What are the causes of glioblastoma brain tumor?
- Risk factors do not necessarily cause cancer to develop (for instance, reaching a certain age does not trigger cancerous changes within the body)
- Many people who have one or more glioblastoma risk factors never develop cancer
- Some people develop glioblastoma without having any of the known risk factors
What can cause a brain tumor to be inoperable?
Inoperable tumors are those that are unable to be removed surgically because of their location in the brain or because there are multiple tumors. Minimally invasive approaches as well as Gamma Knife radiosurgery are available for the treatment of these types of tumors.
What is the diagnosis code for brain tumor?
- Functional MRI (fMRI): Maps areas of the brain responsible for critical functions, such as movement and speech. ...
- Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI): Identifies white matter tracts, the signaling pathways in the brain. ...
- Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS): Measures biochemical changes in the brain, especially in the presence of brain tumors. ...
How is a brain tumor diagnosed without biopsy?
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). ...
- Intravenous (IV) gadolinium-enhanced MRI is typically used to help create a clearer picture of a brain tumor. ...
- An MRI technique called "diffusion weighted imaging" helps show the cellular structure of the brain. ...
- A spinal MRI may be used to diagnose a tumor on or near the spine.
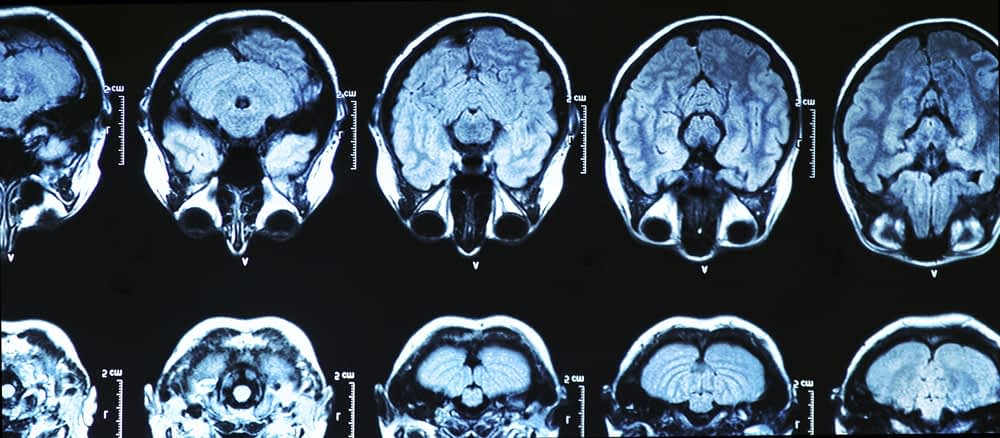
What is the difference between glioblastoma and glioblastoma multiforme?
Grade four gliomas are the most aggressive type and are also known as glioblastoma. These tumors used to be called glioblastoma multiforme, or GBM for short. “Lower grade gliomas typically occur in younger patients,” Dr. Lipinski says.
What does multiforme mean in glioblastoma?
Listen to pronunciation. (GLEE-oh-blas-TOH-muh MUL-tih-form) A fast-growing type of central nervous system tumor that forms from glial (supportive) tissue of the brain and spinal cord and has cells that look very different from normal cells.
What is the difference between glioblastoma and brain tumor?
Glioblastoma (GBM), also referred to as a grade IV astrocytoma, is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. It invades the nearby brain tissue, but generally does not spread to distant organs. GBMs can arise in the brain de novo or evolve from lower-grade astrocytoma.
What is the ICD 10 code for brain tumor?
ICD-10-CM Code for Malignant neoplasm of brain, unspecified C71. 9.
What is multiforme?
multiforme (plural multiformi) multiform. varied. versatile quotations ▼
WHO classification glioblastoma multiforme?
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive diffuse glioma of astrocytic lineage and corresponds to grade IV according to the latest WHO Classification of Tumors of the CNS (4th ed., 2007). It may involve any neuroanatomical level or structure, but is most common in the cerebral hemispheres [1].
What is the longest someone has lived with glioblastoma?
Incredibly, 2021 marks the 17th anniversary of Carmen Rice's survival from Stage 4 Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) brain tumor. Originally given six months to live, Carmen beat the odds to become the longest living survivor of the deadliest form of brain cancer.
Are all brain cancers glioblastoma?
