Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral
- H90.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H90.3 became effective on October 1, 2020.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H90.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 H90.3 may differ.
What is the diagnosis code for hearing loss?
Unspecified hearing loss, bilateral. H91.93 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H91.93 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do doctors diagnose hearing loss?
- Prevention and Early Detection of Hearing Loss are Important. Don’t wait until you show signs of hearing loss. ...
- Children Should Have Their Hearing Tested. ...
- Regular Check-Ups Can Help Identify Early Hearing Loss. ...
- Learn More about Hearing Tests
- For More Information. ...
What is the CPT code for hearing loss?
CPT Code Descriptor; 92593: Hearing aid check; binaural: 92594: Electroacoustic evaluation ...
What is the ICD 10 code for difficulty speaking?
Unspecified speech disturbances 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code R47.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM R47.9 became effective on October 1, 2020.
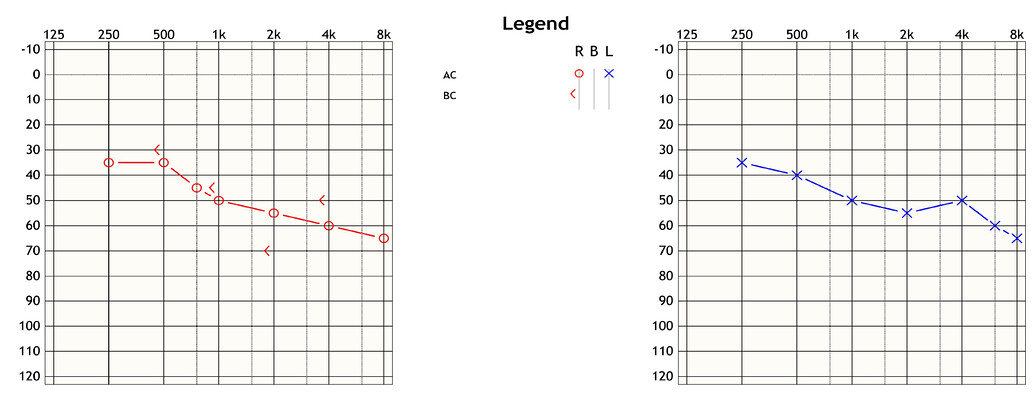
What is the correct ICD-10 code for hearing loss?
ICD-10 code H91. 90 for Unspecified hearing loss, unspecified ear is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is diagnosis code H90 3?
ICD-10 code: H90. 3 Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral.
What is the code H90 5?
5: Sensorineural hearing loss, unspecified.
What is ICD-10 code for sensorineural hearing loss?
3.
When do I code I11 9?
ICD-10 Code for Hypertensive heart disease without heart failure- I11. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What is unspecified sensorineural hearing loss?
Having sensorineural hearing loss means there is damage either to the tiny hair cells in your inner ear (known as stereocilia), or to the nerve pathways that lead from your inner ear to the brain. It normally affects both ears. Once you develop sensorineural hearing loss, you have it for the rest of your life.
What is the difference between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss?
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound conduction is impeded through the external ear, the middle ear, or both. Sensorineural hearing loss occurs when there is a problem within the cochlea or the neural pathway to the auditory cortex.
What is conductive hearing?
Your ear is made up of three parts— the outer, the middle, and the inner ear. A conductive hearing loss happens when sounds cannot get through the outer and middle ear. It may be hard to hear soft sounds. Louder sounds may be muffled. Medicine or surgery can often fix this type of hearing loss.
What is presbycusis caused by?
Presbycusis is usually a sensorineural hearing disorder. It is most commonly caused by gradual changes in the inner ear. The cumulative effects of repeated exposure to daily traffic sounds or construction work, noisy offices, equip- ment that produces noise, and loud music can cause sensorineural hearing loss.
What is sensorineural hearing loss bilateral?
Sensorineural hearing loss, or SNHL, happens after inner ear damage. Problems with the nerve pathways from your inner ear to your brain can also cause SNHL. Soft sounds may be hard to hear. Even louder sounds may be unclear or may sound muffled. This is the most common type of permanent hearing loss.
What is the code for sudden idiopathic hearing loss?
H91. 2 - Sudden idiopathic hearing loss. ICD-10-CM.
What is asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss?
Asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss (ASNHL) is defined as binaural difference in bone conduction thresholds of >10 dB at two consecutive frequencies or >15 dB at one frequency (0.25–8.0 kHz)3 (Figure 1).
What is SNHL hearing?
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss, or deafness, in which the root cause lies in the inner ear (cochlea and associated structures), vestibulocochlear nerve (cranial nerve VIII), or central auditory processing centers of the brain. SNHL accounts for about 90% of hearing loss reported. A hallmark of such hearing loss is that it is asymmetrically distributed usually toward the high frequency region, or may have a notch at some frequency. SNHL is generally permanent and can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H90.3 and a single ICD9 code, 389.18 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.

Overview
- Icd 10 Codes For Hearing LossTinnitus, the word for “ringing in the ears,” occurs when the nerves that provide us with hearing lose their ability to transmit sound from the external environment to the inner ear. Sound waves travel through the hair cells on both sides of the auditory canal. These cells receive signals from all sorts of external sounds such as speech, music, crying, and other human voices. If the hearing mechanisms have been damaged …
What You Need to Know About Tinnitus
- There are many different types of hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss commonly comes with tinnitus. Some researchers think that only subjective tinnitus can exist without some sort of physical damage to the hearing nerve. The underlying deafness might be due to: Noise-induced hearing loss can also be unidirectional (one-sided) and usually makes patients lose hearing just around the frequency of the offending sound. This type of disorder i…
The Initial Causes Icd 10 Codes For Hearing Loss
- There are many causes of hearing loss. These include loss of hair cells (the ganas nerve in the inner ear sends messages to the brain), damage done to the brain stem due to disease or an infection, and a buildup of wax in the ears. Any combination of these can cause the brain to send wrong signals to the ears causing them to lose hearing. Oftentime...
Treatment
- There are two main categories of treatments for tinnitus, objective and non Objective. Objective tinnitus treatments include changing the environment in which you live to reduce the noise. Non Objective tinnitus treatments include medicines that specifically treat disorders of the inner ear, pulsatile tinnitus, hypnosis, or biofeedback therapy. While these Non Objective treatments have had varying levels of success, scientists at the …
Final Thoughts
- Tinnitus may seem like a frustrating issue; however, with enough focus and attention, you can learn how to stop the ringing in your ears. If you’ve tried all of the tips above and still suffer from tinnitus, you should immediately visit your doctor to make sure that there is no serious cause for your symptoms. Some conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, can cause ringing in the ears, so you should also rule those out as well. There ar…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for visual field defect
- 2. icd 10 code for cerebral palsy,
- 3. icd 10 code for benign tumor of the midbrain
- 4. icd 10 code for other diseases of bartholin's gland
- 5. icd 10 code for tubular hernia
- 6. icd 10 pcs code for percutaneous needle biopsy of right breast and mastocomy procedure
- 7. icd 9 code for shoulder ac joint arthritis
- 8. icd 9 code for 87081
- 9. icd 9 code for mild increase in the interstitial markings in the left lung base.
- 10. icd 10 code for knee pain and swelling