A Hill-Sachs lesion is an injury that can occur when you dislocate your shoulder. This injury causes bone damage to the ball of the shoulder . Free, official coding info for 2019 ICD-10-CM S42.29 - includes detailed. Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to S42.29:. Hill-Sachs S42. 29-.
What is a Hill Sachs defect in the shoulder?
Hill Sachs Defect The Hill-Sachs defect occurs when there is an injury to the bone and cartilage of the humeral head. The shoulder joint is made up of the humeral head and the glenoid bone (the socket). Ligaments, cartilage, and tendons help hold these bones in place.
What is the ICD 10 code for Hill Sachs lesion?
A Hill-Sachs lesion, also Hill-Sachs fracture, is a cortical depression in the posterior superior head of the humerus bone. It results from forceful impaction of the humeral head against the anteroinferior glenoid rim when the shoulder is dislocated anteriorly. ICD Code-812.09 (Humerus head). Hope its helps......
What is the ICD 10 code for shoulder lesion?
M75.91 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Shoulder lesion, unspecified, right shoulder. It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021. ↓ See below for any exclusions, inclusions or special notations
What is the prognosis of a dislocated shoulder with Hill Sachs lesion?
The outlook for recovery from a dislocated shoulder and a Hill-Sachs lesion is generally good. But a recurrence of a dislocation is common, especially in younger people. In the long-term, about one-third of people who have surgery for a dislocated shoulder will develop shoulder arthritis.
What is the ICD-10 code for Hill-Sachs deformity?
29.
What is Hill-Sachs deformity?
A Hill-Sachs lesion is a fracture in the long bone in the upper arm (humerus) that connects to the body at the shoulder. You doctor might have discovered this condition if you've experienced a dislocated shoulder. In this case, the arm bone slips out of the socket and is compressed against the socket's rim.
What causes Hill-Sachs deformity?
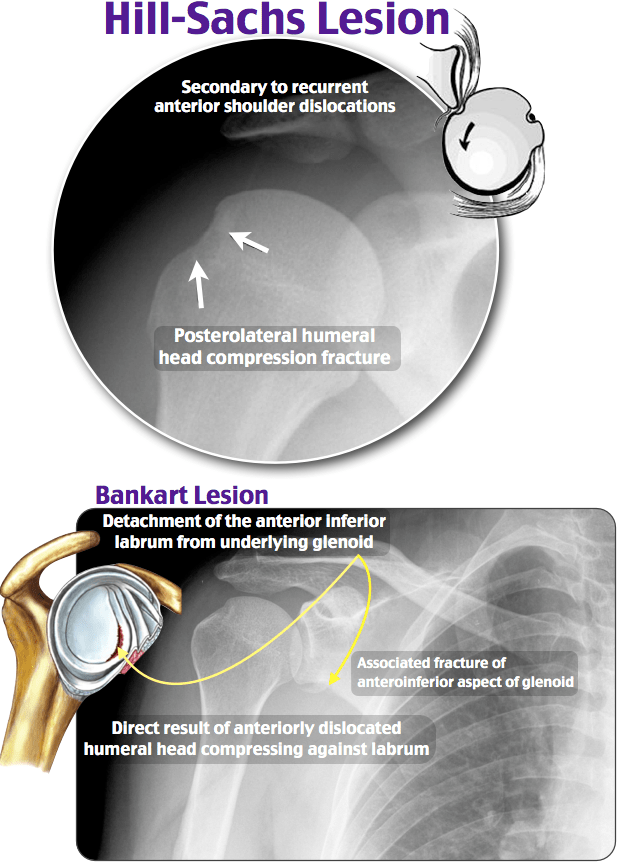
A Hill-Sachs deformity is a compression injury to the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head created by the glenoid rim during dislocation. When driven from the glenohumeral cavity during dislocation, the relatively soft head of the humerus hits against the anterior edge of the glenoid.
What is a reverse Hill-Sachs lesion?
Reverse Hill-Sachs defect, also called a McLaughlin lesion, is defined as an impaction fracture of anteromedial aspect of the humeral head following posterior dislocation of the humerus. It is of surgical importance to identify this lesion and correct it to prevent avascular necrosis.
What is the difference between Hill-Sachs and Bankart lesion?
Anterior dislocation causes a typical impression fracture on the posterior humeral head, known as a Hill–Sachs lesion. The labrum or the glenoid itself may also be damaged; these injuries are known as Bankart lesions.
What is a small Hill-Sachs fracture?
A Hill-Sachs lesion, or Hill-Sachs impaction fracture, is an injury to the back portion of the rounded top of your upper arm bone (humerus). This injury occurs when you dislocate your shoulder. It's named for the two American radiologists who first described the injury in 1940: Harold Hill and Maurice Sachs.
