What is the causative agent of hepatic capillariasis?
Causal Agent. The nematode (roundworm) Capillaria hepatica (= Calodium hepaticum) causes hepatic capillariasis in humans. Nomenclature varies in use globally and by discipline; Capillaria hepatica is most frequently used in medical literature. C. hepatica is a zoonotic parasite with a low host specificity; it primarily exists in rodent...
What are the signs and symptoms of hepatic capillariasis?
Hepatic capillariasis is rare in humans. It typically manifests as an acute or subacute hepatitis with peripheral leukocytosis and eosinophilia, hepatomegaly, and persistent fever (which may be as high as 40℃).
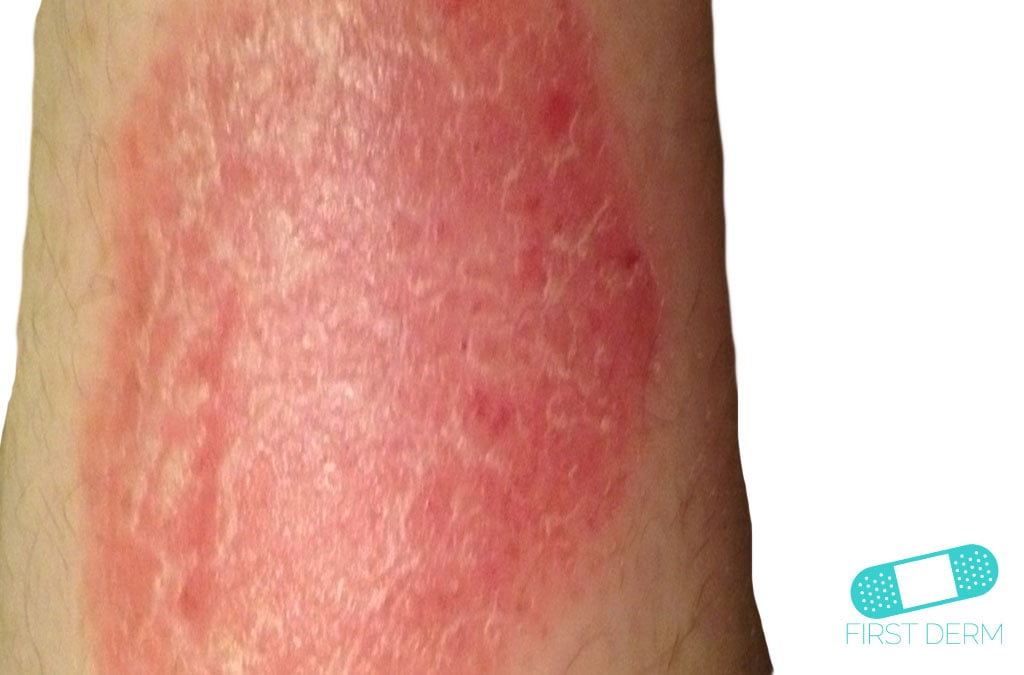
What is the ICD 10 CM code for syphilitic bursitis?
78.
What is the ICD 10 code for right TMA?
The only ICD 10 code I've found that fits is Z89. 9.
What is ICD 10 code for tinea Cruris?
ICD-10 code: B35. 6 Tinea inguinalis [Tinea cruris]
What does Transmetatarsal mean?
Transmetatarsal amputation, also called TMA, is surgery to remove all or part of your forefoot. The forefoot includes the metatarsal bones, which are the five long bones between your toes and ankle. TMA is usually done when the forefoot is badly injured or infected.
What is the difference between 28810 and 28820?
28810 osteotomy is made through the metatarsal (ultimately in this case). What may be throwing you off is that the doc performed the disarticulation at the MTP joint first (28820) and then afterwards performed the osteotomy through the MT (28820).
What is the ICD-10 code for fungal infection?
B49 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B49 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B49 - other international versions of ICD-10 B49 may differ.
What is the ICD-10 code for tinea corporis?
ICD-10 code: B35. 4 Tinea corporis | gesund.bund.de.
What type of infection is tinea corporis?
Ringworm of the body (tinea corporis) is a rash caused by a fungal infection. It's usually an itchy, circular rash with clearer skin in the middle. Ringworm gets its name because of its appearance.
The ICD code B811 is used to code Intestinal capillariasis
Capillariasis is a disease in the group of helminthiasis diseases caused by the nematode Capillaria philippinensis.
Coding Notes for B81.1 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #391-392 - Esophagitis, gastroent and misc digest disorders with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'B81.1 - Intestinal capillariasis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code B81.1. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 127.5 was previously used, B81.1 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
How many hosts does Capillaria hepatica have?
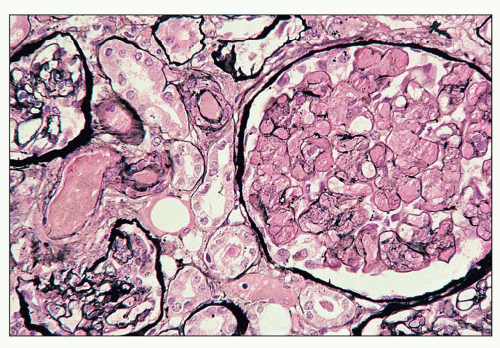
Life Cycle. Capillaria hepatica has a direct life cycle, with no intermediate host. It can develop with only one definitive host, but likely requires two hosts to complete the life cycle. Adult worms are located deep within the liver parenchyma of the host, and lay hundreds of eggs in the surrounding parenchymal tissue .
How long does a capillaria live?
However, they are rarely seen intact due to a relatively short life span (40—60 days) from maturation to death in the parenchyma of the liver.
What does it mean when you find C. hepatica eggs in your stool?
hepatica eggs in human stool during routine ova-and-parasite (O&P) examinations indicates spurious passage of ingested eggs, and not a true infection. Diagnosis in humans is usually achieved by finding adults and eggs in biopsy or autopsy specimens.
What is the most common host for C. hepatica?
C. hepatica has a low host specificity, but rodents such as rats are generally believed to be the most typical host. Infections have also been identified in wild and domestic carnivores (e.g. foxes, dogs, cats), lagomorphs, swine, primates, and humans.
Is hepatic capillariasis a hepatitis?
Clinical Presentation. Hepatic capillariasis is rare in humans. It typically manifests as an acute or subacute hepatitis with peripheral leukocytosis and eosinophilia, hepatomegaly, and persistent fever (which may be as high as 40℃).
Is C. hepatica a spurious infection?
The specific diagnosis of C. hepatica infection is based on demonstrating the adult worms and/or eggs in liver tissue at biopsy or necropsy. Importantly, the identification of C. hepatica eggs in the stool is a spurious finding, which does not result from infection of the human host, but from ingestion by that host of livers from infected animals.
Popular Posts:
- 1. 2016 icd 10 code for ventral hernia repair
- 2. 2017 icd 10 code for asymmetrical right hearing loss
- 3. icd 10 code for aneurysm groin
- 4. icd 10 code for tenosynovitis of of left hip
- 5. icd 10 code for vasodilatory shock
- 6. icd 10 code for pupps in pregnancy
- 7. icd 10 code for muscle spams lumbar
- 8. icd-10-cm code for eye exam, bilateral
- 9. icd 9 code for club foot
- 10. icd 10 code for right shoulder tendinosis