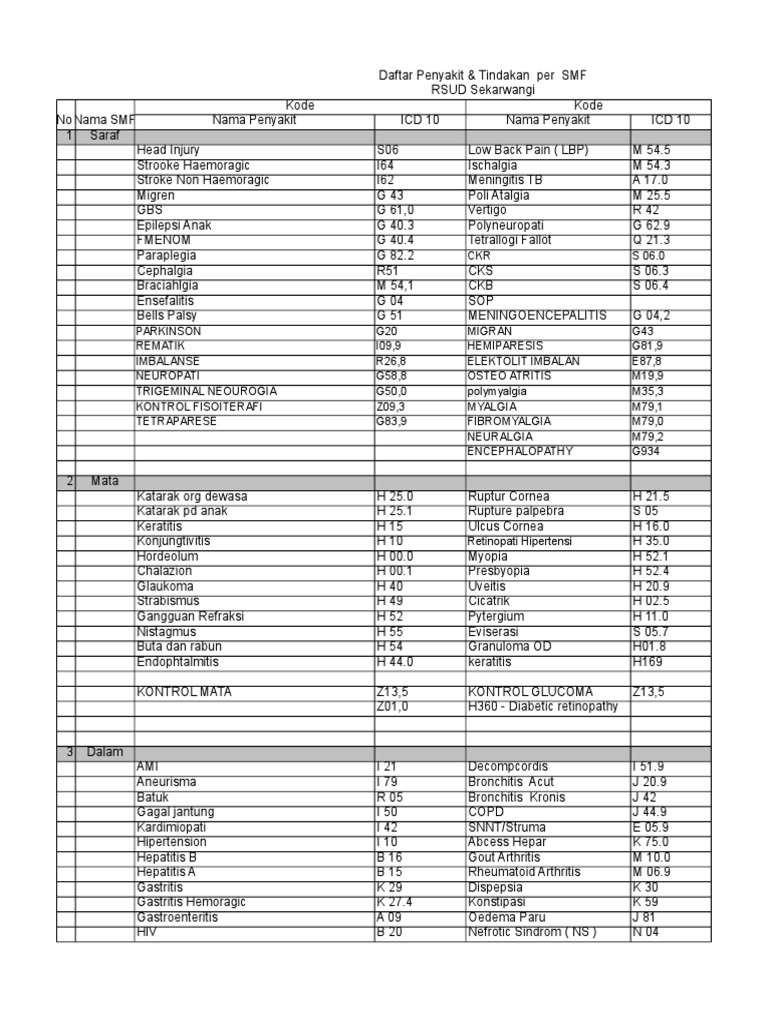
What is the ICD 10 code for peritonitis?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K65.0. Generalized (acute) peritonitis. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. K65.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for chronic periodontitis?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to K05.322: Periodontitis (chronic) (complex) (compound) (local) (simplex) K05.30. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K05.30. Chronic periodontitis, unspecified.
What is the ICD 10 code for peritoneal fistula?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to K65.9: Fistula (cutaneous) L98.8 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code L98.8 Hemoperitoneum K66.1 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K66.1 Peritonitis (adhesive) (bacterial) (fibrinous) (hemorrhagic) (idiopathic) (localized) (perforative) (primary) (with adhesions) (with effusion) K65.9
What are the signs and symptoms of peritonitis?
Peritonitis, unspecified. Inflammation of the peritoneum due to infection by bacteria or fungi. Causes include liver disease, perforation of the gastrointestinal tract or biliary tract, and peritoneal dialysis. Patients usually present with abdominal pain and tenderness, fever, chills, and nausea and vomiting.
What is the ICD-10 for peritonitis?
K65. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K65.
What is generalized peritonitis?
Peritonitis is inflammation of the localized or generalized peritoneum, the lining of the inner wall of the abdomen and cover of the abdominal organs. Symptoms may include severe pain, swelling of the abdomen, fever, or weight loss. One part or the entire abdomen may be tender.
What peritonitis means?
Peritonitis is inflammation of the peritoneum — a silk-like membrane that lines your inner abdominal wall and covers the organs within your abdomen — that is usually due to a bacterial or fungal infection. There are two types of peritonitis: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis.
What is the most common type of peritonitis?
The most common type of peritonitis is secondary peritonitis, usually caused by leakage or perforation of an abdominal organ, like the appendix. However, another common type of peritonitis is spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) that is most often associated with individuals that have abdominal ascites fluid.
