What is Grade 3 AC separation?
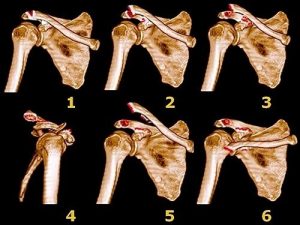
Grade III- The most severe shoulder separation. This completely tears both the AC and CC ligaments and puts the AC joint noticeably out of position, with a larger bump. SEPARATED SHOULDER SYMPTOMS Swelling, tenderness, or pain over/above the joint Visible bump above the shoulder Loss of strength or motion Pain when lying on one’s side
What is an AC separation Grade 3?
The most common severe type of AC separation is a grade III injury. You will see a bump on top of your shoulder. It might be a small bump, or it could be a rather large and disturbing bump. When you have an AC separation the ligaments which connect the collar bone to the scapula have torn.
What is a Grade 3 AC joint separation?
A grade 3 AC joint separation is a true dislocation of the AC joint. However, any direct blunt force can cause an AC joint separation if severe enough. The initial symptoms are very severe pain, localized swelling and the notable presence of a “bump” on the shoulder. Beside above, how long does it take for an AC joint to heal?
What is a third degree AC separation?
A third degree A-C separation represents a complete dislocation of the joint and rupture of all ligaments. The collarbone displacement produces a large painful deformity. The treatment of this injury is controversial. Some orthopaedists believe that no treatment is necessary, and therefore no attempt is made to reduce the separation.
What is the ICD-10 code for AC joint separation?
149: ACROMIOCLAVICULAR JOINT SEPARATION.
What is a Grade 2 Separation?
Grade II - A partial dislocation of the joint in which there may be some displacement that may not be obvious during a physical examination. The acromioclavicular ligament is completely torn, while the coracoclavicular ligaments remain intact. Grade III - A complete separation of the joint.
What is a chronic Grade 2 acromioclavicular?
A grade 2 injury will involve complete rupture of the acromioclavicular ligament and partial tear of the coracoclavicular ligament. This tearing allows the clavicle to move upward, and as a result, the bump on the shoulder is more pronounced. Pain is more severe and movement of the shoulder is restricted.
What is an AC joint separation?
An AC joint separation involves damage to the ligaments supporting the AC joint, either sprains or tears, commonly caused by a fall on the shoulder. This can result in pain, shoulder deformity, and loss of forelimb mobility.
How do you treat a Grade 2 AC separation?
Type II — Type II injuries usually cause greater pain and swelling than type I injuries. Initial treatment may include rest, ice, pain medication, and three to seven days of shoulder immobilization in a sling. Range-of-motion exercises and stretching exercises can be started when tolerable.
Does a Grade 2 AC separation require surgery?
Types of AC Joint Separations Mild AC separations are either grade I or II. Both of them will not require surgery.
How long does it take a Grade 2 AC joint separation to heal?
Return to activities — After a type II AC injury, most people are able to return to full activities when full range of motion and strength are regained, usually after two to four weeks. Gradually, add back activities as tolerated by pain or soreness. Complete healing generally requires several more weeks.
What is a Grade 3 acromioclavicular joint separation?
A type III separation involves injury to both the AC joint ligaments the CC ligaments. This results in complete separation between the acromion and clavicle, and treatment for this type is controversial.
What is a separated shoulder?
What is shoulder separation? A shoulder separation injury occurs when trauma damages the ligaments around the acromioclavicular (AC) joint. It's where the collarbone (clavicle) meets the shoulder blade (scapula). If the injury is severe, part of the shoulder blade may separate from the collarbone.
What is the difference between a dislocated shoulder and a separated shoulder?
Shoulder separation is an injury to the ligament between the shoulder blade and collarbone. Whereas shoulder dislocation occurs when the top of the arm bone loses contact with the socket of the shoulder blade.
How many types of shoulder separations are there?
A shoulder separation is classified according to how severely these ligaments are injured: In a type I injury, the AC ligament is partially torn, but the CC ligament is not injured. In a type II injury, the AC ligament is completely torn, and the CC ligament is either not injured or partially torn.
What is a Grade 4 AC separation?
A grade 4 AC separation occurs when the clavicle is severely displaced posteriorly. It is defined as “significant” posterior displacement. The grade separation definition does not have any quantifiable distance as it is determined simply by the impression of the clinician.
Where is the AC joint located?
The AC joint is located at the distal end of the clavicle, known as the acromial end, and attaches to the acromion of the scapula. Although this is part of the shoulder, a dislocation and a separation are completely different.
What is the ICD code for acute care?
Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code S43.11 is a non-billable code.
What is a separated shoulder?
A separated shoulder (also known as acromioclavicular separation, AC joint separation, AC separation), is a common injury to the acromioclavicular joint. This is not to be confused with shoulder dislocation which occurs when the humerus separates from the scapula at the glenohumeral joint.
What causes acromioclavicular separation?
Acromioclavicular separation occurs as a result of a downward force being applied to the superior part of the acromion, either by something striking the top of the acromion or by falling directly on it. The injury is more likely to occur if the shoulder is struck with the hand outstretched.
Why is the clavicle in its general fixed position?
Despite the scapula pulling on the clavicle during impact, the clavicle remains in its general fixed position because of the sternoclavicular joint ligaments.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
What is the ICd 10 code for acromioclavicular dislocation?
Dislocation of left acromioclavicular joint, greater than 200% displacement, initial encounter 1 S43.132A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 #N#Short description: Dislocation of l acromioclav jt, > 200% displacmnt, init#N#The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM S43.132A became effective on October 1, 2020.#N#This is the American ICD-10-CM version of S43.132A - other international versions of ICD-10 S43.132A may differ.
What is grade 2 AC separation?
A Grade 2 AC Joint Separation results from an incomplete tearing of the acomioclavciular and/or the coracoclavicular ligaments. The joint is incompletely dislocated; the medical term for this is “subluxed”. Comparing the injured side to the normal side one can see an asymmetry when examining the space between the clavicle and coracoid processs (coracoclavicular interval). If the increase in the interval is less than a 25% change then the injury is considered to be a grade 2 separation. As with a grade 1 injury the initial treatment is non-surgical. Although the resulting deformity is barely noticeable this change is permanent. However, in most cases local symptoms will resolve with physical therapy and rest. In some cases the permanent deformity of the joint will cause ongoing symptoms requiring surgical treatment, however.
Is grade 1 deformity permanent?
As with a grade 1 injury the initial treatment is non-surgical. Although the resulting deformity is barely noticeable this change is permanent. However, in most cases local symptoms will resolve with physical therapy and rest. In some cases the permanent deformity of the joint will cause ongoing symptoms requiring surgical treatment, however.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for suicide
- 2. icd 10 code for viral infection left leg
- 3. icd 10 code for chronic smooker
- 4. icd 10 code for degenerative disc disease c6-c7
- 5. case 52 what is the correct icd-10-cm code assignment for this case?
- 6. icd 10 code for sun damaged skin
- 7. icd 10 code for exposure to venereal disease
- 8. icd 10 code for left upper arm skin lesion
- 9. icd-10 code for aftercare following surgery
- 10. icd 10 code for heart valve disease (ar-+++, mr, tr)