What is the ICD-10 code for heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
Oct 01, 2021 · Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code D75.82 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D75.82 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for anticoagulant hemorrhagic disorder?
There are 1 terms under the parent term 'Heparin' in the ICD-10-CM Drugs Index . Heparin. poisoning accidental. poisoning intentional self harm. poisoning assault. poisoning undetermined. adverse effect. underdosing. T45.511.
What is the correct ICD-10 code for Coumadin?
Oct 01, 2021 · Z79.01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z79.01 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z79.01 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z79.01 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for extrinsic circulating anticoagulation?
ICD-10-CM Code for Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) D75.82 ICD-10 code D75.82 for Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
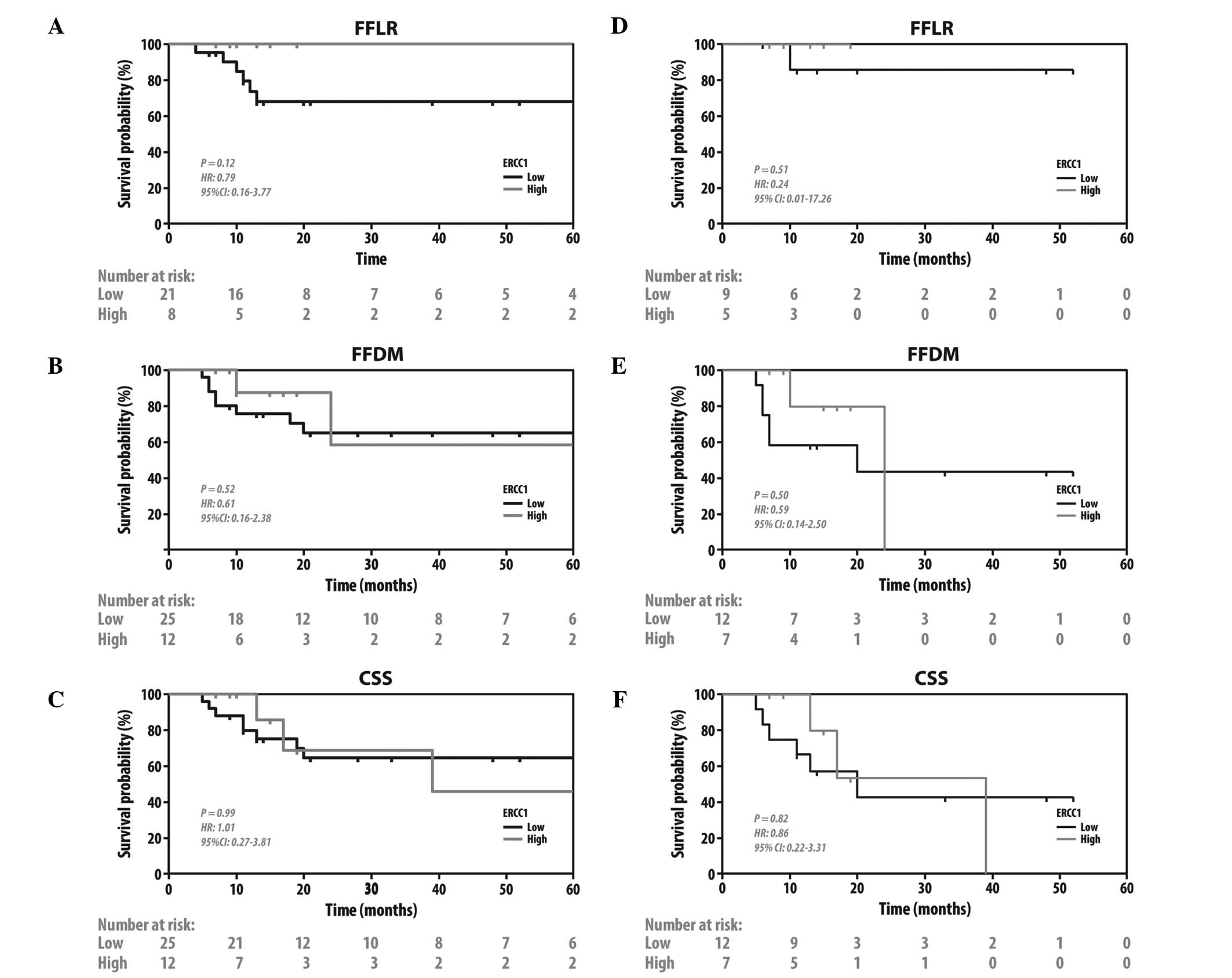
What is the ICD-10 code for anticoagulation?
Z79. 01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z79. 01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is ICD-10 code for long term use of anticoagulant?
What is the ICD-10-CM code for heparin induced thrombocytopenia?
What is the ICD-10 code for clotting disorder?
How do you code long term use of anticoagulants?
Is xarelto an anticoagulant or antiplatelet?
What is the correct ICD 10 code for thrombocytopenia?
What is the code for heparin induced thrombocytopenia drug was properly used This is the initial encounter?
D75. 82 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is heparin only IV?
What is the ICD-10 code for hypokalemia?
Which conditions are associated with clotting disorders?
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) ...
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE) ...
- Arterial Thrombosis. ...
- Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome (APLS) ...
- Factor V Leiden. ...
- Prothrombin Gene Mutation. ...
- Protein C Deficiency, Protein S Deficiency, ATIII Deficiency.
What is the ICD-10 code for hyperkalemia?
The ICD code D758 is used to code Macrocytosis
Macrocytosis is the enlargement of red blood cells with near-constant hemoglobin concentration, and is defined by a mean corpuscular volume (MCV) of greater than 100 femtolitres (the precise criterion varies between laboratories). The enlarged erythrocytes are called macrocytes or megalocytes (both words have roots meaning "big cell").
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'D75.82 - Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code D75.82. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 289.84 was previously used, D75.82 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What does "type 1 excludes" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as Z51.81. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together , such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What is a Z40-Z53?
Categories Z40-Z53 are intended for use to indicate a reason for care. They may be used for patients who have already been treated for a disease or injury, but who are receiving aftercare or prophylactic care, or care to consolidate the treatment, or to deal with a residual state. Type 2 Excludes.
Policy
Aetna considers continuous intravenous heparin infusion medically necessary for members taking oral anti-coagulants (warfarin) who require the maintenance of anti-coagulation prior to and after diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. For most members, pre-procedure weaning of the oral anti-coagulant may be safely accomplished on an outpatient basis.
Background
The most common indications for warfarin therapy are atrial fibrillation, the presence of a mechanical heart valve, prior thromboembolism, a documented left ventricular thrombus or a history of venous thromboembolism with or without a pulmonary embolism.
The above policy is based on the following references
Ansell J, Hirsh J, Dalen J, et al. Managing oral anticoagulant therapy. Chest. 2001;119:22S-38S.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for right bundle branch block
- 2. icd 10 code for unspecified joint swelling
- 3. icd 10 code for sopportiva bilater aom
- 4. icd 10 code for bacterial infection unspecified
- 5. icd 10 code for nightmare
- 6. icd 10 code for diabetic ulcer on right lower extremity
- 7. what is the 2015 icd-10 code for mental status change
- 8. icd 10 code for dropped heavy object on foot
- 9. icd 10 code for hepititis
- 10. icd 10 code for welcome to medicare exam