What is the difference between localized and generalized peritonitis?
Clinically peritonitis is often classified either as local or as diffuse. Local peritonitis refers to loculi of infection, usually walled-off or contained by adjacent organs, whereas diffuse is synonymous with generalized peritonitis, that is spread to the entire cavity.
What is primary and secondary peritonitis?
The two main types of peritonitis are primary spontaneous peritonitis, an infection that develops in the peritoneum; and secondary peritonitis, which usually develops when an injury or infection in the abdominal cavity allows infectious organisms into the peritoneum. Both types of peritonitis are life-threatening.
What is the difference between sepsis and peritonitis?
Symptoms of sepsis are fever, increased breathing and heart rate and infection present in another part of the body, such as a urinary tract infection or an infected tooth. Peritonitis symptoms include abdominal pain, may involve vomiting or diarrhea, dehydration and increased heart rate (so some overlap exists).
What are three causes of peritonitis?
What causes peritonitis?A hole in your stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterus, or bladder.An infection during treatment for end-stage kidney (renal) disease (peritoneal dialysis)An infection of fluid in the belly from end-stage liver disease (cirrhosis)Pelvic inflammatory disease in women.More items...
What is acute peritonitis?
Peritonitis is an acute inflammation of the peritoneal lining due to bacterial infection as well as other causes such as chemicals, irradiation, and foreign-body injury. 1. Insult of the peritoneal lining by any of these agents can lead to an inflammatory response, known as acute peritonitis.
What is the most common complication of peritonitis?
Aggressive fluid resuscitation and early surgical intervention are the mainstay of therapy of peritonitis. Enterocutaneous fistulas, surgical site infection, sepsis, and multiorgan failure are the commonest complications seen in surgical settings.
What are the types of peritonitis?
Tertiary peritonitisPeritonitis (Type)Etiologic OrganismsSecondaryGram-negativeGram-positiveAnaerobicTertiaryGram-negative4 more rows•Jul 23, 2019
How many stages of peritonitis are there?
Peritonitis is divided into three stages. The division is based on the defensive and inhibitory mechanisms of the host.
What is secondary peritonitis?
Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Inflammation of the peritoneum, a condition marked by exudations in the peritoneum of serum, fibrin, cells, and pus. Inflammation of the thin membrane surrounding abdominal cavity, called peritoneum.
Is K65 a reimbursement code?
K65 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM K65 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K65 - other international versions of ICD-10 K65 may differ. Use Additional.
The ICD code K65 is used to code Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of the abdominal organs.
Coding Notes for K65.0 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #371-373 - Major gastrointestinal disorders and peritoneal infections with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'K65.0 - Generalized (acute) peritonitis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code K65.0. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Codes GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code K65.0 and a single ICD9 code, 567.29 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is secondary peritonitis?
Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Inflammation of the peritoneum, a condition marked by exudations in the peritoneum of serum, fibrin, cells, and pus. Inflammation of the thin membrane surrounding abdominal cavity, called peritoneum.
What is the term for a peritoneal infection that covers most of the abdominal organs?
peritonitis with or following appendicitis ( K35.-) retroperitoneal infections ( K68.-) Inflammation of the peritoneum (tissue that lines the abdominal wall and covers most of the organs in the abdomen). Peritonitis can result from infection, injury, or certain diseases.
What is the peritoneum?
Clinical Information. Inflammation of the peritoneum (tissue that lines the abdominal wall and covers most of the organs in the abdomen). Peritonitis can result from infection, injury, or certain diseases. Symptoms may include swelling of the abdomen, severe pain, and weight loss.
Why does my peritoneum hurt?
Inflammation of the peritoneum due to infection by bacteria or fungi. Causes include liver disease, perforation of the gastrointestinal tract or biliary tract, and peritoneal dialysis. Patients usually present with abdominal pain and tenderness, fever, chills, and nausea and vomiting.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left knee pain with effusion
- 2. icd 10 code for l knee replacement
- 3. icd 10 code for left knee pain osteoarthritis
- 4. disease code icd 10 for birth control
- 5. icd-9-cm code for late effects speech deficit due to cva cause
- 6. icd 10 code for perforated abdominal viscus
- 7. icd-10 code for primary open-angle glaucoma, bilateral
- 8. icd 10 code for meningioma with hemorrhage right temporal
- 9. icd 10 code for submandibular adenopathy
- 10. icd 10 code for ischemic necrosis of finger