What is the ICD 10 code for arteritis?
2018/19 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I77.6. Arteritis, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. I77.6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What are the ICD 10 numbers for atherosclerosis of native arteries?
I70.222 Atherosclerosis of native arteries of extremi... I70.223 Atherosclerosis of native arteries of extremi... I70.228 Atherosclerosis of native arteries of extremi...
What are the IAS codes for atherosclerosis?
I70.509 Unspecified atherosclerosis of nonautologous ... I70.51 Atherosclerosis of nonautologous biological b... I70.511 Atherosclerosis of nonautologous biological b...
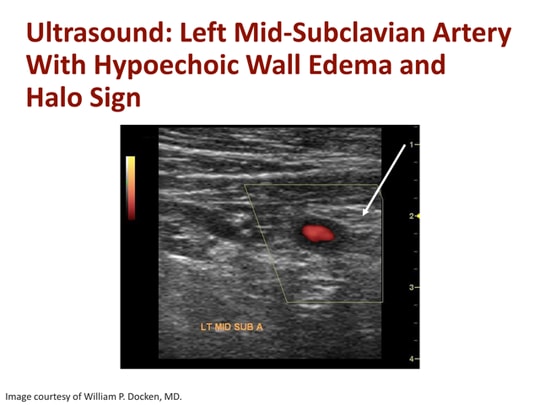
What is the ICD 10 CM code for temporal arteritis?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I77 89 Other specified disorders of arteries and art...
Why is it called giant cell arteritis?
The term “giant cell arteritis” is often used because when one looks at biopsies of inflamed temporal arteries under a microscope, one often sees large or “giant” cells.
Is giant cell and temporal arteritis the same?
Overview. Giant cell arteritis is an inflammation of the lining of your arteries. Most often, it affects the arteries in your head, especially those in your temples. For this reason, giant cell arteritis is sometimes called temporal arteritis.
Is vasculitis the same as giant cell arteritis?
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is a form of vasculitis—a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage vital organs and tissues. Also called temporal arteritis, GCA typically affects the arteries in the neck and scalp, especially the temples.
Is giant cell arteritis life threatening?
Giant cell arteritis, also referred to as temporal arteritis, is a form of vasculitis which predominantly affects older people. It must be treated urgently, as it is associated with a significant risk of permanent visual loss, stroke, aneurysm and possible death.
What is the most feared complication of giant cell arteritis?
Visual loss. Acute visual loss in one or both eyes is by far the most feared and irreversible complication of giant cell arteritis. The main blood supply compromised by giant cell arteritis is to the anterior optic nerve head via the short posterior ciliary arteries and that of the retina via the central retinal artery ...
What is the giant cell?
Giant cells are formed by fusion of various cells such as macrophage, epithelioid cells, monocytes, etc., These are multi-nucleated,[1] large in size, and most of the times present at the site of chronic inflammation and other granulomatous conditions.
What does GCA stand for?
Giant cell arteritis (or GCA) is a medical condition that can cause pain and swelling in blood vessels.
How is giant cell arteritis diagnosed?
The best way to confirm a diagnosis of giant cell arteritis is by taking a small sample (biopsy) of the temporal artery. This artery is situated close to the skin just in front of your ears and continues up to your scalp.
Is giant cell arteritis an autoimmune disease?
Giant cell arteritis is thought to be an autoimmune disorder, where the body's defense system used against invading organisms is used instead to attack normal healthy tissues.
What can mimic giant cell arteritis?
Other clinical mimics of GCA with abnormal biopsies include polyarteritis nodosum, GPA, eosinophilic granulomatosis, mantle cell lymphoma, skull metastasis and epithelioid haemangioma. Histopathologically the vasculitides have much in common and there is much variation even amongst patients with GCA.
What is giant cell tumor of bone?
What is a giant cell tumor? Giant cell tumor of bone is a rare, aggressive non-cancerous tumor. It generally happens in adults between ages 20 and 40 when skeletal bone growth is complete. It usually develops near a joint at the end of the bone.
What is the ICd 9 code for GCA?
No other drugs are effective or contribute to the effect of glucocorticoids. Specialty: Rheumatology. MeSH Code: D013700. ICD 9 Code: 446.5.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code M31.6 and a single ICD9 code, 446.5 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the name of the artery that is occlusion?
The most serious complication is occlusion of the ophthalmic artery, which is a branch of the internal carotid. It can create a medical emergency which can cause irreversible ischemia and blindness if not treated promptly. GCA is treated with glucocorticoids (steroids), which reduce the inflammation and prevent occlusion. No other drugs are effective or contribute to the effect of glucocorticoids.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for low back
- 2. icd 10 code for place of occurrence high school
- 3. icd 10 code for blindness due to glaucoma
- 4. icd 10 diagnosis code for overactive bladder
- 5. icd 10 code for immunoglobulin m
- 6. hemoglobin a1c icd 10 code for medicare
- 7. icd 10 code for presence of left hip prosthesis
- 8. icd 10 pcs code for replacement plantar nerve left foot
- 9. icd 10 code for low ferritin
- 10. icd 10 code for history of scc