Are all brain tumors cancer? All brain cancers are made up of tumors, but not all brain tumors are cancerous. For example, more than half of all gliomas diagnosed in adults are glioblastomas, a very aggressive form of brain cancer. Ependymomas and oligodendrogliomas also are types of brain tumors that may be malignant.
What is the life expectancy of a person with glioblastoma?
The average life expectancy for glioblastoma patients who undergo treatment is 12-15 months and only four months for those who do not receive treatment. Glioblastomas develop from glial cells in the brain and spinal cord.
What is glioma tumor?
Glioma is a common type of tumor originating in the brain. About 33 percent of all brain tumors are gliomas, which originate in the glial cells that surround and support neurons in the brain, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and ependymal cells.
What is the ICD 9 code for brain tumor?
ICD-9 code 191.9 for Malignant neoplasm of brain unspecified site is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range -MALIGNANT NEOPLASM OF OTHER AND UNSPECIFIED SITES (190-199).
Which of these is a malignant tumor of the brain?
Cancerous (malignant) brain tumors Astrocytoma: These tumors are the most common type of glioma. They form in the star-shaped glial cells called astrocytes. They can form in many parts of your brain, but most commonly occur in your cerebrum. Ependymomas: These tumors often occur near the ventricles in your brain.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified ( C25.9 ). A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm affecting the brain. Cancer of the brain is usually called a brain tumor. There are two main types.
What is oligodendroglioma?
Oligodendroglioma of brain. Primary malignant neoplasm of brain. Primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Secondary malignant neoplasm of spinal cord from neoplasm of brain. Clinical Information. A primary or metastatic malignant neoplasm affecting the brain. Cancer of the brain is usually called a brain tumor.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
How do doctors diagnose brain tumors?
doctors diagnose brain tumors by doing a neurologic exam and tests including an mri, ct scan, and biopsy. People with brain tumors have several treatment options. The options are surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Many people get a combination of treatments. nih: national cancer institute.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
Where does a brain tumor start?
A primary brain tumor starts in the brain. A metastatic brain tumor starts somewhere else in the body and moves to the brain. Brain tumors can be benign, with no cancer cells, or malignant, with cancer cells that grow quickly.brain tumors can cause many symptoms. Some of the most common are.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
What is the table of neoplasms used for?
The Table of Neoplasms should be used to identify the correct topography code. In a few cases, such as for malignant melanoma and certain neuroendocrine tumors, the morphology (histologic type) is included in the category and codes. Primary malignant neoplasms overlapping site boundaries.
What is the most aggressive form of brain cancer?
Glioblastoma is a fast-growing type of central nervous system cancer that forms from glial (supportive) tissue of the brain and spinal cord and has cells that look very different from normal cells. It spreads aggressively throughout the brain tissue and is the most malignant of the primary brain cancers.
What is the only definitive test for glioblastoma?
Diagnostic procedures. The only definitive test that can provide a diagnosis of glioblastoma is a biopsy of the cancer. Testing to confirm diagnosis of glioblastoma includes neuroimaging (CT and MRI) to provide information about the location, size and shape of the cancer.
What is the treatment for glioblastoma?
Treatment of glioblastoma may include the following: surgery, radiation and/or chemotherapy. Pathology report of the cancer biopsy or surgical specimen is the critical information necessary for disability evaluation; Results of neuroimaging (e.g. CT scan, MRI scan).
How long does it take to die from glioblastoma?
The prognosis is grim, as most patients die within 2 years and few survive longer than three years. Treatment of glioblastoma may include the following: surgery, radiation and/or chemotherapy.
When does glioblastoma occur?
Glioblastoma most often occurs in adults between the ages of 45 and 70 years and affects the brain more often than the spinal cord. DIAGNOSTIC TESTING, PHYSICAL FINDINGS, AND ICD-9–CM/ICD-10-CM CODING. Diagnostic testing: Diagnosis is based on:
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for systolic chf exacerbation
- 2. icd 10 code for erythema and erosions small intestine
- 3. icd 10 code for lipoma left shoulder
- 4. icd 10 code for insulin growth factor binding protein 3
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for orthostatic hypotension
- 6. icd-10 code for pronounced dead
- 7. icd 10 code for epicondylitis left
- 8. icd 10 cm code for post herpetic neuralgia.
- 9. icd 10 cm code for drug-induced dementia
- 10. icd 10 dx code for atv accident