What is the ICD-10 code for H pylori infection?
Helicobacter pylori [H. pylori] as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. B96. 81 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the stool test for H. pylori called?
A laboratory test called a stool polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test can detect H. pylori infection in your stool and mutations that may be resistant to antibiotics used to treat it.May 18, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal stool?
R19.5ICD-10 code R19. 5 for Other fecal abnormalities is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
Is H. pylori a stool sample?
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria are a common cause of peptic ulcers (sores in the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus). In this test, a stool (feces) sample is used to determine if H. pylori antigens are present in your child's gastrointestinal (GI) system.
What types of stool tests are there?
Types of Stool TestsRotavirus Test. Also called a “nucleic acid detection test” and “isolation in cell culture,” this stool test is used to diagnose a rotavirus infection. ... Yersinia Test. ... Giardia Antigen Test. ... Salmonella Culture Test. ... White Blood Cell Test. ... Calprotectin Test.
How is H. pylori tested for?
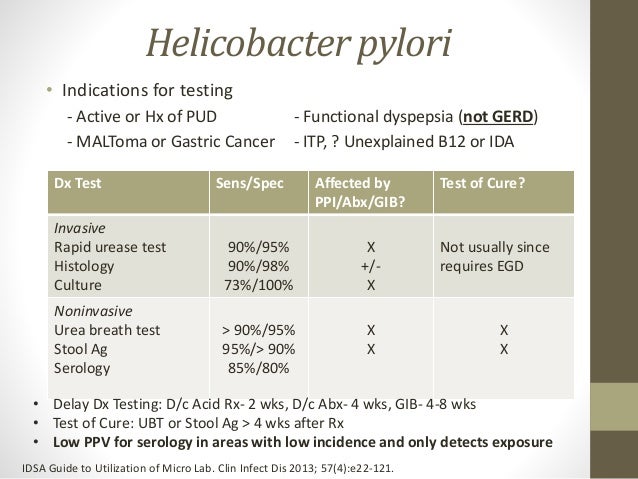
The H. pylori infection can be detected by submitting a stool sample (stool antigen test) or by using a device to measure breath samples after swallowing a urea pill (urea breath test).Apr 5, 2017
What is the ICD-10 for loose stools?
ICD-10 | Diarrhea, unspecified (R19. 7)
What is the ICD-10 code for fecal retention?
ICD-10 | Fecal impaction (K56. 41)
What is fecal abnormality?
Symptoms include abnormal stool frequency (either 4 or more stools per day, or 2 or fewer stools per week), abnormal stool form (either loose and watery or lumpy and hard), abnormal passage of stool (e.g., straining, urgency, feeling of incomplete evacuation), the passage of mucus, and bloating or distention.
Can stool MCS detect H. pylori?
Stool Antigen Testing A stool antigen test can be used in order to assess the presence of H. pylori in the gastrointestinal tract. The test is able to establish the presence of an active infection by analysing the sample for H. pylori antigens.
What color is stool with H. pylori?
The presence of H. pylori does not always cause symptoms; however, if a sore or ulcer is present you may experience abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, bloody or black tarry stools, bloating or change in appetite or weight loss.
Is H. pylori stool test accurate?
This study also showed that stool antigen test can be a very good standard for diagnosing H. pylori infection. This test was the only test with accuracy > 90%, making it very suitable for the use in clinical practice.
Expected Turnaround Time
Turnaround time is defined as the usual number of days from the date of pickup of a specimen for testing to when the result is released to the ordering provider. In some cases, additional time should be allowed for additional confirmatory or additional reflex tests. Testing schedules may vary.
Storage Instructions
Specimen should be kept refrigerated after collection and transported refrigerated to the laboratory within 24 hours. If a longer period is required, the specimen should be frozen at -70°C.
Causes for Rejection
Inappropriate specimen transport conditions (eg, room temperature) or device; unlabeled specimen or name discrepancy between specimen and request label; specimen received after prolonged delay (usually more than 72 hours); leaking specimen; specimen received in inappropriate container (denture cup, “Cool Whip” container, margarine container, or similar container).
Use
Establish the presence and possible etiologic role of Helicobacter pylori in cases of chronic gastric ulcer, gastritis, duodenal ulcer, dyspepsia, etc
Contraindications
Antimicrobials, proton pump inhibitors, and bismuth preparations are known to suppress H pylori, and ingestion of these prior to H pylori testing may give a false-negative result.
Popular Posts:
- 1. billable icd 10 code for history of blood loss
- 2. icd 9 code for leg weakness status post cva with left sided
- 3. icd 10 code for atara
- 4. icd 10 code for panuveitis
- 5. icd 10 code for balance impairment
- 6. icd 10 cm code for smokes a pack a day for 30 years
- 7. icd 10 code for fatigue due to covid 19
- 8. icd 10 code for quadrapleegia secondary to myasthenia gravis
- 9. icd-10 code for spinal fusion
- 10. icd 10 code for thoracic pain unspecified