What is the ICD 10 code for ganglioneuroma?
2021/2022 ICD-10-CM Index › 'G' Terms › Index Terms Starting With 'G' (Ganglioneuroma) Index Terms Starting With 'G' (Ganglioneuroma) Ganglioneuroma D36.10
What is ganglioneuroma of colon?
· Question GANGLIONEUROMA ICD 10. Thread starter [email protected]; Start date Jun 14, 2019; Sort by date. A. [email protected] New. Messages 2 ... Jun 14, 2019 #1 Can anyone help on how to code a Ganglioneuroma of the Sigmoid Colon? 0 D. danachock Expert. Messages 254 Location Brainerd, MN Best answers 0. Jun 14, 2019 #2 Hi …
What is the ICD 10 code for neoplasm of colon?
· Benign neoplasm of colon, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. D12.6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D12.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the prognosis of ganglioneuroma of colon?
· D12.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D12.5 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D12.5 - other international versions of ICD-10 D12.5 may differ.

What is Tubulovillous adenoma ICD-10?
Benign neoplasm of colon, unspecified D12. 6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D12. 6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for adenomatous colonic polyps?
ICD-10 code K63. 5 for Polyp of colon is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the I 10 code for neurofibromatosis I 1?
ICD-10 | Neurofibromatosis, type 1 (Q85. 01)
What is the ICD-10 code for Lipoma?
D17.9ICD-10 | Benign lipomatous neoplasm, unspecified (D17. 9)
What does code Z12 11 mean?
A screening colonoscopy should be reported with the following International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition (ICD-10) codes: Z12. 11: Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of the colon.
What is the ICD 10 code for colonic polyp?
ICD-10 | Polyp of colon (K63. 5)
What is the ICD-10 code for neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis, unspecified Q85. 00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q85. 00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How many types of neurofibromatosis are there?
Neurofibromatoses are a group of genetic disorders that cause tumors to form on nerve tissue. These tumors can develop anywhere in the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord and nerves. There are three types of neurofibromatosis: neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1), neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) and schwannomatosis.
What is the neurofibroma?
A neurofibroma is a type of nerve tumor that forms soft bumps on or under the skin. A neurofibroma can develop within a major or minor nerve anywhere in the body. This common type of benign nerve tumor tends to form more centrally within the nerve.
What is the ICD-10 code for abdominal wall lipoma?
Benign lipomatous neoplasm of intra-abdominal organs D17. 5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D17. 5 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is lipoma a neoplasm?
A lipoma is a non cancerous (benign) lump that forms due to an overgrowth of fat cells. You can get a lipoma anywhere on the body where you have fat cells. Lipomas are not cancer. Cancerous tumours of the fat cells are called liposarcomas.
What is excision of lipoma?
Larger lipomas are best removed through incisions made in the skin overlying the lipoma. The incisions are configured like a fusiform excision following the skin tension lines and are smaller than the underlying tumor.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
A non-metastasizing neoplasm arising from the wall of the colon and rectum . A non-metastasizing neoplasm arising from the wall of the colon.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D12.6. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
When will the ICd 10 D12.6 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D12.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
When will the ICd 10 D12.5 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D12.5 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
When will the ICd 10 D36.10 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D36.10 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for inflammatory colon polyps?
Codes for inflammatory colon polyps, found in category K51, include a description of complications: K51.40 Inflammatory polyps of colon without complications. K51.411 Inflammatory polyps of colon with rectal bleeding. K51.412 Inflammatory polyps of colon with intestinal obstruction.
Is colon cancer benign?
Print Post. Colorectal cancer typically develops from colon polyps, which are abnormal growths of tissue (neoplasms). Most polyps are benign, but may become cancerous. When selecting an ICD-10 diagnosis code for polyp (s) of the colon, you will need to know the precise location of the polyp (s) and the type of polyp (e.g., benign, inflammatory, ...
