What is the prognosis for liver hemangioma?
The prognosis for liver hemangioma is good. Most of the hemangiomas shrink completely. And even if they are present they are of little or no consequence to the body. Sometimes, after the complete involution of the hemangioma, it may leave a faint scar or some mild skin discoloration which is hardly of any consequence to the body, except for the ...
What is the treatment for hemangioma of the liver?
Treatment options may include:
- Surgery to remove the liver hemangioma. If the hemangioma can be easily separated from the liver, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the mass.
- Surgery to remove part of the liver, including the hemangioma. ...
- Procedures to stop blood flow to the hemangioma. ...
- Liver transplant surgery. ...
- Radiation therapy. ...
What does hemangioma in the liver mean?
A liver hemangioma, also known as a hepatic hemangioma, is a benign (non-cancerous) tumor in the liver that is made up of clusters of blood-filled cavities fed by the hepatic (liver) artery. Usually, a patient has only one hemangioma, but in some cases there may be more than one.
Is liver hemangioma life threatening?
Mostly they are found to be single in number, but sometimes there can also be multiple hemangiomas of liver. A liver hemangioma does not usually cause problems in adults; they can however be life threatening when it develops in infants.
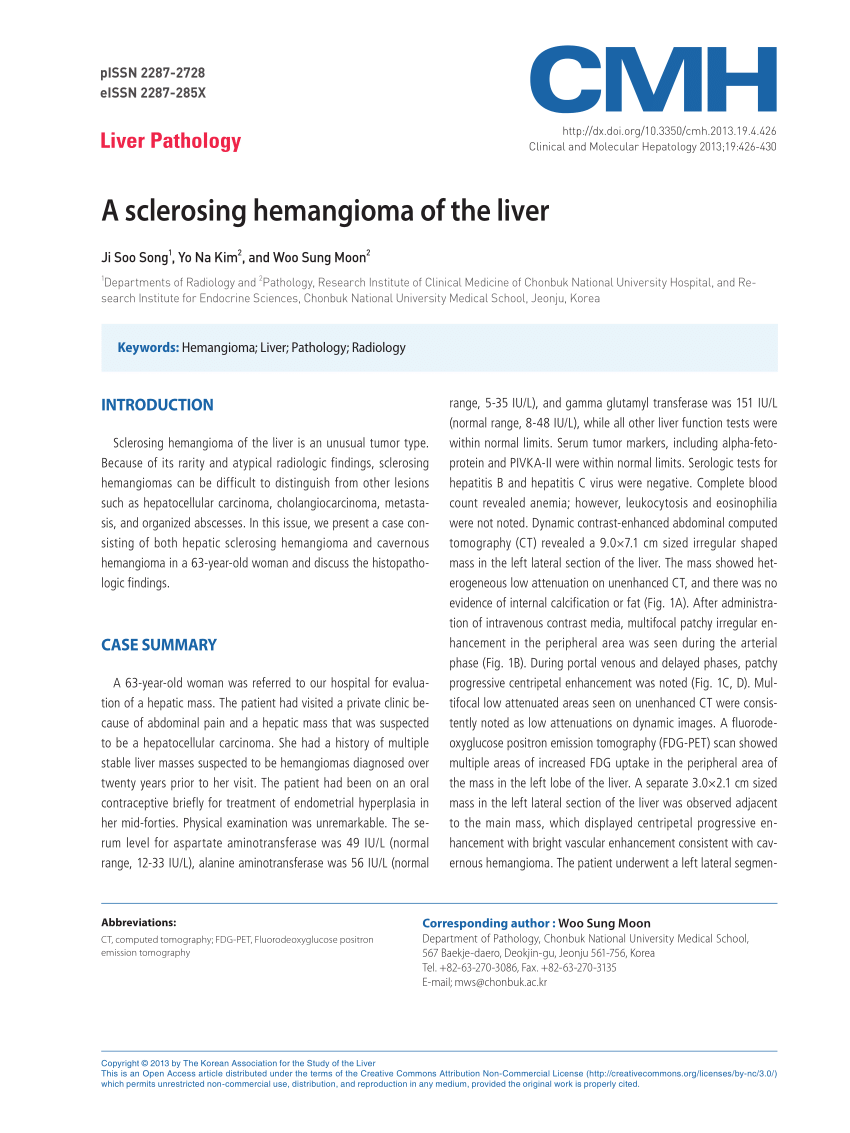
What is the ICD 10 code for hemangioma?
D18. 01 - Hemangioma of skin and subcutaneous tissue | ICD-10-CM.
