What is the diagnosis code for hepatitis B?
Oct 01, 2021 · B18.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B18.1 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B18.1 - other international versions of ICD-10 B18.1 may differ. Applicable To Carrier of viral hepatitis B
What is hepatitis B surface AB QL reactive means?
Oct 01, 2021 · B19.10 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B19.10 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B19.10 - other international versions of ICD-10 B19.10 may differ. Applicable To Unspecified viral hepatitis B NOS
What is a positive hepatitis B surface antibody?
Aug 05, 2019 · For HBV screening in pregnant women at high risk, report the appropriate CPT code with Z11.59, Z72.89 Other problems related to lifestyle and one of the following ICD-10-CM codes, as appropriate: Z34.00 – Z34.03 – Encounter for supervision of normal first pregnancy; Z34.80 – Z34.83 – Encounter for supervision of other normal pregnancy
What is the CPT code for hepatitis B surface antibody?
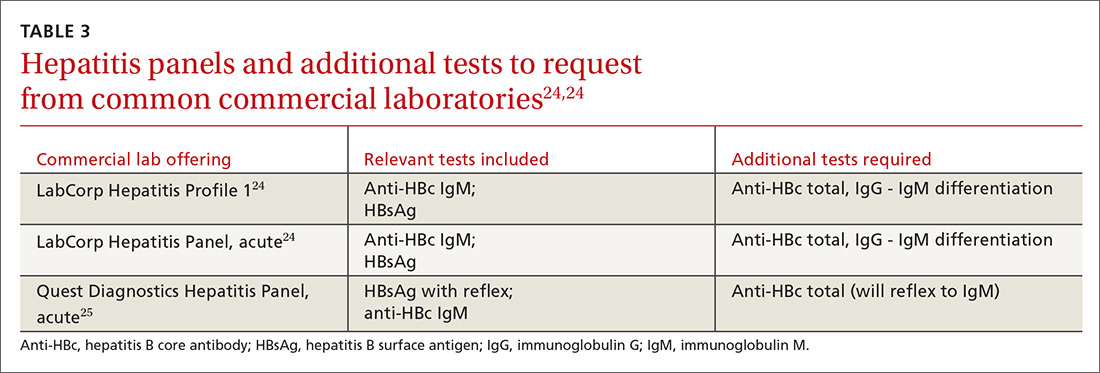
ICD-10-CM Documentation and Coding Best Practices Hepatitis Overview . Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Toxins, certain drugs and diseases, heavy alcohol consumption, and ... Hepatitis B Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is present in acute and chronic infection Anti-hepatitis B core antigen (Anti-HBc IgM) is only positive during ...
Is hepatitis B surface antigen?
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): A protein on the surface of hepatitis B virus; it can be detected in high levels in serum during acute or chronic hepatitis B virus infection. The presence of HBsAg indicates that the person is infectious.
What is the ICD-10 code for hepatitis panel?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B18 B18.
What is the ICD-10 code for screening for hepatitis B?
Encounter for screening for other viral diseases The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z11. 59 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is hepatitis surface antigen test?
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is a blood test ordered to determine if someone is infected with the hepatitis B virus. If it is found, along with specific antibodies, it means the person has a hepatitis B infection.Sep 2, 2021
What is included in hepatitis B panel?
A Hepatitis B (HBV) Blood Test Panel includes a Hepatitis B Core Antibody Total (Test #006718), Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (Test #006510), Hepatitis B Surface Antibody (Test #006395). Preparation: No fasting required. Stop biotin consumption at least 72 hours prior to the collection.
What is included in hepatitis B profile?
Test Includes Hepatitis B surface Antigen (HBsAg) Screen; Hepatitis B Surface Antibody (anti-HBs); Hepatitis B Core Antibody, Total (anti-HBc); and reflexes to Hepatitis B Core Antibody, IgM (IgM anti-Hbc) when indicated.
What is hepatitis B screening?
Screening for hepatitis B involves blood tests that measure HBV antigens and antibodies. The test for hepatitis B surface antigen detects the presence of HBV. A positive result means the person is currently infected and can pass the infection to others.
What is DX code z1159?
For asymptomatic individuals who are being screened for COVID-19 and have no known exposure to the virus, and the test results are either unknown or negative, assign code Z11. 59, Encounter for screening for other viral diseases.Apr 1, 2020
What is diagnosis code Z11 59?
52 will replace Z11. 59 (Encounter for screening for other viral diseases), which the CDC previously said should be used when patients being screened for COVID-19 have no symptoms, no known exposure to the virus, and test results that are either unknown or negative.Dec 21, 2020
What is the CPT code for hepatitis B surface antigen?
CPT Codes: Qualitative or semiquantitative multiple step method; hepatitis B surface antigen 87341 – Hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) neutralization (if appropriate).
What is hepatitis B surface antigen positive?
HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen) - A "positive" or "reactive" HBsAg test result means that the person is infected with hepatitis B. This test can detect the actual presence of the hepatitis B virus (called the “surface antigen”) in your blood.
What is hepatitis B surface AB QN immunity?
Hepatitis B surface antibodies are produced by the body's immune system in response to HBsAg. The presence of adequate hepatitis B surface antibodies in the blood indicates protection against hepatitis B virus infection.Jul 1, 2021
What is a blood typing test?
Blood typing is a screening test to determine blood groups and Rh antigen for blood transfusion and pregnancy. The four blood groups A, B, O, and AB are determined by the presence of antigens A and B or their absence (O) on a patient's red blood cells. In addition to ABO grouping, most immunohematology testing includes evaluation of Rh typing tests for Rh (D) antigen. Blood cells that express Rh (D) antigen are Rh positive. Red blood cells found lacking Rh (D) are considered Rh negative. Rh typing is also important during pregnancy because of the potential for mother and fetus Rh incompatiblity. If the mother is Rh negative but the father is Rh positive, the fetus may be positive for the Rh antigen. As a result, the mother’s body could develop antibodies against the Rh antigen. These antibodies may cross the placenta and cause destruction of the baby’s red blood cells, resulting in a condition known as hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
Why is it important to have blood transfusions?
Transfusion of blood components of the correct blood type is necessary in order to prevent an adverse immunologic reaction. These reactions can range from very mild and sub-clinical to very severe or fatal, depending upon the components involved and condition of the recipient.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for self harming behavior
- 2. icd 10 code change for m54.5
- 3. icd 10 code for lung empyema mrsa
- 4. icd 10 code for decompressive laminectomy
- 5. icd 10 code for headache stiff neck and fever due to viral meningitis how to code
- 6. the icd-10-cm code for history of falling is what
- 7. icd 9 code for hx of hip fracture
- 8. icd 10 code for visual disturbances and blindness
- 9. icd 10 code for montgomery trach
- 10. icd 10 code for dizziness and headache