What is the ICD 10 code for open fracture of distal radius?
Unsp fx the lower end of r radius, init for opn fx type I/2; Open fracture of distal right radius; Open right radius (forearm bone) fracture ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S52.502B [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified fracture of the lower end of left radius, initial encounter for open fracture type I or II
What is the ICD 10 code for lower right radius fracture?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S52.501A [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified fracture of the lower end of right radius, initial encounter for closed fracture. Unsp fracture of the lower end of right radius, init; Closed fracture of distal end of right radius; Right radius (forearm bone) fracture.
What is the ICD 10 code for radial fracture?
Distal Radius Fracture ICD-10 S52.539A. Distal Radius Fracture S52.539A. S52.511A - Displaced fracture of right radial styloid process, initial encounter for closed fracture. S52.514A - Nondisplaced fracture of right radial styloid process, initial encounter for closed fracture.
What is the ICD 10 code for distal phalanx fracture?
Unsp fx the lower end left radius, init for opn fx type I/2; Open fracture of distal end of left radius; Open left radius (forearm bone) fracture ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S62.525S [convert to ICD-9-CM] Nondisplaced fracture of distal phalanx of left thumb, sequela Nondisp fx of distal phalanx of left thumb, sequela
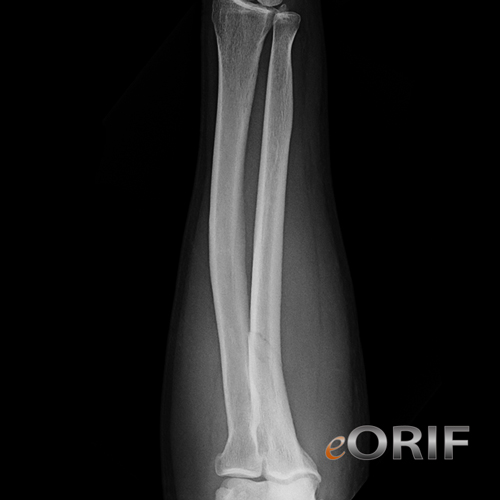
What is the ICD 10 code for fracture distal radius?
ICD-10 code S52. 5 for Fracture of lower end of radius is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
What is a non displaced distal radius fracture?
Distal radius fractures are very common in two subsets of patients: children and the middle-aged. They are the most common arm fracture in kids, as they spend a great deal of time at play, which can lead to falls. These fractures are typically non-displaced, or 'greenstick,' fractures.
How do you code a non union fracture?
733.82 - Nonunion of fracture.
What is the ICD 10 code for left radial shaft fracture?
S52. 302A - Unspecified fracture of shaft of left radius [initial encounter for closed fracture] | ICD-10-CM.
What is a transverse fracture of the distal radius?
When the radius breaks near the wrist, it is called a distal radius fracture. The break usually happens due to falling on an outstretched or flexed hand. It can also happen in a car accident, a bike accident, a skiing accident or another sports activity.
What is a nondisplaced fracture?
A nondisplaced fracture is one in which the bone cracks or breaks but retains its proper alignment. Nondisplaced fractures often require only bracing, booting or casting treatment.
Do you code for displaced or nondisplaced fracture?
In ICD-10-CM a fracture not indicated as displaced or nondisplaced should be coded to displaced, and a fracture not designated as open or closed should be coded to closed. While the classification defaults to displaced for fractures, it is very important that complete documentation is encouraged.
What is the ICD-10 code for nonunion?
Unspecified fracture of sternum, subsequent encounter for fracture with nonunion. S22. 20XK is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the difference between malunion and nonunion?
A malunion occurs when a fractured bone heals in an abnormal position, which can lead to impaired function of the bone or limb and make it look like it is 'bent'. Similarly, a nonunion is the result of a fractured bone failing to heal after an extended period of time – in some cases over a period of 9 to 12 months.
What is ICD 10 code for fracture to right radius?
ICD-10-CM Code for Unspecified fracture of the lower end of right radius, initial encounter for closed fracture S52. 501A.
What is the ICD 10 code for fracture?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S52. 501A: Unspecified fracture of the lower end of right radius, initial encounter for closed fracture.
What is the code for closed fracture left distal radius and ulna?
Table: CodeICD10 Code (*)Code Description (*)S52.50Fracture of lower end of radius, closedS52.51Fracture of lower end of radius, openS52.6Fracture of lower end of both ulna and radiusS52.60Fracture of lower end of both ulna and radius, closed26 more rows
How serious is a distal radius fracture?
In severe cases, the fractured bone is so much out of place that it can't be corrected or realigned without making a surgical incision. An open wrist fracture will require surgical treatment as soon as possible. Surgical treatment methods can possibly affect the future use of the forearm or wrist.
How long does it take a distal radius fracture to heal?
Most distal radius fractures take 3 months or so to heal before you are able to return to all activities, and full recovery from these injuries can take up to 1 year.
Do I need surgery for a distal radius fracture?
Non-Surgical Treatment Distal radius fractures do not always require surgery. Many heal just fine without an operation. Minor fractures with minimal displacement do very well with nonsurgical treatment. Other displaced fractures can be “reduced” and casted.
Do all distal radius fractures need surgery?
Not every patient needs to undergo a distal radial fracture surgery, but regardless of the treatment plan determined by your physician, the goal of the treatment is always to return the bone to its proper position and prevent it from moving out of place until it is sufficiently healed.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for temporal lobe seizures
- 2. icd 10 code for psychosomatic disorder
- 3. icd 10 code for metatarsalgia left foot
- 4. icd 10 code for l97.502
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for complication
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for a patient diagnosed with inverse psoriasis
- 7. icd 10 code for closed fracture left proximal humerus
- 8. icd 10 dx code for short term memory loss
- 9. icd 10 code for pacemaker lead thrombosis
- 10. icd 10 code for preinfarction syndrome