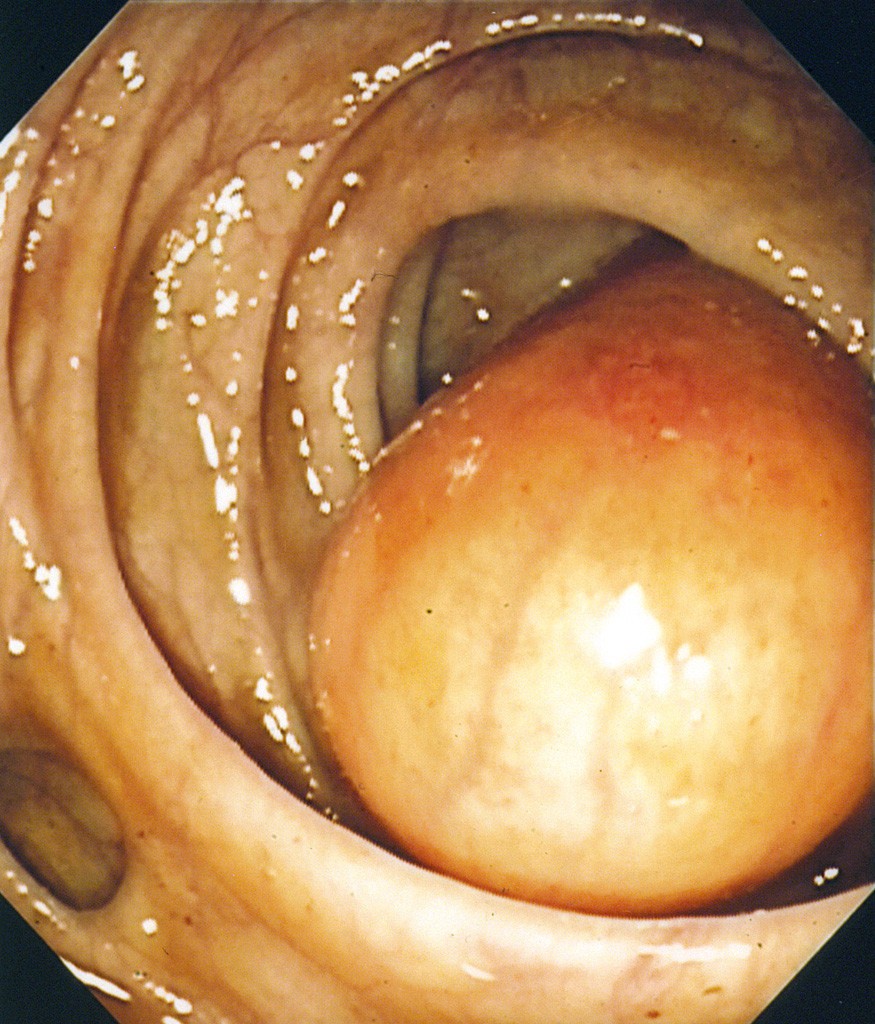
How to tell if you have ganglioneuroma of colon?
Rarely, the signs and symptoms of Ganglioneuroma of Colon may include: Presence of small lesions/polyps in the colon (typically less than 1 cm in size) Bleeding from the anus. Mucus mixed with stools.
Where does ganglioneuroma of colon occur?
Diffuse type of Ganglioneuroma of Colon: It commonly occurs in the terminal ileum, appendix, or cecum. This type can be associated with certain syndromes
What are the risk factors for ganglioneuroma of colon?
In some cases, the risk factors may include: PTEN hamartomatous tumor syndrome (a unified syndrome that includes Cowden disease and Bannayan-Ruvalcaba-Riley syndrome) Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) Juvenile polyposis.
Why do ganglioneuromas form in the colon?
Colonic Ganglioneuromas are benign hamartomatous tumors that arise from the autonomic nervous system. The tumor may also occur due to certain genetic mutations that predispose an individual to developing these polyps.
What age does ganglioneuroma occur?
Ganglioneuroma of Colon usually arises in older adults (both men and women are affected); most commonly in individuals aged 50 years and over
What are the different types of ganglioneuroma?
There are different types of Ganglioneuroma of Colon and these include: Solitary type of Ganglioneuroma of Colon: It is not associated with any syndromes. Multiple mucosal type of Ganglioneuroma of Colon: Also known as ganglioneuromatous polyposis, it can be associated with certain syndromes. Diffuse type of Ganglioneuroma ...
What is the test called when you see the inner lining of the colon?
A colonoscopy is a test that allows the physician to look at the inner lining of the colon and rectum. A typical colonoscopy involves using a thin, flexible tube (called a colonoscope), with an attached video camera, to view the colon and rectum.
Is ganglioneuroma asymptomatic?
Their clinical presentation is mostly asymptomatic, and if any symptoms are present at all, they a …. Ganglioneuromas are very rare clinical entities, and their occurrence in the large bowel lays further emphasis on their rarity. Ganglioneuromas are benign tumors of undifferentiated neural crest cells. Their clinical presentation is mostly ...
Is ganglioneuroma rare?
Ganglioneuromas are very rare clinical entities, and their occurrence in the large bowel lays further emphasis on their rarity. Ganglioneuromas are benign tumors of undifferentiated neural crest cells. Their clinical presentation is mostly asymptomatic, and if any symptoms are present at all, they are usually nonspecific, with excellent prognosis.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for pulsatile cervical mass
- 2. icd-10 code for place of occuenes - friend huls
- 3. icd 10 code for myoleymia left eye
- 4. what is the 2019 icd 10 code for carcinoid syndrome
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for ppd plant
- 6. icd 10 code for pyloric ulcer
- 7. icd 10 code for bibasilar airspace disease
- 8. icd 9 code for vsd
- 9. icd 10 procedure code for iv adimistered by nurse and not md
- 10. icd 9 code for left arm cellulitis