What is the ICD 10 version of dystonia?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G24.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 G24.1 may differ. A condition characterized by focal dystonia that progresses to involuntary spasmodic contractions of the muscles of the legs, trunk, arms, and face.
What is genetic torsion dystonia?
Genetic torsion dystonia. A condition characterized by focal dystonia that progresses to involuntary spasmodic contractions of the muscles of the legs, trunk, arms, and face. The hands are often spared, however, sustained axial and limb contractions may lead to a state where the body is grossly contorted.
What are the different types of dystonia?
These disorders are generally divided into generalized dystonias (e.g., dystonia musculorum deformans) and focal dystonias (e.g., writer's cramp). They are also classified by patterns of inheritance and by age of onset. Difficulty moving; distortion or impairment of voluntary movement, as in tic, spasm, or myoclonus.
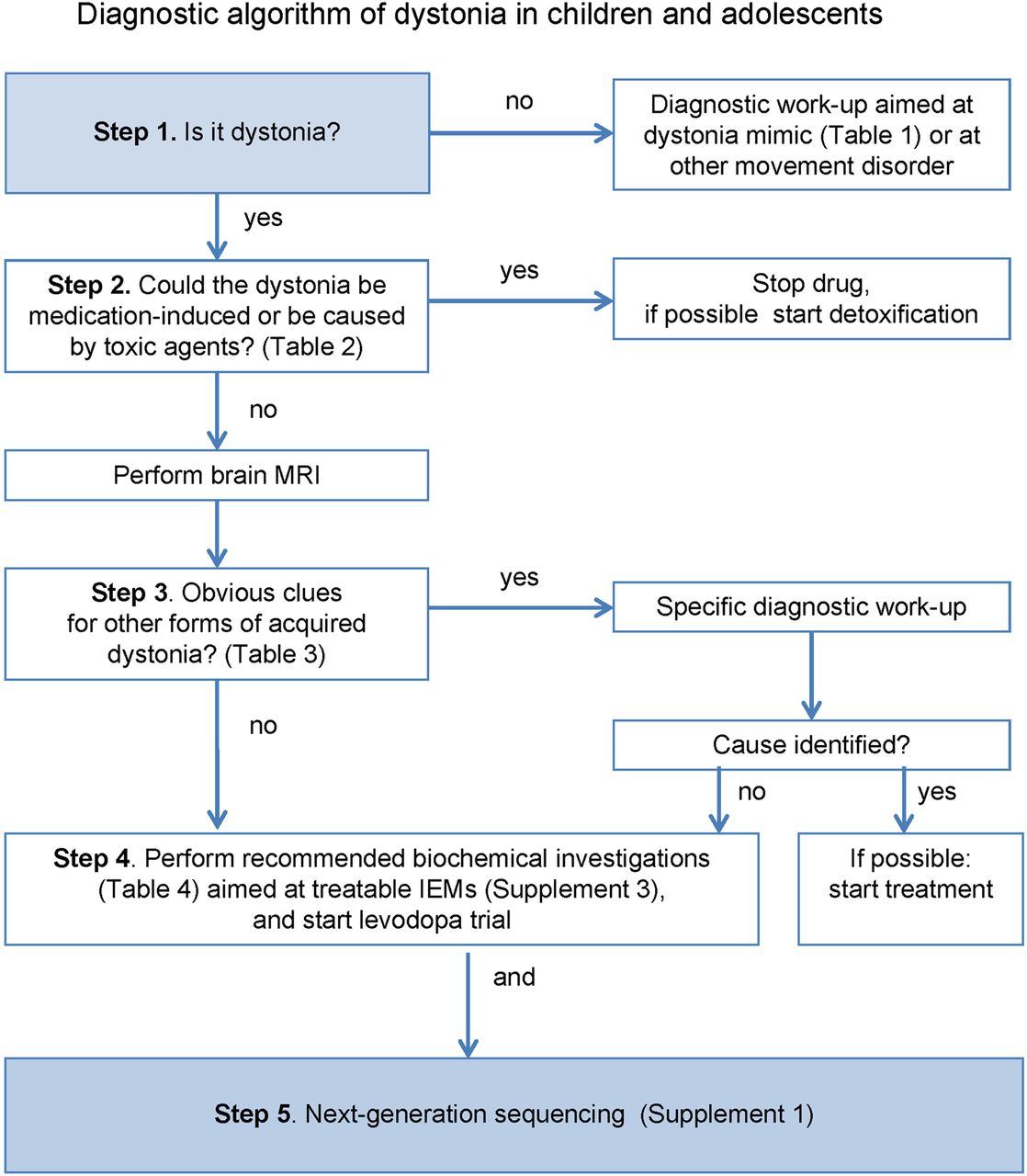
What is genetic torsion dystonia?
Idiopathic torsion dystonia (ITD) is a clinically and genetically heterogeneous group of movement disorders, characterized by sustained dystonic muscle contractions causing involuntary twisting movements and/or postures, where causes like cerebral lesions (especially of the basal ganglia), drugs or other neurological ...
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for dystonia?
ICD-10 code G24. 9 for Dystonia, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
What is code G24 9?
Dystonia, unspecified9: Dystonia, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for torticollis?
ICD-10 code M43. 6 for Torticollis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Dorsopathies .
What is generalized dystonia?
Generalised dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterised by continuous or intermittent muscle contractions which cause abnormal, often painful, repetitive movements in the whole body. Typically, the condition starts in a limb and then 'generalises' to other areas.
