What is the new CPT code for flexible transoral EGD?
CPT codes 43235-43259 have been placed in the new EGD subsection. These codes have been revised to describe flexible transoral EGD and include five new codes, revision and renumbering of several existing codes and the deletion of two codes.
What is the CPT code for EGD with control of bleeding?
The parentheticals for code 43255, EGD with control of bleeding code 43255 have been revised. Code 43255 should not be reported for treatment of esophageal/gastric varices, which are reported with more specific codes 43243 (sclerotherapy) or 43244 (banding). Code 43236, submucosal injection, would also not be reported if
What is the CPT code for endoscopic jejunum examination?
Endoscopic ultrasound codes 43242 and 43259 have been revised to include examination of a surgically altered stomach where the jejunum is examined distal to the anastomosis. Clarification language has been included to address the extent of performance of the EUS examination as distinguished from the extent of the endoscopic visualization.
Is there a CPT code for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and visualization?
Regulations regarding billing and coding were removed from the CMS National Coverage Policy section of the related Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and Visualization L34434 LCD and placed in this article. Under CPT/HCPCS Codes Group 2: Paragraph added the verbiage “of the Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy and Visualization L34434 LCD”.
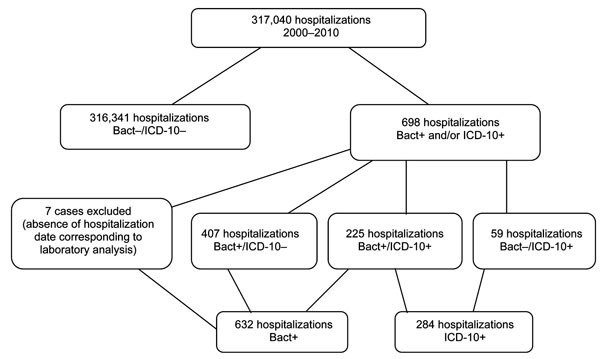
What is the ICD-10 Procedure Code for EGD with biopsy?
EGD with Biopsy of Antrum: 0DB78ZX.
What is diagnosis code Z98 89?
Other specified postprocedural statesICD-10 code Z98. 89 for Other specified postprocedural states is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
Can Z76 89 be used as a primary diagnosis?
The patient's primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patient's primary diagnostic code is Z76. 89, look in the list below to see which MDC's "Assignment of Diagnosis Codes" is first.
What is a R20 2 diagnosis code?
R20. 2 - Paresthesia of skin | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for status post surgery?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on specified body systems Z48. 81.
What does other specified Postprocedural States mean?
890 for Other specified postprocedural states is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
Is Z76 89 a billable code?
Z76. 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Can you use Z codes as primary diagnosis?
Z codes may be used as either a first-listed (principal diagnosis code in the inpatient setting) or secondary code, depending on the circumstances of the encounter. Certain Z codes may only be used as first-listed or principal diagnosis.
Can Z15 01 be used as primary diagnosis code?
Codes from category Z15 should not be used as principal or first-listed codes.
What is ICD-10 code R51?
ICD-10 code R51 for Headache is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
What is the ICD-10 code for generalized weakness?
ICD-10 code M62. 81 for Muscle weakness (generalized) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Soft tissue disorders .
Can you bill for establishing care?
You can't code or bill a service that is performed solely for the purpose of meeting a patient and creating a medical record at a new practice.
What is the ICD-10 code for annual physical exam?
Z00.00ICD-10 Code for Encounter for general adult medical examination without abnormal findings- Z00. 00- Codify by AAPC.
What does obesity unspecified mean?
Having a high amount of body fat (body mass index [bmi] of 30 or more). Having a high amount of body fat. A person is considered obese if they have a body mass index (bmi) of 30 or more.
What is the ICD-10 code for referral to specialist?
Encounter for other administrative examinations The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z02. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z02.
What is the code for EGD ablation?
Ablation of Tumors A new code has been established for EGD with ablation (43270). The new code includes pre- and post-dilation and guide wire passage when performed. Separate reporting of pre- or post-dilation or guide wire passage when performing ablation of the same lesion during the same session would not be appropriate. Ablation procedures are reported without a reduced services modifier 52, even if all three components (pre-dilation, post-dilation or guide wire passage) are not performed during the same session.
