What is the ICD 10 code for endometriosis?
N85.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM N85.8 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N85.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 N85.8 may differ. endometriosis ( N80.-)
What is the ICD 10 code for endometrial hyperplasia?
Endometrial hyperplasia, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code N85.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM N85.00 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for uterine fibroids?
Other specified noninflammatory disorders of uterus. N85.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM N85.8 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of N85.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 N85.8 may differ.
What is the diagnosis code for fluid in the endometrial cavity?
Question: A patient was referred to one of our gynecologists because of fluid in the endometrial cavity. What diagnosis code should I report? Answer: You should report abnormal finding on ultrasound: 793.5 ( Nonspecific [abnormal] findings on radiological and other examination of genitourinary organs ).
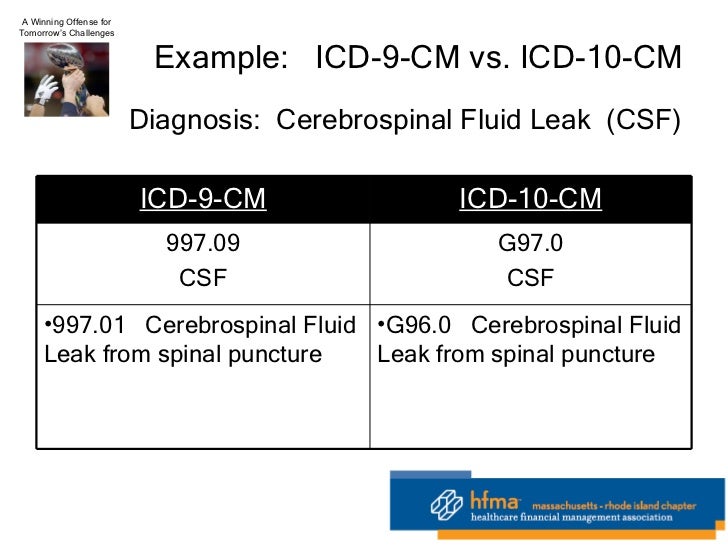
What is endometrial fluid?
Endometrial cavity fluid (ECF) is a fluid accumulation within the endometrial cavity. It is not a common complication during assisted reproductive techniques (ARTs), but it, especially the excessive one, is detrimental to embryo implantation and thus negatively impacts the ART outcome [1••,2–10].
What is the cause of endometrial fluid?
A small amount of fluid in the endometrial canal is likely related to benign cervical stenosis and does not require further evaluation. An intrauterine fluid collection in a postmenopausal patient, although possibly related to cervical stenosis, should raise concern for endometrial (or cervical) carcinoma.
Is endometrial fluid normal?
Although a tiny amount of fluid within the postmenopausal endometrial canal may be considered normal (,44), any significant fluid collection is abnormal and requires careful evaluation of the uterus and adnexal structures for associated findings.
What is the ICD-10 code for pelvic fluid collection?
ICD-10 code R19. 00 for Intra-abdominal and pelvic swelling, mass and lump, unspecified site is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is endocervical fluid?
The endocervical canal transports sperm into the uterine cavity, allows the escape of blood from the uterus during menstruation, and supplies mucus (a thick lubricating protein) to the female reproductive…
What type of fluid is found in a uterus that has Hematometra?
Hematometra is a collection or retention of blood in the uterus most commonly due to an imperforate hymen or transverse vaginal septum.
What does fluid in the uterus mean after menopause?
Several investigators reported that endometrial fluid collection in postmenopausal women is a sign of serious endometrial or cervical disease, hyperplasia, or cancer.
What is the ICD-10 code for abdominal fluid collection?
ICD-10 code R18. 8 for Other ascites is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is pelvic fluid?
Physiological pelvic intraperitoneal fluid refers to the presence of a small volume of free fluid in the pelvis, particularly the pouch of Douglas. It occurs in young females of reproductive age and can be a mimic of traumatic free fluid in abdominal trauma.
What is the ICD-10 code for endometriosis?
ICD-10 code N80 for Endometriosis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
Can endometrial fluid cause pain?
It can get worse before and during your period. You may also have very heavy bleeding. Pain during sex is likely. Some women who have an endometrial cyst feel sore or notice pressure.
How can I reduce fluid in my uterus?
Treatment may include:Drainage of excess amniotic fluid. Your health care provider may use amniocentesis to drain excess amniotic fluid from your uterus. ... Medication. Your health care provider may prescribe the oral medication indomethacin (Indocin) to help reduce fetal urine production and amniotic fluid volume.
How is fluid in the endometrial cavity treated?
Treatment options of ECF include expectant treatment, freeze all or transvaginal aspiration of ECF on the day of embryo transfer [1] . In this pilot study, we describe management of ECF at our center by aspiration of ECF at the time of egg collection and not at the time of embryo transfer (ET). ...
Can you get pregnant with fluid in uterus?
Two of the 20 cycles of women with transient fluid accumulation were pregnant, and none of those with fluid retention on the day of embryo transfer conceived. The pregnancy rate was only 5.7% (2/35) in women with uterine fluid accumulation detected during IVF cycles.
What are noninflammatory disorders of the uterus?
Approximate Synonyms. Disease of uterus. Disorder of uterus. Endometrial lesion. Lesion of endometrium. Lesion of uterus. Clinical Information. Deviation from or interruption of the normal structure or function of the uterus.
What is the first sign of uterine disease?
It is the place where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. If you have a uterine disease, the first sign may be bleeding between periods or after sex.
What is benign proliferation of the endometrium in the uterus?
Benign proliferation of the endometrium in the uterus. Endometrial hyperplasia is classified by its cytology and glandular tissue. There are simple, complex (adenomatous without atypia), and atypical hyperplasia representing also the ascending risk of becoming malignant.
How many types of endometrial hyperplasia are there?
There are four types of endometrial hyperplasia: simple endometrial hyperplasia, complex endometrial hyperplasia, simple endometrial hyperplasia with atypia, and complex endometrial hyperplasia with atypia. These differ in terms of how abnormal the cells are and how likely it is that the condition will become cancer.
What is a benign form of endometrial hyperplasia?
A benign form of endometrial hyperplasia with increased number of cells with atypia. The atypical cells are large and irregular and have an increased nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio. The risk of progression to endometrial carcinoma rises with the increasing degree of cell atypia.
Is endometrial hyperplasia a neoplasm?
An endometrial hyperplasia characterized by cytologic and architectural changes which may lead to endometrial carcinoma. Despite the atypical features and possible course, there is debate on whether to consider this a neoplasm. The relationship with endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia is also unclear.
What is a benign condition in which tissue that looks like endometrial tissue grows in abnormal places in the abdomen
A benign condition in which tissue that looks like endometrial tissue grows in abnormal places in the abdomen. A condition in which functional endometrial tissue is present outside the uterus. It is often confined to the pelvis involving the ovary, the ligaments, cul-de-sac, and the uterovesical peritoneum.
Where does endometriosis grow?
It can grow on the ovaries, behind the uterus or on the bowels or bladder. Rarely, it grows in other parts of the body. This "misplaced" tissue can cause pain, infertility, and very heavy periods.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for restless leg
- 2. icd 10 code for bacteremia
- 3. icd 10 cm code for screening colonoscopy for colon cancer
- 4. icd 10 code for inability to move shoulder
- 5. icd 10 code for hx of myeloma
- 6. icd 10 code for hypertension without diagnosis
- 7. icd 10 cm code for acute gallstone pancreatitis
- 8. icd 9 code for abscess in mouth
- 9. need icd code for copd
- 10. icd-10 code for benign neoplasm of kidney