Hemangioma, lymphangioma, or glomus tumor, any site (228.0) Excision, tumor or vascular malformation, hand or finger; deep, subfascial, intramuscular (26116) Radical resection of tumor eg, malignant neoplasm), soft tissue of hand or finger (26117)
What is the ICD 10 Index for glomus?
Glomus ICD-10-CM Neoplasms Index. The ICD-10-CM Neoplasms Index is designed to allow medical coders to look up various medical terms and connect them with the appropriate ICD codes. There are 2 terms under the parent term 'Glomus' in the ICD-10-CM Neoplasms Index .
What is a glomus tumor?
Glomus Tumors are rare benign tumors of the glomus body, often occurring in the subungual region. The condition is typically seen in patients between the ages of 20 and 40 who present with a painful subungal mass with bluish discoloration.
What is the pathophysiology of glomangiomatosis?
Well circumscribed mass composed of 3 components: glomus cells, vasculature and smooth muscle cells Solid glomus tumor (75% of cases): predominantly glomus cells, poor vasculature and rare smooth muscle cells Rare variants have microscopically infiltrative and diffuse growth and are known as glomangiomatosis
What is the ICD 10 code for lymphangioma with neoplasm?
D18 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D18. Hemangioma and lymphangioma, any site 2016 2017 2018 2019 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. Type 1 Excludes benign neoplasm of glomus jugulare (D35.6) blue or pigmented nevus (D22.-) nevus NOS (D22.-) vascular nevus (Q82.5) Hemangioma and lymphangioma, any site.
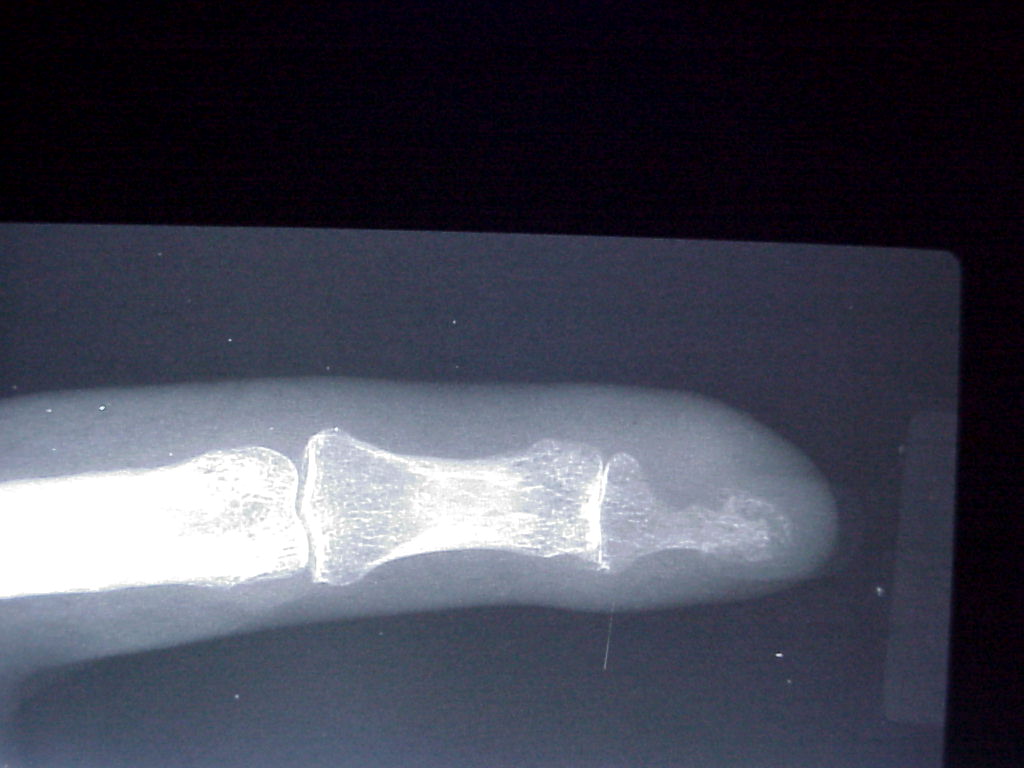
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Hemangioma?
ICD-10 code D18. 0 for Hemangioma is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Neoplasms .
What is ICD-10 code for granular cell tumor?
9: Benign neoplasm of connective and other soft tissue, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for swelling left hand?
Localized swelling, mass and lump, left upper limb The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R22. 32 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R22.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for a cavernous Hemangioma?
02.
What is c49 99?
Malignant neoplasm of connective and soft tissue, unspecified.
What is a granular cell tumor?
Listen to pronunciation. (GRAN-yoo-lur sel TOO-mer) A rare type of soft tissue tumor that usually begins in Schwann cells (cells that hold nerve cells in place). It can occur anywhere in the body, but it usually occurs in or under the skin of the head and neck (especially the mouth or tongue).
What is the ICD-10 code M79 89?
Other specified soft tissue disorders SiteICD-10 code: M79. 89 Other specified soft tissue disorders Site unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for swollen finger?
R22. 31 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R22. 31 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is a cavernous angioma?
