How do you code recurrent UTI?
Excessive, frequent and irregular menstruation ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N92.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Excessive and frequent menstruation with irregular cycle ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R35.0 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Frequency of micturition ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z87.440 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Personal history of urinary (tract) infections
What is the diagnosis code for UTI?
Oct 01, 2021 · History of recurrent uti History of urinary tract infection History of urinary tract infection (uti) Present On Admission Z87.440 is considered exempt from POA reporting. ICD-10-CM Z87.440 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 951 Other factors influencing health status Convert Z87.440 to ICD-9-CM Code History
What are ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O23.40 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified infection of urinary tract in pregnancy, unspecified trimester. Unsp infection of urinary tract in pregnancy, unsp trimester; Urinary tract infection in pregnancy; Urinary tract infection in pregnancy, before birth. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O23.40.
What is the ICD 10 code for difficulty urination?
Oct 01, 2021 · Your doctor can tell if you have a uti by testing a sample of your urine. Treatment with medicines to kill the infection will make it better, often in one or two days. ICD-10-CM N39.0 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 689 Kidney and urinary tract infections with mcc 690 Kidney and urinary tract infections without mcc
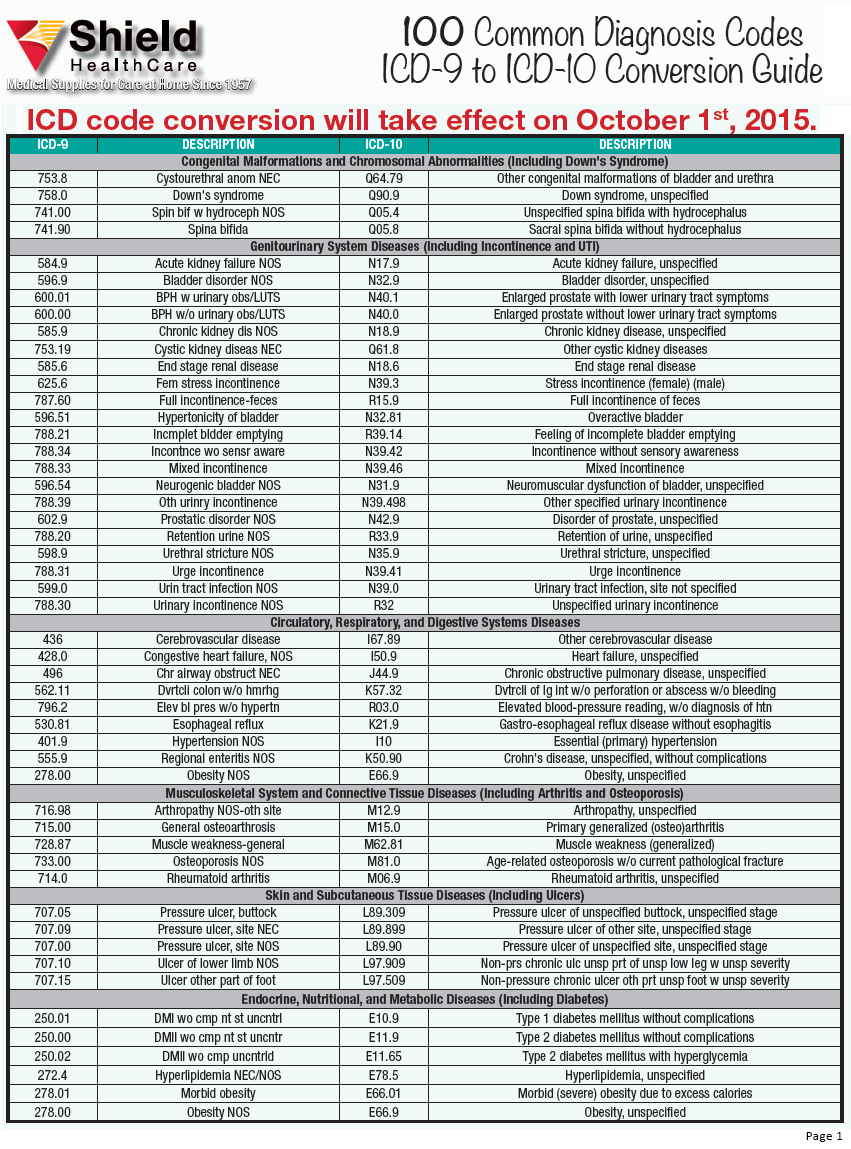
What is the ICD-9 code for recurrent UTI?
ICD-9 code 599.0 for Urinary tract infection site not specified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -OTHER DISEASES OF URINARY SYSTEM (590-599).
What is the ICD-10 code for history of recurrent UTI?
Z87. 440 - Personal history of urinary (tract) infections. ICD-10-CM.
What is the diagnosis code for UTI?
The ICD-9 code 599.0 is an unspecified urinary tract infection (ICD-10 N39.
What is the ICD-10 code for recurrent infections?
Acute recurrent sinusitis, unspecified The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J01. 91 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J01.
How do you code UTI history?
ICD-10 code Z87. 440 for Personal history of urinary (tract) infections is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What causes recurrent UTI?
Recurrent UTIs (RUTI) are mainly caused by reinfection by the same pathogen. Having frequent sexual intercourse is one of the greatest risk factors for RUTIs. In a subgroup of individuals with coexisting morbid conditions, complicated RUTIs can lead to upper tract infections or urosepsis.
