impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG) is sometimes called pre-diabetes. This is when blood glucose levels in the body are raised, but are not high enough to mean that the person has diabetes. IFG means that the body isn't able to use glucose as efficiently as it should.
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What diagnosis will cover 83036?
Diabetes Hemoglobin A1c Testing Claims including procedure code 83036 or 83037 should include a line item with the resulting CPT procedure code below and be billed with a zero charge.
Can you code E11 21 and E11 22 together?
21 and E11. 22 have an excludes 1 notes therefore they can be coded together as long as a separate renal manifestation is present, I would just be careful when coding the actual renal condition as there are some renal codes that are excluded when using CKD codes.
What is 83036 used for?
Group 1CodeDescription83036HEMOGLOBIN; GLYCOSYLATED (A1C)
How is impaired fasting glucose diagnosis?
How is IFG diagnosed? IFG and diabetes are diagnosed by testing blood glucose levels If your fasting blood glucose level is found to be between 3.6mmol/l and 6mmol/l, this means that your blood glucose level is normal. If your fasting blood glucose level is 7mmol/l or higher, this may mean that you have diabetes.
What is the difference between impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose?
Impaired glucose tolerance is defined as two-hour glucose levels of 140 to 199 mg per dL (7.8 to 11.0 mmol) on the 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, and impaired fasting glucose is defined as glucose levels of 100 to 125 mg per dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol per L) in fasting patients.
Is impaired fasting glucose the same as prediabetes?
Prediabetes is when a person's blood glucose levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as Type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes is the same as impaired glucose intolerance (IGT) or impaired fasting glucose (IFG).
What diagnosis covers CBC with diff?
Specific indications for CBC with differential count related to the WBC include signs, symptoms, test results, illness, or disease associated with leukemia, infections or inflammatory processes, suspected bone marrow failure or bone marrow infiltrate, suspected myeloproliferative, myelodysplastic or lymphoproliferative ...
What ICD 10 code covers CBC with diff?
89.
Does Medicare cover hemoglobin A1c test?
Hemoglobin A1c Tests: Your doctor might order a hemoglobin A1c lab test. This test measures how well your blood glucose has been controlled over the past 3 months. Medicare may cover this test for anyone with diabetes if it is ordered by his or her doctor.
How often does medicare pay for hemoglobin A1c?
Diabetes screenings covers glucose laboratory test screenings (with or without a carbohydrate challenge) if your doctor determines you're at risk for developing diabetes. You may be eligible for up to 2 screenings each year.
What does it mean when you have high glucose levels?
Higher than normal amount of glucose (a type of sugar) in the blood. Hyperglycemia can be a sign of diabetes or other conditions.
When will the ICD-10-CM R73.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R73.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the difference between fasting glucose and glucose tolerance?
A condition referring to fasting plasma glucose levels being less than 140 mg per deciliter while the plasma glucose levels after a glucose tolerance test being more than 200 mg per deciliter at 30, 60, or 90 minutes. It is observed in patients with diabetes mellitus. Other causes include immune disorders, genetic syndromes, and cirrhosis.
What does it mean when you have a high blood glucose level?
This condition is seen frequently in diabetes mellitus, but also occurs with other diseases and malnutrition. Pre-diabetes means you have blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Glucose comes from the foods you eat.
What is the state of latent impairment of carbohydrate metabolism in which the criteria for diabetes mellitus are?
State of latent impairment of carbohydrate metabolism in which the criteria for diabetes mellitus are not all satisfied; sometimes controllable by diet alone; called also impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glucose. The time period before the development of symptomatic diabetes.
When will ICD-10-CM R73.09 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R73.09 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can diabetes cause high blood glucose levels?
Too much glucose in your blood can damage your body over time. If you have pre-diabetes, you are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.most people with pre-diabetes don't have any symptoms. Your doctor can test your blood to find out if your blood glucose levels are higher than normal.
What is the ICd 10 code for impaired glucose tolerance?
Impaired glucose tolerance (oral) 1 R73.02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM R73.02 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R73.02 - other international versions of ICD-10 R73.02 may differ.
When will ICD-10-CM R73.02 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R73.02 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for diabetes mellitus?
Encounter for screening for diabetes mellitus 1 Z13.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Z13.1 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z13.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z13.1 may differ.
When will the ICD-10 Z13.1 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z13.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for type 1 diabetes with gastroparesis
- 2. icd 10 code for bcc forehead
- 3. icd 10 code for six weeks pregnant
- 4. icd 10 code for right upper extremity lymphedema
- 5. icd-10-cm code for hyperanticoagulation with contusion of left arm
- 6. icd 10 code for diziness
- 7. icd 9 code for enterococcal bacteremia
- 8. icd-10 code for prevnar 13 vaccine
- 9. what is the icd 10 code for symptomatic fibroids?
- 10. icd code for acl repair