What dystonia means?
Dystonia is a disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause slow repetitive movements or abnormal postures. The movements may be painful, and some individuals with dystonia may have a tremor or other neurological symptoms.
What type of muscle does dystonia affect?
Cranial dystonia affects the head, face, and neck muscles. Oromandibular dystonia causes spasms of the jaw, lips, and tongue muscles. This dystonia can cause problems with speech and swallowing. Spasmodic dystonia affects the throat muscles that are responsible for speech.
What is the ICD-10 code for cervical dystonia?
G24. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G24. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are dystonic reactions?
Introduction. An acute dystonic reaction is characterized by involuntary contractions of muscles of the extremities, face, neck, abdomen, pelvis, or larynx in either sustained or intermittent patterns that lead to abnormal movements or postures.
What is ICD-10 code R51?
ICD-10 code R51 for Headache is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is muscular torticollis?
What is congenital muscular torticollis? Congenital muscular torticollis is a condition in which an infant's neck muscle is shortened causing the neck to twist. Congenital means present at birth and torticollis means twisted neck. The condition is sometimes called wryneck.
What causes cervical dystonia?
The cause of Cervical dystonia is often unknown. In some cases there is a family history. Several genes have been associated with Cervical dystonia, including GNAL, THAP1, CIZ1, and ANO3. Other cases may be linked to an underlying disease (e.g. Parkinson disease), neck trauma, or certain medications.
The ICD code G241 is used to code Dopamine-responsive dystonia
Dopamine-responsive dystonia (DRD), also known as hereditary progressive dystonia with diurnal fluctuation, Segawa's disease, or Segawa's dystonia, is a genetic movement disorder which usually manifests itself during early childhood at around ages 5–8 years (variable start age).
Coding Notes for G24.1 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'G24.1 - Genetic torsion dystonia'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code G24.1. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 333.6 was previously used, G24.1 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is dystonia 6?
Dystonia 6 is one of many forms of dystonia, which is a group of conditions characterized by involuntary movements, twisting (torsion) and tensing of various muscles, and unusual positioning of affected body parts. Dystonia 6 can appear at any age from childhood through adulthood; the average age of onset is 18.
What are the symptoms of dystonia?
The signs and symptoms of early-onset primary dystonia vary from person to person, even among affected members of the same family. The mildest cases affect only a single part of the body, causing isolated problems such as a writer's cramp in the hand. Severe cases involve abnormal movements affecting many regions of the body.
What is the term for a condition that involves involuntary tensing of the muscles?
Early-onset primary dystonia is a condition characterized by progressive problems with movement, typically beginning in childhood. Dystonia is a movement disorder that involves involuntary tensing of the muscles (muscle contractions), twisting of specific body parts such as an arm or a leg, rhythmic shaking (tremors), and other uncontrolled movements. A primary dystonia is one that occurs without other neurological symptoms, such as seizures or a loss of intellectual function (dementia). Early-onset primary dystonia does not affect a person's intelligence.
When does dystonia start?
On average, the signs and symptoms of early-onset primary dystonia appear around age 12. Abnormal muscle spasms in an arm or a leg are usually the first sign. These unusual movements initially occur while a person is doing a specific action, such as writing or walking. In some affected people, dystonia later spreads to other parts of the body and may occur at rest. The abnormal movements persist throughout life, but they do not usually cause pain.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code G24.1:
When was the ICd 10 code implemented?
FY 2016 - New Code, effective from 10/1/2015 through 9/30/2016 (First year ICD-10-CM implemented into the HIPAA code set)
Can dystonia affect just one muscle?
Dystonia can affect just one muscle, a group of muscles or all of your muscles. Symptoms can include tremors, voice problems or a dragging foot. Symptoms often start in childhood. They can also start in the late teens or early adulthood. Some cases worsen over time. Others are mild.
What is a primary manifestation of dystonia?
Acquired and inherited conditions that feature dystonia as a primary manifestation of disease. These disorders are generally divided into generalized dystonias (e.g., dystonia musculorum deformans) and focal dystonias (e.g., writer's cramp). They are also classified by patterns of inheritance and by age of onset.
How does dystonia affect the body?
Sometimes they are painful. Dystonia can affect just one muscle, a group of muscles or all of your muscles. Symptoms can include tremors, voice problems or a dragging foot. Symptoms often start in childhood. They can also start in the late teens or early adulthood. Some cases worsen over time. Others are mild. Some people inherit dystonia. Others have it because of another disease. Either way, researchers think that a problem in the part of the brain that handles messages about muscle contractions might cause dystonia. There is no cure. Instead, doctors use medicines, surgery, physical therapy and other treatments to reduce or eliminate muscle spasms and pain. national institute of neurological disorders and stroke
What is abnormal involuntary motor?
Abnormal involuntary motor processes that occur due to underlying disease processes. Abnormal involuntary movements which primarily affect the extremities, trunk, or jaw that occur as a manifestation of an underlying disease process.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for prothrombin time
- 2. icd 10 cm code for postpartum condition of retained placenta without hemorrhage
- 3. icd 10 cm code for inability to care for self
- 4. icd 10 code for lower right leg bleeding
- 5. icd 10 code for right exotropia
- 6. icd 9 code for status post surgery
- 7. 2021 icd 10 code for pyelonephritis
- 8. icd 10 code for chronic abdominal gastritis
- 9. icd-9 code for pelvic congestion syndrome
- 10. icd 10 code for igreular cycle