Localization-related (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with simple partial seizures, not intractable, without status epilepticus. G40.109 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for epilepsy?
Oct 01, 2021 · This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G40.209 - other international versions of ICD-10 G40.209 may differ. Applicable To Localization-related (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with complex partial seizures NOS
What is the ICD 10 code for seizures in children?
Oct 01, 2021 · G40.919 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Epilepsy, unsp, intractable, without status epilepticus The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G40.919 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for partial seizure?
ICD-10-CM Code. G40.1. G40.1 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Localization-related (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with simple partial seizures. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more …
What is the ICD 10 code for temporal lobe epilepsy?
ICD-10 code G40.211 for Localization-related (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with complex partial seizures, intractable, with status epilepticus is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .

What is focal epilepsy?
Focal epilepsy is a neurological condition in which the predominant symptom is recurring seizures that affect one hemisphere (half) of the brain.
Is focal epilepsy the same as partial?
When an epileptic seizure starts in one side of the brain, it's called a focal onset seizure or a focal seizure. Both terms mean the same thing. Until recently these seizures were called partial seizures.
Is focal epilepsy the same as temporal lobe epilepsy?
What is temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE)? Temporal lobe epilepsy is the most common form of focal epilepsy. About 6 out of 10 people with focal epilepsy have temporal lobe epilepsy. Seizures in TLE start or involve in one or both temporal lobes in the brain.
What is generalized and focal epilepsy?
Focal onset seizures start in one area and can spread across the brain and cause mild or severe symptoms, depending on how the electrical discharges spread. Generalized seizures can start as focal seizures that spread to both sides of the brain.
What are the four types of focal seizures?
Focal epilepsy seizures come in four categories:Focal aware seizures. If you know what's happening during the seizure, it's an "aware" seizure. ... Focal impaired awareness seizures. ... Focal motor seizures. ... Focal non-motor seizures.Aug 2, 2021
What is the difference between focal and absence seizures?
How can I tell the difference between absence seizures and focal impaired awareness seizures? Seizures that involve staring and a change in awareness are sometimes mislabeled as absence seizures. People often confuse absence seizures with focal impaired awareness seizures.
What is the cause of focal epilepsy?
A focal onset seizure may occur for many reasons. Epilepsy, brain tumors, or damage from head trauma or from a stroke can cause recurrent focal onset seizures. Infections, heatstroke, or low blood sugar can trigger a seizure. A seizure can be treated.
Are focal seizures epilepsy?
Focal seizures are the most common type of seizures in people with epilepsy.
Why is temporal lobe epilepsy common?
Causes. The causes of TLE include mesial temporal sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, brain infections, such as encephalitis and meningitis, hypoxic brain injury, stroke, cerebral tumours, and genetic syndromes. Temporal lobe epilepsy is not the result of psychiatric illness or fragility of the personality.
How can you tell the difference between focal and generalized seizures?
Focal seizures are divided into those in which the affected person is aware and those with impaired awareness; these events can be motor or non-motor. Generalized seizures are also categorized as motor and non-motor, but loss of awareness occurs with most events.Jun 1, 2021
How is focal vs generalized seizures diagnosed?
Complex focal seizures can make a person with epilepsy confused or dazed. The person will be unable to respond to questions or direction for up to a few minutes. Secondary generalized seizures begin in one part of the brain, but then spread to both sides of the brain.
Can you have both focal and generalized epilepsy?
Patients may have both generalized and focal seizure types, with interictal and/or ictal EEG findings that accompany both seizure types. Patients with Dravet syndrome and Lennox Gastaut syndrome may have generalized and focal epilepsy.
What is the diagnosis code for epilepsy?
G40.109 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of localization-related (focal) (partial) symptomatic epilepsy and epileptic syndromes with simple partial seizures, not intractable, without status epilepticus.
Can you cure epilepsy?
It is important to start treatment right away. There is no cure for epilepsy, but medicines can control seizures for most people. When medicines are not working well, surgery or implanted devices such as vagus nerve stimulators may help. Special diets can help some children with epilepsy.
What is the brain disorder that causes seizures?
Information for Patients. Epilepsy. Epilepsy is a brain disorder that causes people to have recurring seizures. The seizures happen when clusters of nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain send out the wrong signals. People may have strange sensations and emotions or behave strangely.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code G40.109:
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code G40.109 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
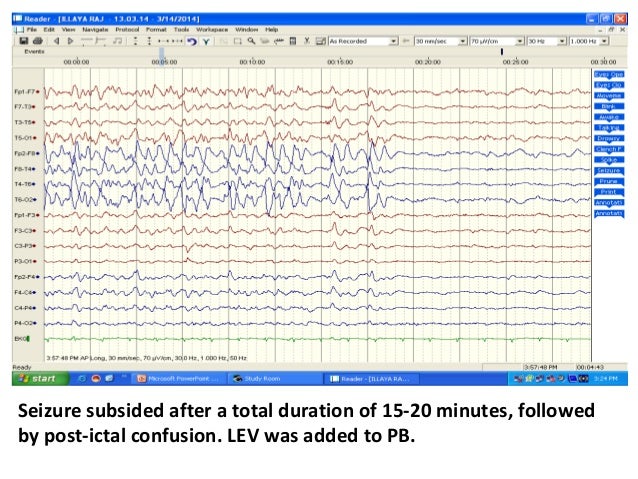
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for fournier's gangrene female
- 2. icd-10 code for a review of diagnostic testing
- 3. icd 10 code for postmenopausal osteoporosis
- 4. icd 10 code for infected amputation site right great toe
- 5. icd 10 code for chronic over active bladder
- 6. icd code for myopia
- 7. icd-10 code for tonsilitis
- 8. icd 10 code for back pain due to large breasts
- 9. icd 10 code for thumb pain left
- 10. icd 10 code for peg tube malfunction