A cavernoma is a cluster of abnormal blood vessels, usually found in the brain and spinal cord. They're sometimes known as cavernous angiomas, cavernous hemangiomas, or cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM). A typical cavernoma looks like a raspberry.
What is the ICD 10 code for Dermatofibroma?
Other benign neoplasm of skin, unspecified D23. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D23. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is capillary hemangioma?
Capillary hemangioma is one of the most common benign orbital tumors of childhood affecting up to 5% of infants under the age of 1 year. It can be superficial, presenting as a red, raised lesion, it can be deep, presenting as a dark blue lesion that may extend into the orbit or may present both of the above components.
Where do benign tumors occur?
Extremely common benign tumor, occurring most commonly in infancy and childhood, made up of newly formed blood vessels, and resulting from malformation of angioblastic tissue of fetal life; can occur anywhere in the body but is most frequently noticed in the skin and subcutaneous tissues.
When will the ICd 10 D18.00 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D18.00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a benign vascular neoplasm?
It is characterized by the formation of capillary-sized or cavernous vascular channels. The majority of cases are congenital.
Where is the benign glomus tumor found?
Benign glomus tumor component can often be found at the periphery and help with diagnosis. Glomus tumor of uncertain malignant potential: Tumors that do not fulfill criteria for malignancy but have at least 1 atypical feature other than nuclear pleomorphism.
What is the shape of a glomus cell?
Glomus cell has a round shape with indistinct borders with a rounded, sharply punched out nucleus in an amphophilic to eosinophilic cytoplasm.
What is glomangiopericytoma used for?
Glomangiopericytoma may be used for glomus tumors with prominent hemangiopericytic vasculature; however, these tumors are different from the pericytic site specific sinonasal glomangiopericytoma
Is doxorubicin used for glomus tumors?
No clinical trial data is available for treatment of malignant glomus tumors, but doxorubicin and olaratumab have been approved for recurrent / metastatic disease
Is myopericytoma a pericytic tumor?
Differential diagnosis. Myopericytoma and other pericytic tumors: deri ved from perivascular cells and may lie on a spectrum with glomus tumors; can have histologic and immunohistochemical overlap in areas with more prominent spindled differentiation.
What are the criteria for glomus tumor diagnosis?
Criteria for the diagnosis of malignancy in glomus tumors are: Tumor size of more than 2 centimeters and subfascial or visceral location. Atypical mitotic figures. Marked nuclear atypia and any level of mitotic activity. Pericytes of Zimmerman.
What is the size of a glomus tumor?
The tumor is the translucent oblate spheroid in the center of the incision, approximate horizontal dimension is 4 millimeters. Surgical excision is the preferred treatment for benign glomus tumors.
How often do glomus tumors occur?
Solitary glomus tumors are more frequent in adults than in others. Multiple glomus tumors develop 11–15 years earlier than single lesions; about one third of the cases of multiple tumors occur in those younger than 20 years. Congenital glomus tumors are rare; they are plaguelike in appearance and are considered a variant of multiple glomus tumors.
Where are glomus tumors found?
Glomus tumors are usually solitary and small lesions. The vast majority are found in the hand, wrist, foot, and under the fingernails. They are often painful, and the pain is reproduced when the lesion is placed in cold water. Multiple tumors are less likely to be painful.
Where does a malignant glomus tumor come from?
Another report of a malignant glomus tumor ( glomangiosarcoma) with metastases from the skin. A malignant glomus tumor one arose from the kidneys.
What is glomangioma inherited?
Familial glomangiomas have been associated with a variety of deletions in the GLMN ( glomulin) gene, and are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, with incomplete penetrance.
Is a glomus tumor benign?
The majority of glomus tumors are benign, but they can also show malignant features. Glomus tumors were first described by Hoyer in 1877 while the first complete clinical description was given by Masson in 1924. Histologically, glomus tumors are made up of an afferent arteriole, anastomotic vessel, and collecting venule.
What is the gene for glomus tumor?
There is a familial variant of glomus tumor, linked to chromosome 1p21–22, encoding the glomulin gene ( GLMN ). Multiple glomus tumors are inherited as an autosomal dominant trait and are usually found on the legs. They are often present in younger children.
Where do glomus tumors come from?
A glomus tumor is benign neoplasm that originates from cells of the glomus body. Glomus bodies are highly concentrated in the fingertips, so not surprisingly, glomus tumors are most common in the hands and subungual region. Small single tumors are most frequent, and women are affected more often than men. Most patients are between 30 and 50 years ...
How old do you have to be to have subungual glomus?
Most patients are between 30 and 50 years of age. Subungual glomus tumors may present with a triad: pain, pinpoint tenderness, and cold sensitivity. Physical examination may show a small reddish or bluish papule several millimeters in diameter.
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2016 icd 10 code for leiomyoma of esophagus
- 2. icd-10-cm code for iron deficiency anemia
- 3. icd 10 diagnosis code for ipoma of breast
- 4. icd 10 code for hsv1
- 5. icd 10 code for left nephrolithiasis
- 6. icd 10 code for mass to head
- 7. icd 10 code for other dorsalgia
- 8. icd 10 code for peripheral neuropathy nos
- 9. 2019 icd 10 code for gastric antral vascular ectasia
- 10. icd 10 code for i and d boil right medial thigh