ICD-10 codes for feeding tube K94.1 Enterostomy complications K94.10 Enterostomy complication, unspecified
What is the ICD 10 code for feeding difficulties?
Feeding difficulties 1 R63.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM R63.3 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R63.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 R63.3 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for attention to gastrostomy?
Encounter for attention to gastrostomy Attention to gastrostomy (artificial opening to stomach); Attention to gastrostomy done; Care of gastrostomy tube done; Gastrostomy (artificial opening to stomach) tube care; artificial opening status only, without need for care (Z93.-) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K94.23 [convert to ICD-9-CM]
What is the ICD-10 code for sensory food aversion?
Sensory food aversion ICD-10-CM R63.3 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 640 Miscellaneous disorders of nutrition, metabolism, fluids and electrolytes with mcc 641 Miscellaneous disorders of nutrition, metabolism, fluids and electrolytes without mcc
See more
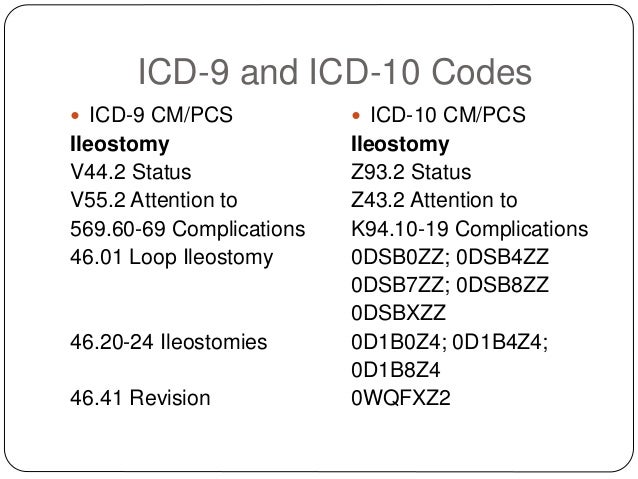
What is the ICD-10 code for presence of feeding tube?
Other artificial openings of gastrointestinal tract status The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z93. 4 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z93.
What is the ICD-10 code for enteral feeding?
Encounter for attention to gastrostomy The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z43. 1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z43. 1 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z43.
How do you code a feeding tube?
For coding insertion of percutaneous gastrostomy tube placement, medical coders can report CPT code 49440 and 49441.
What is the ICD-10 code for NG tube?
Therefore, if the sole objective of inserting the NGT (Dobhoff tube) is for feeding purposes, then code only 3E0G36Z, Introduction of nutritional substance into upper GI, percutaneous approach. In intubated patients, an NG or OG (orogastric) tube is often in place and set to low-intermittent suction (LIS).
What is diagnosis code Z71 3?
Dietary counseling and surveillanceICD-10 code Z71. 3 for Dietary counseling and surveillance is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
Is PEG tube A ICD-10?
ICD-10-CM Code for Gastrostomy status Z93. 1.
How do you code a PEG tube placement?
43246 is probably the most appropriate code if you are looking for a true percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy(PEG) tube.
What is the ICD 10 code for feeding difficulties?
ICD-10 code R63. 3 for Feeding difficulties is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Is an NG tube a gastrostomy?
Gastrostomy tubes, also called G-tubes or PEG tubes, are short tubes that go through the abdominal wall straight into the stomach. Nasogastric tubes, or NG tubes, are thin, flexible tubes inserted through the nose that travel down the esophagus into the stomach.
Can you bill for NG tube placement?
This is endoscopic guidance of an NG tube which is placed by the physician from start to finish and not just to look that the tube placed by anesthesia or nurse is in good position. If done by ancillary personnel, this can't be billed by the physician.
How do you bill for feeding?
What CPT codes do I use for evaluation and treatment of swallowing and feeding disorders? Report a clinical evaluation of swallowing and feeding with CPT 92610 (evaluation of oral and pharyngeal swallowing function). For treatment, use CPT 92526 (treatment of swallowing dysfunction and/or oral function for feeding).
What is procedure code 43246?
Group 1CodeDescription43246Egd place gastrostomy tube43247Egd remove foreign body43248Egd guide wire insertion43249Esoph egd dilation <30 mm60 more rows
What is the CPT code for placement of upper GI feeding tube?
