What is the ICD 10 code for gastrostomy tube placement?
Gastrostomy complication, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K94.22 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Gastrostomy infection. Infection of gastrostomy; Infection of gastrostomy site; code to specify type of infection, such as:; cellulitis of abdominal wall (L03.311); sepsis (A40.-, A41.-) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K94.22.
What is the ICD 10 code for esophageal tube placement?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z93.1 Gastrostomy status 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Z93.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z93.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is the insertion of a nasogastric (NG) feeding tube ICD 10 Compliant?
2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F18.21 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Inhalant dependence, in remission. Glue sniffing dependence in remission; Inhalent dependence, in remission; Inhalant use disorder, moderate, in early remission; Inhalant use disorder, moderate, in sustained remission; Inhalant use disorder, severe, in early …
What is the ICD 10 code for nasogastric drainage?
Type 1 Excludes. biotin-dependent carboxylase deficiency due to dietary deficiency of biotin ( E53.8) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z99.3 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Dependence on wheelchair. Dependent on wheelchair; Wheelchair bound; cause of dependence, such as:; muscular dystrophy (G71.0-); obesity (E66.-);
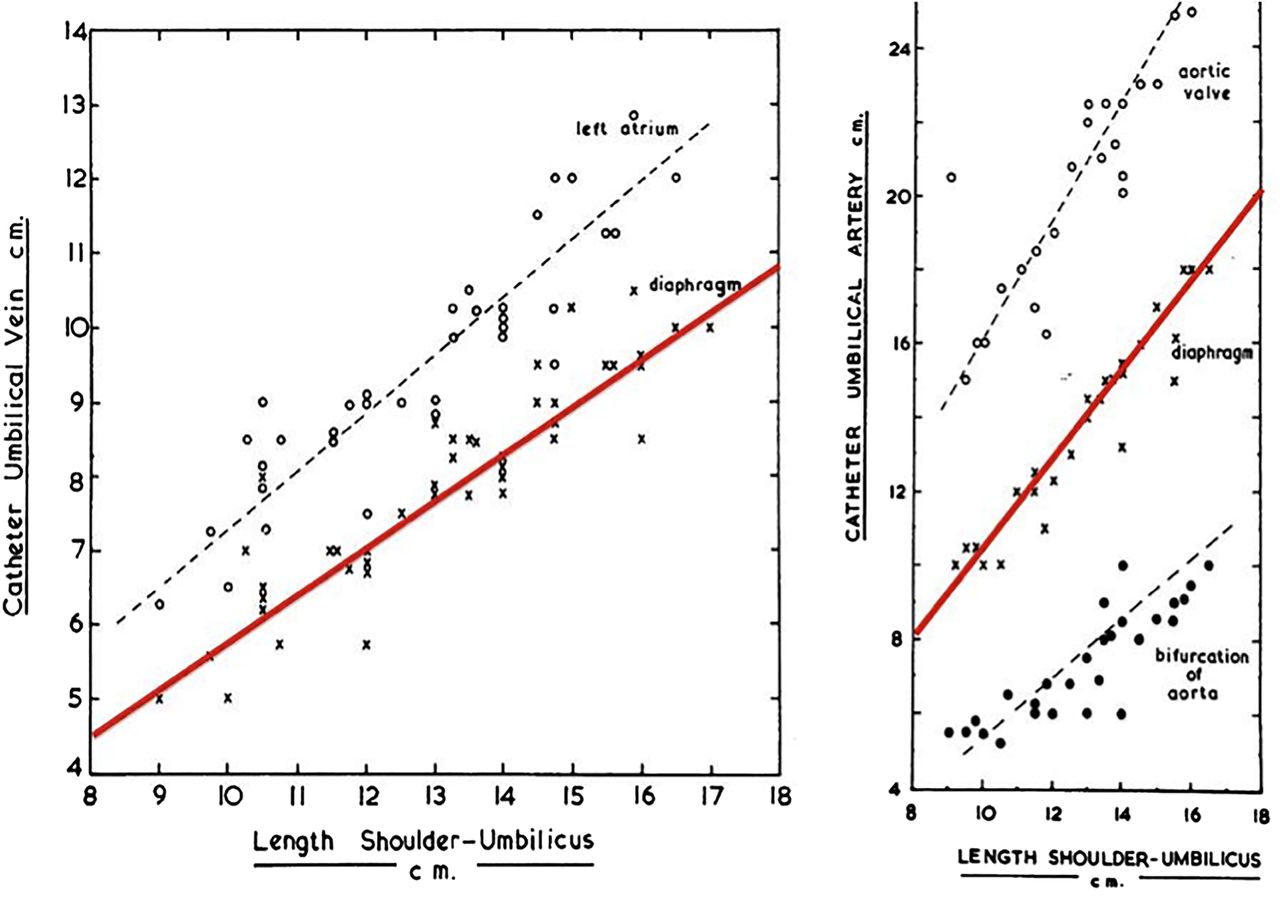
What is the ICD-10 code for placement of gastrostomy tube?
