What is Stage 2 diastolic dysfunction?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G92.02 Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome, grade 2 Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity synd, grade 2; ICANS, grade 2 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code P52.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Intraventricular (nontraumatic) hemorrhage, grade …
Does your patient really have diastolic dysfunction?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.3 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.3 Diastolic (congestive) heart failure 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code I50.3 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
How is diastolic dysfunction diagnosed?
Jan 25, 2020 · Herein, what is the diagnosis code for diastolic dysfunction? Unspecified diastolic (congestive) heart failure I50. 30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I50. 30 became effective on October 1, 2019.
How to diagnose type 1 vs Type 2 diabetes?
Diastolic (congestive) heart failure (I50.3) I50.23 I50.3 I50.30 ICD-10-CM Code for Diastolic (congestive) heart failure I50.3 ICD-10 code I50.3 for Diastolic (congestive) heart failure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
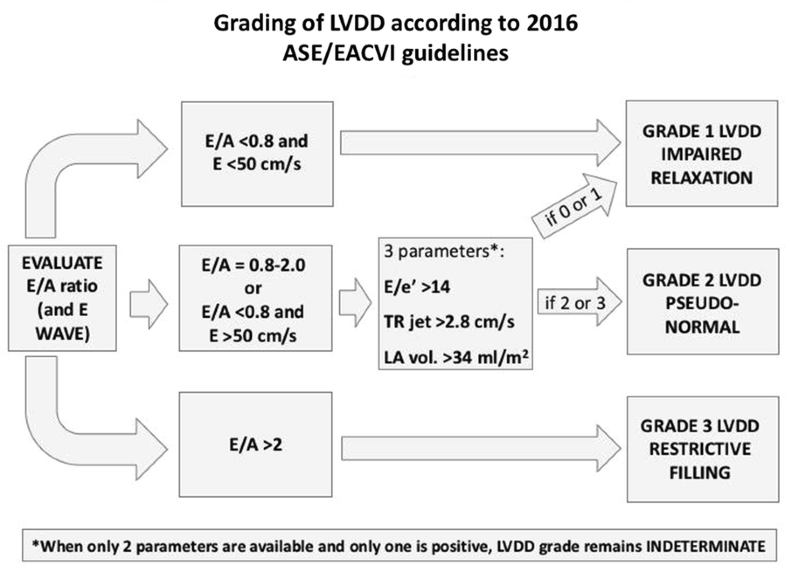
What is Grade II diastolic dysfunction?
Grade II – This diastolic dysfunction is characterized by increased filling pressure in the atrium and is considered to be moderate stage disease. The left atrium may also increase in size due to the increased pressure.
What is the ICD-10 code for diastolic dysfunction?
3.
Is grade 2 diastolic dysfunction treatment?
In patients with grade 2 or 3 diastolic dysfunction (abnormal relaxation and elevated filling pressures), the addition of diuretics should be considered due to elevated filling pressures.
What does diastolic dysfunction grade mean?
Grade 1 diastolic dysfunction occurs when the left lower chamber of the heart (the left ventricle) has trouble relaxing in between beats because it has stiffened over time. It interferes slightly with the heart's most important job—getting oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body.Oct 8, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for OSA?
Code G47. 33 is the diagnosis code used for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. It is a sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or instances of shallow breathing during sleep.
Is diastolic dysfunction same as heart failure?
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), also called diastolic failure (or diastolic dysfunction): The left ventricle loses its ability to relax normally (because the muscle has become stiff). The heart can't properly fill with blood during the resting period between each beat.May 31, 2017
How long can you live with grade 2 diastolic dysfunction?
Patients who avail of diagnosis and treatment at early stages tend to have a better outlook and longer life than those who are diagnosed during later stages. Generally, 50% of patients with left ventricular dysfunction go one to live beyond 5 years after being diagnosed. 2.
How many grades are there in diastolic dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction was diagnosed according to the echocardiographic examination results and categorized into 3 grades based on 2009 version of recommendations, that is, grade 1 (mild diastolic dysfunction or impaired relaxation phase: E/A <0.8, DT >200 milliseconds, E/e′ ≤8), grade 2 (moderate diastolic dysfunction ...
What 3 foods cardiologists say to avoid?
Here are eight of the items on their lists:Bacon, sausage and other processed meats. Hayes, who has a family history of coronary disease, is a vegetarian. ... Potato chips and other processed, packaged snacks. ... Dessert. ... Too much protein. ... Fast food. ... Energy drinks. ... Added salt. ... Coconut oil.Feb 28, 2022
What grade is mild diastolic dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction was graded on a four-point ordinal scale: 1) normal; 2) mild diastolic dysfunction = abnormal relaxation without increased LV end-diastolic filling pressure (decreased E/A ratio <0.75); 3) moderate or “pseudonormal” diastolic dysfunction = abnormal relaxation with increased LV end-diastolic ...
