ICD-10-CM Code H60.8X3. H60.8X3 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Other otitis externa, bilateral . It is found in the 2019 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2018 - Sep 30, 2019 .
What is the ICD 10 code for otitis externa?
May result in cases of cellulitis and osteomyelitis. Otomycosis – Infection of the ear canal secondary to fungus species such as Candida or Aspergillus. In ICD-10-CM, Otitis externa is coded to H60 and H62. Example codes include: Note that these codes require a 5 th character.
What is the ICD 10 code for fungal infection?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code L08.9. Local infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. due to fungus B36.9.
What is the ICD 10 code for otomycosis?
Otomycosis (ear condition) ICD-10-CM H62.40 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 154 Other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with mcc 155 Other ear, nose, mouth and throat diagnoses with cc
What is the ICD 10 code for dermatomycosis?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to B36.9: Dermatitis (eczematous) L30.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code L30.9 Dermatomycosis B36.9 Ear - see also condition tropical NEC B36.9 Infection, infected, infective (opportunistic) B99.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B99.9 Mycosis, mycotic B49 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B49
What is fungal otitis externa?
Otomycosis is an ear infection caused by a fungus. It's more commonly seen in tropical and subtropical parts of the world, and during times of intense heat and humidity. It's also known as fungal otitis externa. Otomycosis usually affects the outer ear canal.
What is the ICD-10 code for fungal skin infection?
SUPERFICIAL FUNGAL INFECTIONS ICD-10: B36 Superficial fungal infections are the most common mucocutaneous infections, often caused by an imbalanced overgrowth of mucocutaneous microbiome.
What is the ICD-10 code for external otitis left ear?
ICD-10 Code for Unspecified otitis externa, left ear- H60. 92- Codify by AAPC.
How do you treat fungal otitis externa?
Mild fungal infections can usually be treated with an acetic acid solution, whereas more severe cases may have to be treated with a topical antifungal agent, such as 1% clotrimazole.
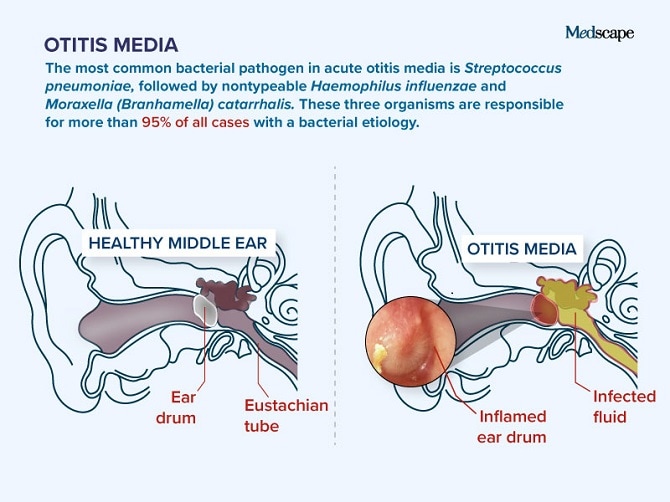
What is the ICD-10 code for otitis media?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66. 9.
What is this fungal infection?
What Is a Fungal Infection? A fungal infection, also called mycosis, is a skin disease caused by a fungus. There are millions of species of fungi. They live in the dirt, on plants, on household surfaces, and on your skin. Sometimes, they can lead to skin problems like rashes or bumps.
What is actinic otitis externa?
External otitis is an acute infection of the ear canal skin typically caused by bacteria (Pseudomonas is most common). Symptoms include pain, discharge, and hearing loss if the ear canal has swollen shut; manipulation of the auricle causes pain. Diagnosis is based on inspection.
What is malignant otitis externa?
Malignant otitis externa is a disorder that involves infection and damage of the bones of the ear canal and at the base of the skull.
What is the ICD-10 code for tinea corporis?
ICD-10 code: B35. 4 Tinea corporis | gesund.bund.de.
What does fungal otitis externa look like?
Typically, the ear starts to look red and the skin on the outer part of the ear becomes scaly. It may start to itch and become quite uncomfortable. You may notice discharge beginning to leak out of the ear. The itching is often worse with fungal infections than with other types of ear infection.
How can you tell the difference between a fungal and bacterial ear infection?
Your doctor may look into your ears using an otoscope that helps them see your ear canal and eardrum. They may also take swabs of any discharge, fluid or build-up in your ears for laboratory tests. This will help them differentiate between a fungal and a bacterial infection.
What is Aspergillus otomycosis?
Otomycosis is subacute or chronic superficial fungal infection of the external auditory canal and auricle. It is the most frequently encountered fungal infection in ear, nose and throat clinics.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hsv chronic
- 2. icd 10 code for unspecified osteoarthritis, femoral acetabular
- 3. icd 10 code for altered behavior
- 4. icd 9 code for venous reflux disease
- 5. icd 10 code for dvts
- 6. icd 10 cm code for hyperphosphatemia
- 7. icd 10 code for solid renal lesion
- 8. icd 10 code for multiple small chronic infarcts
- 9. icd 10 code for hyperbilirubinemia photo therapyn newborn
- 10. icd-10 code for right arm pain