What is the ICD 10 code for Neurologic diagnosis?
G90.09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM G90.09 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G90.09 - other international versions of ICD-10 G90.09 may differ.
What is the latest version of ICD 10 for neuropathy?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G62.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 G62.9 may differ. Applicable To. Neuropathy NOS.
What is the ICD 10 code for folic acid?
folate (folic acid) D52.9 folate D52.9 (folic acid) Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for multifocal motor neuropathy?
MMN G61.82 (multifocal motor neuropathy) Neuropathy, neuropathic G62.9. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G62.9. Polyneuropathy, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Neuropathy NOS. multifocal motor G61.82 (MMN) ICD-10-CM Codes Adjacent To G61.82.
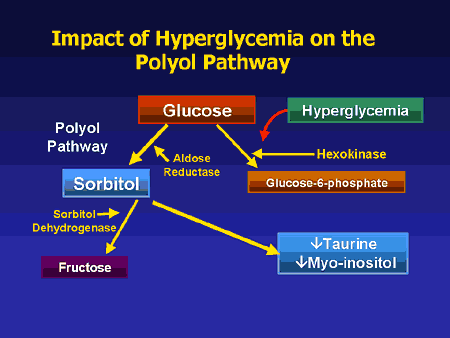
What is the ICD-10 code for folate deficiency?
ICD-10 code D52. 9 for Folate deficiency anemia, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism .
What ICD-10 codes cover B12 and folate?
Vitamin B-12 (82607) and folate (82746) can be tested up to four times per year for malabsorption syndromes (K90. 9) or deficiency disorders (D81. 818, D81.
Can folic acid cause neuropathy?
In conclusion, our results suggest that folate deficiency is a risk factor for neuropathy in patients younger than 40 years. Importantly, the risk of peripheral neuropathy increased as serum folate decreased, and even insufficient serum folate of 6.8 to 13.5 nmol/L appeared to be important.
What is a folic acid deficiency?
Folate-deficiency anemia is the lack of folic acid in the blood. Folic acid is a B vitamin that helps your body make red blood cells. If you don't have enough red blood cells, you have anemia. Red blood cells carry oxygen to all parts of your body.
What diagnosis covers folic acid?
Folate deficiency anemia, unspecified D52. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D52. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What diagnosis code will cover folate?
Group 3CodeDescriptionD52.8Other folate deficiency anemiasD52.9Folate deficiency anemia, unspecifiedD53.1Other megaloblastic anemias, not elsewhere classifiedD53.9Nutritional anemia, unspecified84 more rows
Does folic acid help peripheral neuropathy?
We suggest that folic acid may play a role in improving the repair of peripheral nerve injury by promoting the proliferation and migration of Schwann cells and the secretion of nerve growth factors.
What are the neurological symptoms of folate deficiency?
Neurological changesvision problems.memory loss.pins and needles (paraesthesia)loss of physical co-ordination (ataxia), which can affect your whole body and cause difficulty speaking or walking.damage to parts of the nervous system (peripheral neuropathy), particularly in the legs.
Can low folic acid cause numbness?
Common symptoms of folate deficiency can include: Tiredness, fatigue and lethargy. Muscle weakness. Neurological signs, such as a feeling of pins and needles, tingling, or burning, or peripheral neuropathy, i.e. a numbness in the extremities.
What is the most common cause of folate deficiency?
One of the most common causes of folate deficiency is not eating a healthy, balanced diet. A healthy diet includes foods that naturally contain folate or are enriched with folic acid.
Is folic acid and B12 the same?
Vitamin B12 is an especially important vitamin for maintaining healthy nerve cells, and it helps in the production of DNA and RNA, the body's genetic material. Vitamin B12 works closely with vitamin B9, also called folate or folic acid, to help make red blood cells and to help iron work better in the body.
What vitamin deficiencies cause tingling in the hands and feet?
Tingling hands or feet Vitamin B-12 deficiency may cause “pins and needles” in the hands or feet. This symptom occurs because the vitamin plays a crucial role in the nervous system, and its absence can cause people to develop nerve conduction problems or nerve damage.
What supplements can cause neuropathy?
Excess of vitamin B6 can lead to a sensory neuropathy or neuronopathy, which most obviously occurs with megadoses of vitamin B6 (greater than 2 g/d), but has also been reported in patients taking lower doses (50 mg/d) over long periods.
How much folic acid should you take for neuropathy?
Dr. McGuire will prescribe 800 mcg of folic acid daily for patients with neuropathy. If a patient cannot get L-methylfolate, methylcobalamin and pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (Metanx, Nestle Health Science), an active form of vitamin B, he will prescribe 1,000 mcg of vitamin B12 and 50 mg of vitamin B6 daily.
Does folic acid have side effects?
When taken by mouth: It is likely safe for most people to take folic acid in doses of no more than 1 mg daily. Doses higher than 1 mg daily may be unsafe. These doses might cause stomach upset, nausea, diarrhea, irritability, confusion, behavior changes, skin reactions, seizures, and other side effects.
What happens when you take too much folate?
Excess folic acid is excreted in urine. A high folate intake can mask vitamin B-12 deficiency until its neurological effects become irreversible. This can typically be remedied by taking a supplement containing 100 percent of the daily value of both folic acid and vitamin B-12.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for kyphosis
- 2. icd 10 code for paroxsymal svt
- 3. icd 10 code for right cervical strain
- 4. icd 10 code for bilateral foot swelling
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for repair of femoral av fistula
- 6. icd 10 code for orbital injury
- 7. icd 10 code for tetany due to hypoparathyroidism
- 8. icd 9 code for diabetes type 2 with neurological complications
- 9. icd 9 code for patient pulled out nj tube
- 10. 2017 icd 10 diagnosis code for paronychia left fingers