Z93. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What does encounter for attention to gastrostomy meaning?
Attention to gastrostomy (artificial opening to stomach)
Is a PEG tube a gastrostomy?
A PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) feeding tube insertion is the placement of a feeding tube through the skin and the stomach wall. It goes directly into the stomach. PEG feeding tube insertion is done in part using a procedure called endoscopy. Feeding tubes are needed when you are unable to eat or drink.Jul 1, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for presence of jejunostomy tube?
The ICD-10-CM code Z93. 4 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like history of intubation of gastrointestinal tract via jejunostomy or jejunostomy present. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.
What is the ICD-10 Code for critical illness myopathy?
ICD-10 | Critical illness myopathy (G72. 81)
What does gastrostomy status mean?
1 : the surgical formation of an opening through the abdominal wall into the stomach.
Is PEG tube same as G-tube?
A percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) is a procedure to place a feeding tube. These feeding tubes are often called PEG tubes or G tubes. The tube allows you to receive nutrition directly through your stomach.Apr 19, 2021
What is the difference between PEG and gastrostomy tube?
They are often used as the initial G-tube for the first 8-12 weeks post-surgery. PEG specifically describes a long G-tube placed by endoscopy, and stands for percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy. Sometimes the term PEG is used to describe all G-tubes. Surgeons may place other styles of long tubes.Mar 3, 2020
Which of the following is considered a relative contraindication of PEG tube?
Generally, ascites is considered a relative contraindication for PEG tube placement due to concerns regarding ascitic fluid leakage.
What is a GJ tube?
A gastrostomy-jejunostomy tube -- commonly abbreviated as "G-J tube" -- is placed into your child's stomach and small intestine. The “G” portion of this tube is used to vent your child's stomach for air or drainage, and / or drainage, as well as give your child an alternate way for feeding.
What is a Dobhoff tube?
A Dobhoff tube is a narrow-bore flexible tube with a diameter of 4 mm, used to deliver enteral nutrition. It is used in patients with a functional gastrointestinal tract, but who are unable to meet their nutritional requirements through oral intake [1,2].Mar 5, 2018
What is the ICD 10 code for CVA?
9.
What is the procedure called when a tube is inserted into the intestines?
Gastro Jejunostomy Tube (GJ-Tube) Procedure. This is a feeding tube which is inserted through the gastrostomy stoma in the abdominal wall, passes through the stomach and advanced into the jejunum. This tube feeding directly into the intestines is called Gastrojejunostomy tube (GJ-Tube).
What is a gastrostomy tube?
Gastrostomy Tube (G-Tube) Procedure. This is a tube inserted into the stomach through a small incision in the abdomen. The tube goes through the skin (percutaneous) to the stomach wall and then into the stomach. This tube feeding into the stomach is called gastrostomy tube (G-Tube).
Why do doctors insert G tubes?
The physician inserts G-tube in those patients so that they can take adequate nutrition by mouth. However, some patients (mostly children) are unable to tolerate feeding of food directly into the stomach. The G-tube is required to be converted into GJ tube in these cases. This article covers all the ICD Codes and CPT Codes required for ...
Where is the tube placed for gastric tube placement?
Gastrostomy Tube Placement Procedures. The patient is placed supine on the procedure table and prepped and draped sterilely. The physician places a tube through the skin and into the stomach and uses x-rays to make sure it is in the right place.
Can a G tube be converted to a GJ tube?
The G-tube is required to be converted into GJ tube in these cases. This article covers all the ICD Codes and CPT Codes required for the medical billing of this conversion procedure under fluoroscopic guidance. There are some adult patients, who cannot take enough food through the mouth or have swallowing food problems, ...