What is the EGD code for insertion of guide wire?
Insertion of guide wire code 43248 has been revised to describe passage of dilator (s ) over a guide wire rather than dilation. Codes 43248 and 43249 (dilation codes) should not be reported with codes 43266 and 43270, as these codes (stent, ablation) include dilation.
What is the EGD code for balloon dilation?
EGD code 43233 (out of sequence) has been established to report balloon dilation of 30 mm in diameter or larger. This dilation procedure includes fluoroscopic guidance, when used.
What is the EUS code for the esophagus?
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) examination codes 43237 and 43238 have been revised to describe EUS limited to the esophagus, stomach or duodenum and adjacent structures. Endoscopic ultrasound codes 43242 and 43259 have been revised to include examination of a surgically altered stomach where the jejunum is examined distal to the anastomosis. Clarification language has been included to address the extent of performance of the EUS examination as distinguished from the extent of the endoscopic visualization.
What is the CPT code for gastric washing?
Gastroenterological procedures included in CPT code ranges 43753-43757 and 91010-91299 are frequently complementary to endoscopic procedures. Esophageal and gastric washings for cytology when performed are integral components of an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (e.g., CPT code 43235). Gastric or duodenal intubation with or without aspiration (e.g., CPT codes 43753, 43754, 43756) shall not be separately reported when performed as part of an upper gastrointestinal endoscopic procedure. Gastric or duodenal stimulation testing (e.g., CPT codes 43755, 43757) may be facilitated by gastrointestinal endoscopy (e.g., procurement of gastric or duodenal specimens).
What is the code for transmural drainage of pseudocyst?
In addition to transmural drainage of pseudocyst as described in the current code 43240 , EGD with transmural drainage of pseudocyst has been revised to specify that it includes endoscopic ultrasound, transmural drainage and placement of stent (s) to facilitate drainage, when performed.
What is the code for dilation of gastric/duodenal stricture?
to describe dilation of gastric/duodenal stricture (s) and the guide wire example has been removed from the examples in parentheses. Code 43233 includes moderate sedation, as indicated by the moderate sedation symbol.
When is C1052 retroactive?
This revision is due to the Q1 2021 CPT/HCPCS Code Update and is retroactive effective for dates of service on or after 1/1/2021.
What is a bill and coding article?
Billing and Coding articles provide guidance for the related Local Coverage Determination (LCD) and assist providers in submitting correct claims for payment. Billing and Coding articles typically include CPT/HCPCS procedure codes, ICD-10-CM diagnosis codes, as well as Bill Type, Revenue, and CPT/HCPCS Modifier codes. The code lists in the article help explain which services (procedures) the related LCD applies to, the diagnosis codes for which the service is covered, or for which the service is not considered reasonable and necessary and therefore not covered.
What is an EGD?
EGD is a diagnostic procedure used to diagnose and treat conditions of the upper gastrointestinal tract. An endoscope is guided through the individual’s mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, and into the duodenum. The endoscope contains a video camera which allows the physician to visually examine the upper gastrointestinal tract. The endoscope may also be used to guide the physician in obtaining biopsies, remove foreign objects, or perform other therapeutic procedures.
What is an EGD test?
Background: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test used to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and the duodenum. EGD is also known as upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, gastroscopy, or upper endoscopy. EGD is indicated for the diagnosis of numerous conditions such as, but not limited to, Celiac disease, esophageal varices, esophagitis, gastritis, GERD, hiatal hernia, ulcers, Mallory-Weiss syndrome, and esophageal rings. EGD may also be indicated for the investigation of symptoms such as upper gastrointestinal symptoms and upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Abnormal imaging or caustic ingestion may also indicate the need for EGD.
What is the code for incomplete colonoscopy?
7. Incomplete Colonoscopy – The inability to extend beyond the splenic flexure is billed and paid using colonoscopy code 45378 with modifier –53.
Do colonoscopy and EGD need a modifier?
