What is the ICD 10 code for digestive system disease?
Disease of digestive system, unspecified. K92.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K92.9 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for intestinal infection?
Bacterial intestinal infection, unspecified. A04.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for bacterial overgrowth syndrome?
Bacterial overgrowth syndrome; Bile acid malabsorption syndrome; ICD-10-CM K90.89 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 38.0): 391 Esophagitis, gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders with mcc; 392 Esophagitis, gastroenteritis and miscellaneous digestive disorders without mcc; Convert K90.89 to ICD-9-CM. Code History
What is the ICD 10 code for functional intestinal disorder?
Functional intestinal disorder, unspecified. K59.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM K59.9 became effective on October 1, 2019.
What is the ICD-10 code for bacterial overgrowth?
Bacterial intestinal infection, unspecified A04. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A04. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for GI issues?
9: Disease of digestive system, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for GI dysmotility?
K59. 8 - Other specified functional intestinal disorders | ICD-10-CM.
What is K31 89 diagnosis?
K31. 89 - Other diseases of stomach and duodenum. ICD-10-CM.
What is diagnosis code Z51 11?
ICD-10 code Z51. 11 for Encounter for antineoplastic chemotherapy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for gastroenteritis?
ICD-10 code A09 for Infectious gastroenteritis and colitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain infectious and parasitic diseases .
What is gut dysmotility?
The actions of the muscles and nerves in the gastrointestinal tract that mix and move food (muscle contraction and relaxation) along is the known as motility. When something goes wrong with this action in the muscles or in the nerves of the intestines, this is referred to as intestinal dysmotility.
What is ICD-10 code for gastroparesis?
ICD-10 code K31. 84 for Gastroparesis is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD-10 code for bloating?
R14. 0 - Abdominal distension (gaseous) | ICD-10-CM.
What is Gastroptosis?
Gastroptosis is the abnormal downward displacement of the stomach. Although this condition is not life threatening is associated with constipation, discomfort, vomiting, dyspepsia, tenesmus, anorexia, nausea and belching.
What is the ICD-10 code for epigastric abdominal pain?
ICD-10 code R10. 13 for Epigastric pain is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is intestinal metaplasia of gastric mucosa?
Gastric intestinal metaplasia is a precancerous change of the mucosa of the stomach with intestinal epithelium, and is associated with an increased risk of dysplasia and cancer.
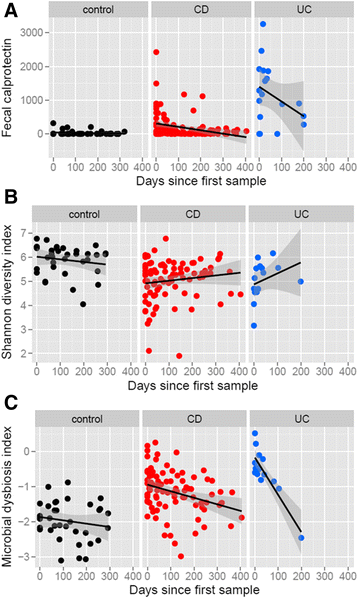
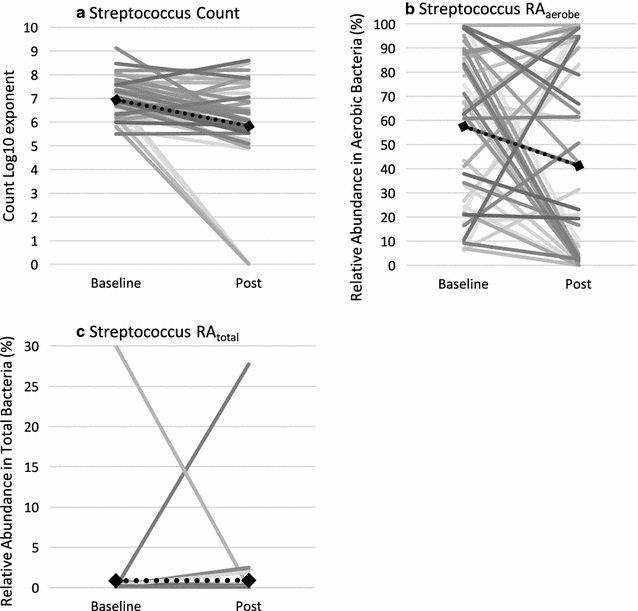
What is intestinal dysbiosis?
The concept of intestinal dysbiosis rests on the assumption that abnormal patterns of intestinal flora, such as overgrowth of some commonly found microorganisms, have an impact on human health. Symptoms and conditions attributed to intestinal dysbiosis include chronic disorders (e.g., irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory or autoimmune disorders, food allergy, atopic eczema, unexplained fatigue, arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis), malnutrition, or neuropsychiatric symptoms (e.g., autism), and breast and colon cancer.
Is stool a marker of dysbiosis?
Laboratory analysis of both stool and urine has been investigated as markers of dysbiosis. Reference laboratories specializing in the evaluation of dysbiosis may offer comprehensive testing of various aspects of digestion, absorption, microbiology, and metabolic markers. For example, Genova Diagnostics (1) offers the Comprehensive Digestive Stool Analysis 2.0 test, which evaluates a stool sample for components listed in Table 1.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for diverticulitis of intestine
- 2. icd 10 code for abscess of right lower leg
- 3. icd 9 code for bone lesions
- 4. icd 10 code for personal history of preeclampsia
- 5. icd 10 code for bursitis of elbow
- 6. icd 10 code for abdominal pain suspected acute appendicitis
- 7. icd 10 code for pap conjunctivitis
- 8. icd 10 code for shoulder strain
- 9. icd 10 code for methadone use in pregnancy
- 10. icd 10 code for spondylosis