What are the different types of diagnostic codes?
The following clinical terms are approximate synonyms or lay terms that might be used to identify the correct diagnosis code: 1 Finding of gastrointestinal device 2 Finding of gastrointestinal device 3 Finding of gastrointestinal device 4 Gastrointestinal tube in situ 5 Gastrostomy present 6 Gastrostomy tube in situ 7 H/O: gastrostomy 8 PEG externally removable 9 PEG internally removable
What is the Z93.1 code?
Valid for Submission. Z93.1 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of gastrostomy status. The code Z93.1 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is an ostomy?
An ostomy is surgery to create an opening (stoma) from an area inside the body to the outside. It treats certain diseases of the digestive or urinary systems. It can be permanent, when an organ must be removed. It can be temporary, when the organ needs time to heal. The organ could be the small intestine, colon, rectum, or bladder. With an ostomy, there must be a new way for wastes to leave the body.
What is an unacceptable principal diagnosis?
Unacceptable principal diagnosis - There are selected codes that describe a circumstance which influences an individual's health status but not a current illness or injury, or codes that are not specific manifestations but may be due to an underlying cause.
Is diagnosis present at time of inpatient admission?
Diagnosis was not present at time of inpatient admission. Documentation insufficient to determine if the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission. Clinically undetermined - unable to clinically determine whether the condition was present at the time of inpatient admission.
Is Z93.1 a POA?
Z9 3.1 is exempt from POA reporting - The Present on Admission (POA) indicator is used for diagnosis codes included in claims involving inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals. POA indicators must be reported to CMS on each claim to facilitate the grouping of diagnoses codes into the proper Diagnostic Related Groups (DRG).
How long does a NG tube last?
When an NG tube is used for nutrition alone, it either runs continuously, 16 hours on and eight hours off, or by bolus feedings, meaning feeding is delivered en masse at one time. Bolus feedings are tantamount to eating meals three to five times a day. A Look at the Codes.
How big is a Dobhoff tube?
A Dobhoff tube is a small-bore, flexible tube that typically has an inside diameter of about 0.15 inches (4 mm) that is inserted into the stomach by way of the nasal passage. Use of this particular type of NG tube is considered a best practice. Following insertion, correct placement is confirmed by X-ray.
What is NG tube?
For inpatients, the NG tube (NGT) is generally used to aspirate stomach contents or administer nourishment and medicine to people who cannot ingest anything by mouth.
Why is NG intubation necessary?
NG intubation is medically necessary for a variety of clinical situations, including: Patients who can’t eat or swallow. Cases of neck or facial injuries. When mechanical ventilation is required or the patient is comatose. To relieve pressure on intestinal obstruction or blockage.
Who is Kim Carr?
Kim Carr brings more than 30 years of health information and clinical documentation improvement management experience and expertise to her role as Director of Clinical Documentation, where she provides oversight for auditing and documentation improvement for HRS clients. Prior to joining HRS, Kim worked as a consultant implementing CDI programs in varied environments such as level-one trauma centers, small community hospitals and all levels in between.#N#Before joining the consultant arena, Kim served as Manager of CDI in an academic level-one trauma center. She was responsible for education and training for physicians and clinical documentation specialists. Over the past 30 years, Kim has held several HIM positions; including HIM Coding Educator, Quality Assurance/Utilization Management Coordinator, DRG Coding Coordinator and Coding Manager. Kim holds a degree in Health Information Management and is a member of AHIMA, THIMA, ACDIS and AAPC.
Does the stomach make a lot of its own secretions?
Also, the stomach makes a lot of its own secretions that need to be suctioned out in patients whose stomachs are not performing normal digestive functions. Buildup of normal stomach secretions can lead to an erosive event in the stomach or esophagus (or aspiration of stomach acid into the trachea or lungs).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for encephalopally
- 2. what is the icd 10 cm code for twisting from a horse as the cause of an injury?
- 3. icd 10 code for arthritis low back pain
- 4. icd 10 code screening for hypothyroidism
- 5. icd 10 code for hx nstemi
- 6. icd 10 code for mixed headache
- 7. icd 10 code for subacromium and subdeltoid bursitis left shoulder
- 8. icd code 10 for angiomyolipoma
- 9. icd code for sirs in abdominal
- 10. icd 10 code for scabs