What is the ICD 10 code for gastroesophageal reflux disease?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I50.9 Heart failure, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I50.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I50.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are common ICD 10 codes?
Heart failure I50-. Code First. Code First Help. Certain conditions have both an underlying etiology and multiple body system manifestations due to the underlying etiology. For such conditions, ICD-10-CM has a coding convention that requires the underlying condition be sequenced first followed by the manifestation.
What is the ICD - 10 code for high phosphorus?
This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I50 - other international versions of ICD-10 I50 may differ. Code First heart failure complicating abortion or ectopic or molar pregnancy ( O00 - O07, O08.8) heart failure due to hypertension ( I11.0) heart failure due to hypertension with chronic kidney disease ( I13.-) heart failure following surgery (
What is ICD 10 used for?
ICD-10-CM Code I50Heart failure. ICD-10-CM Code. I50. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code I50 is a non-billable code.
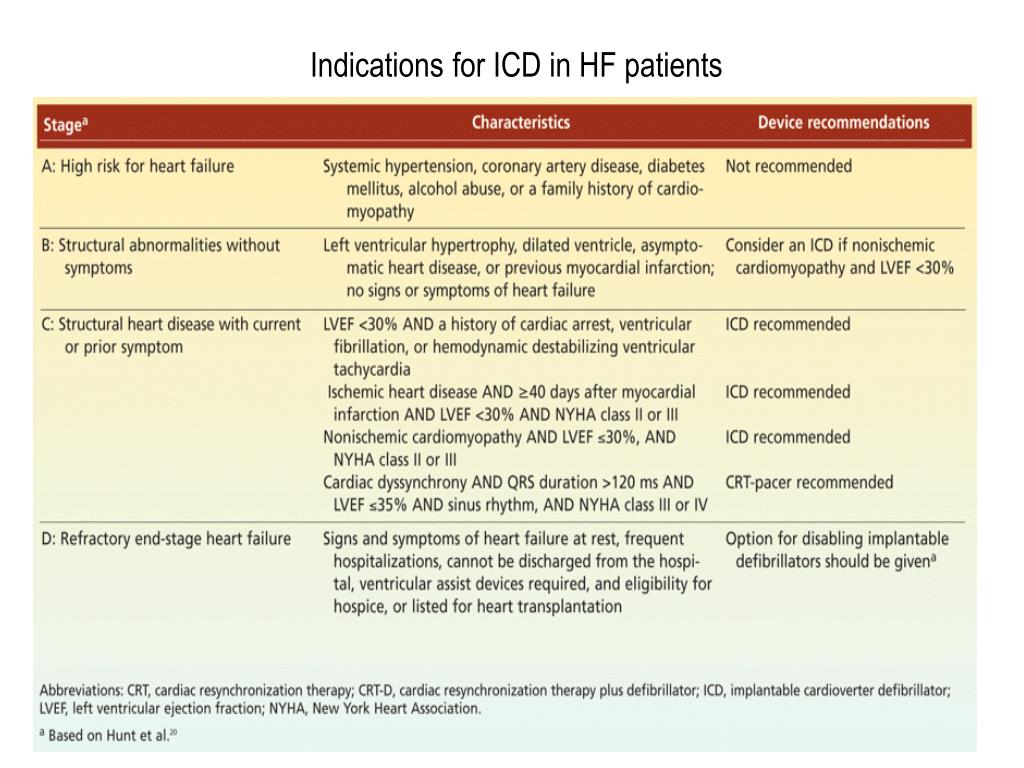
What is the ICD-10 code for HTN with HF?
Heart failure is assumed to be due to hypertension when coded using I11. 0, “Hypertensive heart disease with heart failure.” In ICD-10, the word “with” presumes a causal relationship between the two conditions linked by this term.Jul 27, 2018
What is the ICD-10 code for systolic CHF?
ICD-10 | Unspecified systolic (congestive) heart failure (I50. 20)
What is acute decompensated heart failure?
Acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) is a clinical syndrome of new or worsening signs and symptoms of HF, often leading to hospitalization or a visit to the emergency department. Patients with ADHF represent a heterogeneous population with high post-discharge readmission rates [1-13].Aug 18, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for diastolic CHF?
ICD-10 | Chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure (I50. 32)
What does HFrEF mean?
systolic heart failure or heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is a complex clinical syndrome characterized by structural and/or functional impairment of the left ventricle, resulting in a decrease in heart pump function (left ventricular ejection fraction ≤ 40%), which is associated with an ...
What is the difference between congestive heart failure and acute decompensated heart failure?
What is the difference between compensated and decompensated heart failure? In compensated heart failure, symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and edema are stable or absent. In decompensated heart failure, those symptoms are worse, to the point where medical attention is required.Jun 30, 2021
What is the difference between decompensated and compensated heart failure?
Decompensated. Your doctor may describe your heart failure based on the strength of your heart and how your body is responding. Compensated heart failure means your heart works well enough that you either don't notice any problems or the symptoms are easy to manage.May 7, 2021
Is acute decompensated heart failure the same as acute heart failure?
ADHF is a common and potentially serious cause of acute respiratory distress. The condition is caused by severe congestion of multiple organs by fluid that is inadequately circulated by the failing heart....Acute decompensated heart failure.Heart failureSpecialtyCardiology2 more rows
What is the ICD-10 code for acute respiratory failure with hypoxia?
J96.01Acute respiratory failure with hypoxia J96. 01 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is diastolic CHF?
Diastolic heart failure, a major cause of morbidity and mortality, is defined as symptoms of heart failure in a patient with preserved left ventricular function. It is characterized by a stiff left ventricle with decreased compliance and impaired relaxation, which leads to increased end diastolic pressure.Jun 1, 2004
Is diastolic dysfunction considered heart failure?
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), also called diastolic failure (or diastolic dysfunction): The left ventricle loses its ability to relax normally (because the muscle has become stiff). The heart can't properly fill with blood during the resting period between each beat.May 31, 2017
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 diagnosis code for lipoma
- 2. icd 10 code for j45.991
- 3. icd-9 code for acute on chronic renal failure
- 4. icd 10 code for autoimmune neuropathy
- 5. icd 10 cm code for stenosis of dialysis arteriovenous fistula
- 6. icd 10 cm code for preterm premature rupture of membranes
- 7. icd 10 code for brca2 mutation positive
- 8. icd 10 code for pre ulcerative foot callus
- 9. icd 10 code for right 5th mc base fracture
- 10. icd 10 code for postoperative pelvic fluid collection