How do you diagnose diastolic dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction, a type of heart failure in which the heart isn't able to fully relax after each beat, is diagnosed with an echocardiogram (ECG) and, sometimes, other imaging tests.Jun 10, 2021
Should I worry about grade 1 diastolic dysfunction?
The fact of the matter is true diastolic dysfunction is indeed dangerous, if not more dangerous than systolic dysfunction for the simple reason there is no specific treatment for this condition.Apr 16, 2016
What is the ICD-10 code for heart failure?
I50.30 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of unspecified diastolic (congestive) heart failure. The code I50.30 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code I50.30 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like at high risk for heart failure, at high risk for heart failure, at risk for heart failure, at risk for heart failure, diastolic heart failure , diastolic heart failure stage a, etc.#N#The code is commonly used in cardiology medical specialties to specify clinical concepts such as heart failure.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like I50.30 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
When to use unspecified codes?
Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record. ICD-10: I50.30. Short Description:
What is the I50.30 code?
The code is commonly used in cardiology medical specialties to specify clinical concepts such as heart failure. Unspecified diagnosis codes like I50.30 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition.
What does it mean when your heart is not working?
Heart failure does not mean that your heart has stopped or is about to stop working. It means that your heart is not able to pump blood the way it should. It can affect one or both sides of the heart. The weakening of the heart's pumping ability causes. Blood and fluid to back up into the lungs.
What does it mean when your heart is not pumping enough blood?
Information for Patients. Heart failure is a condition in which the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Heart failure does not mean that your heart has stopped or is about to stop working. It means that your heart is not able to pump blood the way it should.
How do doctors diagnose heart failure?
Your doctor will diagnose heart failure by doing a physical exam and heart tests. Treatment includes treating the underlying cause of your heart failure, medicines, and heart transplantation if other treatments fail. NIH: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
What causes shortness of breath and tiredness?
Tiredness and shortness of breath. Common causes of heart failure are coronary artery disease, high blood pressure and diabetes. It is more common in people who are 65 years old or older, African Americans, people who are overweight, and people who have had a heart attack.
What is 429.9?
In 2009, Q1, Coding Clinic noted that you could not assume heart failure in a patient with diastolic dysfunction, and that it should be coded as 429.9, heart disease, unspecified. The term dysfunction is very non-specific, and runs the gamut from very mild, to extremely severe.
Is heart dysfunction indexed?
There may be minimal dysfunction present, or life threatening dysfunction. As with a lot of documentation, there's simply not enough information there to select a specific diagnosis code. Therefore, the best you can do is choose a non-specific code, that is not more severe than the documentation. In ICD-10, "heart dysfunction" is indexed ...
What is Grade 3 left ventricular diastolic dysfunction?
Grade III – This is a severe form of diastolic dysfunction characterized by restrictive filling of the heart that leads to symptoms of advanced heart failure. When the patient is asked to perform the Valsalva manoeuvre during echocardiography, the diastolic abnormalities seem to reverse.
What are the grades of diastolic dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction was diagnosed according to the echocardiographic examination results and categorized into 3 grades based on 2009 version of recommendations, that is, grade 1 (mild diastolic dysfunction or impaired relaxation phase: E/A <0.8, DT >200 milliseconds, E/e′ ≤8), grade 2 (moderate diastolic dysfunction …
What does diastolic dysfunction grade mean?
Grade I diastolic dysfunction, impaired relaxation: First stage of diastolic dysfunction. Decreased suction of the LV. Grade II diastolic dysfunction, pseudonormalization: Increased stiffness of the LV, elevated LAP. Grade III, restrictive filling (reversible): High LAP, noncompliant LV.
Is diastolic dysfunction the same as congestive heart failure?
Conclusions: The results of this study support the hypothesis that patients with normal left ventricular ejection fractions but diastolic dysfunction develop congestive heart failure because of underlying renal insufficiency.
What is the ICD 10 code for diastolic dysfunction?
People also ask, what is the diagnosis code for diastolic dysfunction? Unspecified diastolic (congestive) heart failure I50. 30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I50. 30 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What are the symptoms of diastolic dysfunction Grade III?
The left atrium may also increase in size due to the increased pressure. Grade III – This is a severe form of diastolic dysfunction characterized by restrictive filling of the heart that leads to symptoms of advanced heart failure.
When does grade IV diastolic dysfunction cause heart failure?
Diuresis will not have a major effect on the left atrial pressures and clinic heart failure is likely permanent. Grade IV diastolic dysfunction is present only in very advanced heart failure and frequently seen in end-stage restrictive cardiomyopathies such as amyloid cardiomyopathy.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for egg allergy
- 2. icd 10 code for esophageal fb
- 3. icd 9 code for fungating mass of groin
- 4. icd 10 code for lisinopril cause cough
- 5. 2016 icd 10 code for atheroscerotic heart disease
- 6. icd 10 code for radius painful hardware
- 7. icd 10 code for type 1 diabetes uncontrolled
- 8. icd 10 code for pulsation in aorta
- 9. icd 10 code for status post embolic cva
- 10. icd 10 code for chronic pharyngitis