What is the ICD-10 code for UTI site not specified?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N39. 0: Urinary tract infection, site not specified.
What is the ICD-10 code for E coli UTI?
2 for Escherichia coli [E.
What is diagnosis code N39?
9 Disorder of urinary system, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for infection?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B99. 9: Unspecified infectious disease.
What is the ICD-10 code for bacterial infection?
ICD-10 code: A49. 9 Bacterial infection, unspecified - gesund.bund.de.
How do you code history of sepsis?
Septic shock – Code first the underlying systemic infection, such as 038.0 (Streptococcal septicemia), then code 995.92 for severe sepsis, then code 785.52 for septic shock and finally assign the code for the specific type of organ failure inherent to septic shock, such as 584.9 for acute renal failure.
When to avoid coding unspecified UTI?
Avoid coding unspecified UTI (N39.0) when specific site infection is mentioned. For example if both cystitis and UTI are mentioned it is not necessary to code UTI, instead code only cystitis. Urosepsis – This does not lead to any code in the alphabetic index.
What is UTI in women?
Urinary Tract infection (UTI) is a very common infectious disease occurs commonly in aged women. As age goes up there will be structural changes happening in kidney. Muscles in the bladder, urethra and ureter become weaken. Urinary retention gets increased in the bladder and this creates an environment for bacterial growth.
What is it called when you have a urinary infection?
Infection can happen in any part of the urinary tract – kidney, ureter, bladder or urethra. It is called as Cystitis, Urethritis and Pyelonephritis based on the site.
What are the symptoms of a symtom?
Patients may complain of one or multiple symptoms which include fever, dysuria, hematuria, incontinence, decreased urine output, pain in abdomen or back, nausea, vomiting or diarrhea. Physician does a thorough physical examination and takes clinical history of the patient.
Is Andrea a diabetic?
Andrea is a 50-year-old woman coming to emergency room for pain when urinating and burning sensation. She does feel lower back pain from 3 weeks. She never had any urinary problems earlier. She is a diabetic patient and takes insulin daily. Physical examination shows abdominal tenderness. Pelvic examination is normal. No signs of vaginitis or cervicitis found. Urinalysis is done based on the examination. After reviewing the results the case was diagnosed as UTI.
Is it necessary to mention the infectious agent when using ICD N39.0?
Urethritis. It is not necessary to mention the infectious agent when using ICD N39.0. If the infectious organism is mentioned, place the UTI code primary and organism secondary. Site specified infection should be coded to the particular site. For example, Infection to bladder to be coded as cystitis, infection to urethra to urethritis.
How many women have UTI?
More than 60 percent of females will be diagnosed with a UTI at some point in their lives. More than 30 percent of females will suffer from a subsequent infection within 12 months of the initial symptoms being resolved despite the appropriate antibiotic.
Why do I have a recurrent UTI?
One of the reasons for a recurrent UTI may be drug resistance, as many urinary tract infections are resistant to certain antibiotics. This resistance makes it increasingly difficult to treat UTIs.
What is the most common bacterial infection in women?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common, recurrent bacterial infections in individuals, mostly women. Bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), enters the urethra and infects one or several parts of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, or kidneys. UTIs can be mild to serious and even result in death.
What is the name of the infection that occurs in the urethra?
A UTI that occurs in the urethra only is called urethritis. A kidney infection, called pyelonephritis, often starts in the bladder and then progresses up through the ureters to infect one or both kidneys in the upper urinary tract. Pyelonephritis is less common than a bladder infection, but is more serious.
Why is the urethra shorter?
A woman’s urethra is shorter and closer to the rectum, making it easier for bacteria to get into the urinary tract. Sexual intercourse can also introduce bacteria into the urinary tract and can be associated with sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and mycoplasma.
What is the first course of treatment for urinary tract infections?
Antibiotics are often the first course of treatment for urinary tract infections. An analgesic may also be prescribed to relieve the pain while urinating. Severe UTIs may require intravenous antibiotics given in a hospital.
What type of imaging is used to see the urinary tract?
For frequent infections, an ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be taken of the urinary tract. The physician may also use a contrast dye to view the structures in the urinary tract and perform a cystoscopy to see inside the urethra and bladder.
What is the ICd 10 code for urinary tract infection?
N39.0 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Urinary tract infection, site not specified . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
What is a list of terms?
List of terms is included under some codes. These terms are the conditions for which that code is to be used. The terms may be synonyms of the code title, or, in the case of “other specified” codes, the terms are a list of the various conditions assigned to that code.
What does NEC not elsewhere mean?
NEC Not elsewhere classifiable#N#This abbreviation in the Tabular List represents “other specified”. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the “other specified” code.
What does "excludes" mean in a note?
An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A type 2 Excludes note represents 'Not included here'.
When an excludes2 note appears under a code, is it acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code
When an Excludes2 note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code and the excluded code together. A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hx of thryroisd ca
- 2. icd 10 code for histoty of overseas travel
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for lateral tongue cancer
- 4. icd 10 code for rash due to therapeutic use of penicillin
- 5. icd 10 code for amblyopia unspecified eye
- 6. icd 10 code for chemo induced fatigue
- 7. icd 10 code for fungal infection left ankle
- 8. icd 10 code for encounter for drug monitoring
- 9. icd 10 code for adhd medication management
- 10. icd 10 code for rett syndrome