43246What to look for: The operative note for 43246 will describe an upper GI endoscopy with insertion of the gastrostomy tube. As the code descriptor specifies, placement of this type involves both an endoscopic and a percutaneous (through the skin) component.
What is the CPT code 43761?
Introduction Procedures on the StomachThe Current Procedural Terminology (CPT®) code 43761 as maintained by American Medical Association, is a medical procedural code under the range - Introduction Procedures on the Stomach.
What is the ICd 9 code for feeding tube insertion?
In ICD-9-CM, if the NGT was used for feeding only, it was captured with ICD-9-CM code 96.6, enteral infusion of concentrated nutritional substances. In ICD-10, however, proper coding of NG feeding tube insertion requires coders to consider a few more details.
What is the code for a Dobhoff tube?
Therefore, if the sole objective of inserting the NGT (Dobhoff tube) is for feeding purposes, then code only 3E0G36Z, Introduction of nutritional substance into upper GI, percutaneous approach.
How long does a NG tube last?
When an NG tube is used for nutrition alone, it either runs continuously, 16 hours on and eight hours off, or by bolus feedings, meaning feeding is delivered en masse at one time. Bolus feedings are tantamount to eating meals three to five times a day. A Look at the Codes.
How big is a Dobhoff tube?
A Dobhoff tube is a small-bore, flexible tube that typically has an inside diameter of about 0.15 inches (4 mm) that is inserted into the stomach by way of the nasal passage. Use of this particular type of NG tube is considered a best practice. Following insertion, correct placement is confirmed by X-ray.
What is NG tube?
For inpatients, the NG tube (NGT) is generally used to aspirate stomach contents or administer nourishment and medicine to people who cannot ingest anything by mouth.
What is the ICD-10 PCS?
The ICD-10-PCS reference manual defines introduction as “putting in or on a therapeutic, diagnostic, nutritional, physiological, or prophylactic substance, except blood or blood products,” and gives the example of “infusion of total parenteral nutrition via central venous catheter: 3E0436Z.”
Why is NG intubation necessary?
NG intubation is medically necessary for a variety of clinical situations, including: Patients who can’t eat or swallow. Cases of neck or facial injuries. When mechanical ventilation is required or the patient is comatose. To relieve pressure on intestinal obstruction or blockage.
What is the code for a gastrostomy tube?
Prior to 2019, a single code, 43760, was used to report replacement of a G-tube without imaging or endoscopic guidance. As of January 1, 2019, 43760 is no longer valid. Instead, CPT® introduced two new codes to better reflect the work involved when replacing gastrostomy tubes:
What is the code for a G tube replacement?
In these cases, replacement of the G-tube is “straightforward and would be reported with code 43762,” CPT Assistant continues, and provides the following example:
How long does it take for a G tube to be removed?
If the gastrostomy tract has had time to mature (eg, at least four-weeks old), and the G-tube has not been removed for more than four to six hours, a replacement tube may be placed through the same gastrostomy tract. Removal and replacement may also be scheduled for a clogged tube.
Is CPT code 43760 still valid?
As of January 1, 2019, 43760 is no longer valid. Instead, CPT® introduced two new codes to better reflect the work involved when replacing gastrostomy tubes: 43762 Replacement of gastrostomy tube, percutaneous, includes removal, when performed, without imaging or endoscopic guidance; not requiring revision of gastrostomy tract.
Can a gastrostomy tube be removed?
As explained in the February 2019 CPT Assistant: Gastrostomy tubes (G-tubes) may be inadvertently removed if traction is placed on the tube.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for grocery store as place of occurrence
- 2. icd-10 code for congest
- 3. icd 10 code for hypoxic hypercapnic respiratory failure
- 4. icd 10 code for acute resp failure
- 5. icd 10 code for mania?trackid=sp-006
- 6. icd 10 code for nasal sprain
- 7. icd 10 code for 20 weeks pregnant
- 8. icd 10 code for left shoulder pain with radiculopathy
- 9. icd 10 code for general deconditioning
- 10. icd 10 code for adverse effect of coumadin