Abnormal glucose complicating pregnancy. O99.810 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM O99.810 became effective on October 1, 2018.
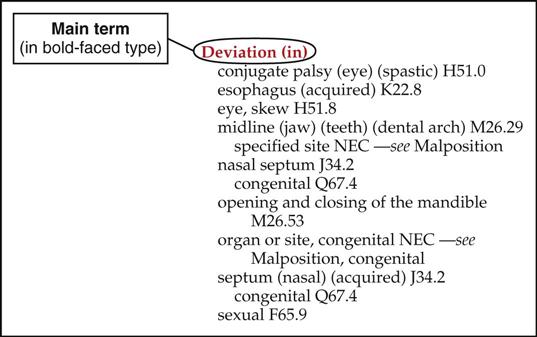
What is the ICD 10 code for excluded note?
D48.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM D48.1 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D48.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 D48.1 may differ. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes.
What does gctb stand for?
Giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB) is a locally aggressive and rarely metastasizing neoplasm composed of neoplastic mononuclear stromal cells admixed with macrophages and osteoclast-like giant cells
What are the ICD 10 codes for diseases?
2021 ICD-10-CM Codes. A00-B99. Certain infectious and parasitic diseases C00-D49. Neoplasms D50-D89. Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism E00-E89. Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases F01-F99 ...
What is the ICD 10 code for neoplasm?
Code is only used for female patients. C56.9 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of malignant neoplasm of unspecified ovary. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.

What ICD-10 code covers hemoglobin a1c screening?
1.
What is the ICD-10 code for glucose tolerance test?
ICD-10 code R73. 02 for Impaired glucose tolerance (oral) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for pre diabetes?
The ICD-10 code for prediabetes is R73. 09.
What is Tenosynovial giant cell tumor?
Listen to pronunciation. (TEH-noh-sih-NOH-vee-ul JY-unt sel TOO-mer) A type of rare tumor that forms in the synovium (tissue that lines the joints), the tendon sheath (tissue that covers the tendons), or the bursa (a fluid-filled sac between bones, tendons, and muscles).
What diagnosis covers HbA1c?
“HbA1c may be used for the diagnosis of diabetes, with values >6.5% being diagnostic.
How do you code an elevated glucose tolerance test?
Impaired glucose tolerance (oral) R73. 02 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R73. 02 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for type 2 diabetes?
ICD-Code E11* is a non-billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 250. Code I10 is the diagnosis code used for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetes?
E08. 3531 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition... E08. 3532 Diabetes mellitus due to underlying condition...
What is the ICD-9 code for prediabetes?
ICD-9-CM Diagnosis Code 790.29 : Other abnormal glucose.
Is Tenosynovial giant cell tumor a sarcoma?
We conclude that malignant tenosynovial giant cell tumors are highly aggressive sarcomas with significant potential for locally destructive growth, distant metastases, and death from disease.
What is giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath?
Giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath (GCTTS) is the second most common tumor of the hand after ganglion cysts (1,2). It is a slowly growing, usually painless benign lesion of soft tissues. The tumor affects individuals between the age of 30 and 50 years old and is found more often in women than men (3–6).
Is giant cell tumor of tendon sheath malignant?
Conclusions: Malignant giant cell tumor of tendon sheath is an extremely rare malignant tumor, some cases have a poor outcome, the others, despite the histologically malignant features, have a good prognosis if wide surgical excision ablates the tumor completely.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
The ICD code C56 is used to code Germ cell tumor
A germ cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from germ cells. Germ cell tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous tumors. Germ cells normally occur inside the gonads (ovary and testis). Germ cell tumors that originate outside the gonads may be birth defects resulting from errors during development of the embryo.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #736-741 - Uterine and adnexa procedure for ovarian or adnexal malignancy with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'C56.9 - Malignant neoplasm of unspecified ovary'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code C56.9. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code C56.9 and a single ICD9 code, 183.0 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is a GCT tumor?
ALTERNATE NAMES. Pediatric Malignant Germ Cell Tumor; Adult Malignant Germ Cell Tumor. DESCRIPTION. Malign ant Germ Cell Tumors (GCT) are malignant tumors that are formed by immature cells that begin in the reproductive cells of the testes or ovaries. These germ cells travel into the pelvis as ovarian cells or into the scrotal sac as testicular ...
What are the physical findings of a malignant GCT?
Physical findings: Physical examination of malignant GCT depend on the size and location of the tumor. Symptoms of malignant GCTs depend on the size and location of the tumor. Mid chest GCT may cause: Fevers. Lower back GCTs may present as a mass in the lower abdomen or buttocks.
How old is too old to get a GCT?
Adult GCT generally occurs between 30- 40 years of age. Treatment for malignant GCT depends on the type of tumor, the stage at diagnosis, and the age of the affected person. The primary treatment of most GCTs involves surgical removal of the tumor.
Sex cord stromal tumors
Cite this page: Zarei S. Granulosa cell tumor-adult. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorgctadult.html. Accessed November 28th, 2021.
Granulosa cell tumor-adult
Cite this page: Zarei S. Granulosa cell tumor-adult. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarytumorgctadult.html. Accessed November 28th, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for stromal tumor?
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor, unspecified site 1 C49.A0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM C49.A0 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C49.A0 - other international versions of ICD-10 C49.A0 may differ.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
Why is my GGT curve abnormal?
Glucose intolerance is due to obesity in some subjects. Abnormal curves may be caused by Cushing's syndrome, pheochromocytoma, or acromegaly. Emesis is probably an indication to cancel the remainder of a GGT for that day; decision is up to the patient's physician.
What is the GTT used for?
The GTT only establishes the presence of glucose intolerance. It is used in patients with borderline fasting and postprandial glucose to support or rule out the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Some use it in unexplained hypertriglyceridemia, neuropathy, impotence, diabetes-like renal diseases, retinopathy, reevaluation of prior diagnosis made under substandard conditions and with necrobiosis lipoidica diabeticorum.
What is the ADA criteria for diagnosing diabetes?
The ADA criteria for diagnosing diabetes includes typical symptoms of diabetes (polydipsia, polyuria, and unexplained weight loss plus casual plasma glucose >200 mg/dL. "Casual" meaning any random glucose obtained at any time of the day without respect to fasting or not fasting.); plus Hb A 1c ≥6.5% or fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dL after no caloric intake for at least eight hours or two-hour plasma glucose ≥200 mg/dL during a 75-gram oral glucose tolerance test and any of the initial findings (above) must be confirmed on a subsequent day. OGTT is contraindicated in the presence of obvious diabetes mellitus.
What causes glucose tolerance to decrease?
Excessive growth hormone, adrenocortical and thyroid hormones, and catecholamines cause decreased glucose tolerance. Diabetes is much more than glucose intolerance, but until now we have not been able to measure other factors pertinent to prediction of the complications of diabetes.
Can a three day high carbohydrate diet cause false positive GTT?
Failure to have patient on three-day high carbohydrate diet may result in a false-positive GTT. Impaired glucose tolerance is not equivalent to diabetes mellitus. A normal result does not ensure that diabetes will not subsequently develop.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for metastasis to the intrathoracic lymph nodes
- 2. icd 10 code for deficient alkaline
- 3. icd 10 code for abnormal x ray
- 4. icd 10 code for knee wound
- 5. icd 10 code for tear anterior talofibular ligament right ankle
- 6. icd 10 code for prophylaxis antibiotic therapy
- 7. icd 10 code for left preseptal cellulitis
- 8. icd 10 code for sclerosis of hip
- 9. icd 10 code for pansystolic murmur
- 10. icd-10 code for loss of consciousness