Is a liver hemangioma a tumor?
A liver hemangioma (hepatic hemangioma) is a noncancerous tumor in your liver. It's made up of clumped, malformed blood vessels that are fed by the hepatic artery. Hemangioma tumors can occur in various organs, including the brain, where they can sometimes cause problems. In the liver, though, they rarely do.
What is meant by hemangioma?
A hemangioma (he-man-jee-O-muh) is a bright red birthmark that shows up at birth or in the first or second week of life. It looks like a rubbery bump and is made up of extra blood vessels in the skin. A hemangioma can occur anywhere on the body, but most commonly appears on the face, scalp, chest or back.
Is a hemangioma considered a tumor?
What Is a Hemangioma? Spinal hemangiomas are benign tumors that are most commonly seen in the mid-back (thoracic) and lower back (lumbar). Hemangiomas most often appear in adults between the ages of 30 and 50. They are very common and occur in approximately 10 percent of the world's population.
Do liver hemangiomas need to be removed?
Most liver hemangiomas don't require treatment, and only some need monitoring. However, a hemangioma may need to be removed surgically if it's large and growing or causing symptoms. If it causes significant pain or damage to a part of the liver, your doctor may decide to remove the entire affected section of the liver.
What is considered a large liver hemangioma?
Giant liver hemangiomas are defined by a diameter larger than 5 cm. In patients with a giant liver hemangioma, observation is justified in the absence of symptoms. Surgical resection is indicated in patients with abdominal (mechanical) complaints or complications, or when diagnosis remains inconclusive.
What are the two types of hemangiomas?
Types of Hemangiomas Superficial (on the surface of the skin): These look flat at first, and then become bright red with a raised, uneven surface. Deep (under the skin): These appear as a bluish-purple swelling with a smooth surface.
How is liver hemangioma treated?
TreatmentSurgery to remove the liver hemangioma. If the hemangioma can be easily separated from the liver, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the mass.Surgery to remove part of the liver, including the hemangioma. ... Procedures to stop blood flow to the hemangioma. ... Liver transplant surgery. ... Radiation therapy.
What is atypical hemangioma liver?
Atypical hemangioma is a variant of hepatic hemangioma with atypical imaging finding features on CT and MRI that can be confused with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) and mixed hepatocellular cholangiocarcinoma (HCC-CC).
What kind of tumor is a hemangioma?
A hemangioma is a benign (noncancerous) tumor made up of blood vessels. There are many types of hemangiomas, and they can occur throughout the body, including in skin, muscle, bone, and internal organs.
What size liver hemangioma should be removed?
TAE is recommended to reduce hemangioma size, especially when the tumor is larger than 20 cm in diameter [13,14,15,16], and is used in cases of preoperative hepatic hemangioma rupture [17].
What is the difference between a hemangioma and an Hemangioblastoma?
A hemangioma is an abnormal buildup of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs. Two types of hemangiomas are discussed here: Hemangioblastoma: These tumors are benign, slow-growing, and well defined. They arise from cells in the linings of blood vessels.
Should I be worried about liver hemangioma?
If your liver hemangioma is small and doesn't cause any signs or symptoms, you won't need treatment. In most cases a liver hemangioma will never grow and will never cause problems. Your doctor may schedule follow-up exams to check your liver hemangioma periodically for growth if the hemangioma is large.
Is hemangioma in liver serious?
The hemangioma, or tumor, is a tangle of blood vessels. It's the most common noncancerous growth in the liver. It's rarely serious and doesn't turn into liver cancer even when you don't treat it.
What size liver hemangioma should be removed?
TAE is recommended to reduce hemangioma size, especially when the tumor is larger than 20 cm in diameter [13,14,15,16], and is used in cases of preoperative hepatic hemangioma rupture [17].
How fast do liver hemangiomas grow in adults?
Although the overall rate of growth is slow, hemangiomas that exhibit growth do so at a modest rate (2 mm/y in linear dimension and 17.4% per year in volume). Further research is needed to determine how patients with more rapidly growing hemangiomas should be treated.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D18.09 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D18.09 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for left fibula stress fracture
- 2. icd 10 code for acute pain of both knees
- 3. icd 10 code for nasal ulcer
- 4. icd 9 code for post operative cholecystectomy
- 5. icd 10 code for generalized sepsis due to breast implant
- 6. icd 10 code for presence of indwelling suprapubic catheter
- 7. icd-10 code for aortic valve replacement
- 8. icd 10 code for upper airway cough syndrome
- 9. icd 10 cm code for laryngoplegia
- 10. icd 10 code for fractured ribs