5. EGD and colonoscopies performed at the same session do not need a –59 modifier on either procedure as they are not bundled together.
Is anemia unspecified covered by Medicare?
9. Anemia unspecified (285.9) is not covered by most Medicare payers for colonoscopy and/or upper GI endoscopy. •Be specific as to iron deficiency anemia substantiated by iron studies. •This needs to be in the report. 280.0 or 280.9 is most often a covered contributing diagnosis.
What is the purpose of an esophagogastroduodenoscopy?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), also known as upper gastro-intestinal (GI) endoscopy, upper endoscopy, or gastroscopy, refers to examination of the esophagus, stomach, and upper duodenum (first part of the small intestine) by means of a flexible fiber-optic endoscope. It has been employed for investigating the cause (s) of abdominal pain, dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD), hematemesis (vomiting up blood), persistent nausea and vomiting, as well as occult and obscure GI bleeding. It can also be used in diagnosing esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), Schatzki's ring (also known as esophagogastric ring and lower esophageal ring), Mallory-Weiss syndrome (tear in the mucous membrane where the esophagus connects to the stomach), gastritis (inflammation of the stomach), duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenum), GI ulcer and polyps (growth of tissue), diverticula (abnormal pouches in the lining of the intestines), as well as obstruction, stricture (abnormal narrowing), and tumors of the esophagus, stomach, and upper duodenum.
How long does it take to be monitored for low grade dysplasia?
Surveillance of persons with BE and low-grade dysplasia (LGD) at 6 months. If LGD is confirmed, then surveillance at 12 months and yearly thereafter as long as dysplasia persists. Surveillance of persons with BE and high-grade dysplasia every 3 months for at least 1 year.
What is an endoluminal probe?
According to Michigan Health Lab, endoluminal functional lumen imaging probe (EndoFLIP; Crospon Ltd, Galway, Ireland) is a new, minimally invasive device created to complement traditional diagnostic tests, such as high resolution esophageal manometry and barium esophagram. EndoFLIP uses a balloon mounted on a thin catheter placed trans-orally at the time of a sedated endoscopy. In comparison to the traditional diagnostic tests, EndoFLIP offers the additional capability of measuring the cross-sectional area (CSA) and intra-luminal pressure of the esophagus while under distension (as if a solid bolus was present). The technology uses impedance planimetry to estimate CSA.
Can you have an endoscopy at age 60?
Hence, endoscopy should not be pursued in individuals younger than age 60 if H. pylori testing has not been performed. The guideline further states : "we do not suggest endoscopy to investigate alarm features for dyspepsia patients under the age of 60 to exclude upper GI neoplasia.".
Does EGJ cause gastroesophageal reflux disease?
Ilczyszyn and Botha (2014) noted that increased esophago-gastric junction (EGJ) distensibility has been implicated in the development of gastro-esophageal reflux disease (GERD). Previous investigators have reported a reduction in distensibility following anti-reflux surgery, but the changes during the operation are unclear. These researchers determined the feasibility of measuring intra-operative distensibility changes and examined if this would have potential to modify the operation. A total of 17 patients with GERD were managed in a standardized manner consisting of pre-operative assessment with symptom scoring, endoscopy, 24-hour pH studies, and manometry. Patients then underwent laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication with intra-operative distensibility measurement using an EndoFLIP EF-325 functional luminal imaging probe. This device measures CSA and distensibility within a balloon-tipped catheter. This was inflated at the EGJ to fixed distension volumes. Thirty-second median CSA and intra-balloon pressure measurements were recorded at 30 and 40 ml balloon distensions. Measurement time-points were

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for acute hepatitis panel screening
- 2. icd-10 code for multiple breast cysts
- 3. icd 10 code for adverse effect of statin
- 4. icd 10 code for exacerbation of sprain injury
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for perimenopausal
- 6. icd 10 code for right hip fracturwe
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for screening colonoscopy
- 8. icd 10 code for de quervain's tenosynovitis right hand
- 9. icd 10 procedure code for repair of the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon
- 10. icd 10 pcs code for bilateral percutaneous achilles tendon lengthening