Is Hill-Sachs or Bankart more common?
Bankart lesions are up to 11x more common in patients with a Hill-Sachs lesion, with increasing incidence with increasing size 8.
What is Hill-Sachs Remplissage?
The remplissage technique is a procedure designed to fill a posterosuperior humeral head defect with the infraspinatus tendon and posterior-superior capsule in patients with engaging Hill-Sachs lesions.
How is Hill-Sachs defect measured?
The glenoid track and the Hill–Sachs interval was measured using MRI and compared to the results of engagement in arthroscopy. The authors found a moderate to high accuracy of this method using MRI with an overall accuracy of 84.2%, a sensibility of 72.2% and a specificity of 87.9%.
What is a glad lesion in shoulder?
Abstract. A GLAD (glenolabral articular disruption) lesion is caused by a forced adduction injury to the shoulder from an abducted and external rotated position; patients with GLAD lesions present with anterior shoulder pain as their chief complaint.
What is a Bankart lesion of the shoulder?
One of the most common labral injuries is known as a Bankart lesion. This condition occurs when the labrum pulls off the front of the socket. This occurs most often when the shoulder dislocates. If a Bankart tear doesn't heal properly, it can cause future dislocations, instability, weakness and pain.
How is a Hill-Sachs lesion repair?
Large or engaging Hill-Sachs lesions are addressed by either reconstructing (rebuilding) any lost bone on the glenoid side or performing a “Remplissage” procedure which repairs the posterior capsule and rotator cuff tendon to the Hill-Sachs bone defect.
What is the ICd 10 code for a fracture of the humerus?
S42.296S is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other nondisplaced fracture of upper end of unspecified humerus, sequela. The code S42.296S is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code S42.296S might also be used to specify conditions or terms like articular cartilage disorder of upper arm, fracture of head of humerus, hill-sachs lesion or reverse hill-sachs lesion. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.#N#S42.296S is a sequela code, includes a 7th character and should be used for complications that arise as a direct result of a condition like other nondisplaced fracture of upper end of unspecified humerus. According to ICD-10-CM Guidelines a "sequela" code should be used for chronic or residual conditions that are complications of an initial acute disease, illness or injury. The most common sequela is pain. Usually, two diagnosis codes are needed when reporting sequela. The first code describes the nature of the sequela while the second code describes the sequela or late effect.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like S42.296S are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
How are fractures of specified sites coded?
Fractures of specified sites are coded individually by site nd the level of detail furnished by medical record content. A fracture not indicated as open or closed should be coded to closed. A fracture not indicated whether displaced or not displaced should be coded to displaced.
What character is used for trauma fracture?
Traumatic fractures are coded using the appropriate 7th character for initial encounter (A, B, C) for each encounter where the patient is receiving active treatment for the fracture. The appropriate 7th character for initial encounter should also be assigned for a patient who delayed seeking treatment for the fracture or nonunion.
What is the most common sequela?
The most common sequela is pain. Usually, two diagnosis codes are needed when reporting sequela. The first code describes the nature of the sequela while the second code describes the sequela or late effect. Unspecified diagnosis codes like S42.296S are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition.
What is a broken bone called?
Also called: Broken bone. A fracture is a break, usually in a bone. If the broken bone punctures the skin, it is called an open or compound fracture. Fractures commonly happen because of car accidents, falls, or sports injuries. Other causes are low bone density and osteoporosis, which cause weakening of the bones.
What do you need to wear to keep a fractured bone in place?
You may need to wear a cast or splint. Sometimes you need surgery to put in plates, pins or screws to keep the bone in place. Broken bone (Medical Encyclopedia) Closed reduction of a fractured bone (Medical Encyclopedia) Closed reduction of a fractured bone - aftercare (Medical Encyclopedia)
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code S42.296S its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is Hill Sachs?
The Hill-Sachs defect occurs when there is an injury to the bone and cartilage of the humeral head. The shoulder joint is made up of the humeral head and the glenoid bone (the socket). Ligaments, cartilage, and tendons help hold these bones in place. A shoulder dislocation occurs when the ball of the ball-and-socket shoulder joint comes out ...
What bone is the ball on the top of the arm?
As the bones in the shoulder joint dislocate, the round humeral head (the ball on the top of the arm bone) can strike the edge of the glenoid bone (the socket) with force. This creates a compression fracture in the humeral head. A small divot in the bone is often seen on MRI, and larger Hill-Sachs injuries may also be seen on an X-ray. 1.
What percentage of the humeral head is affected by Hill-Sachs?
Injuries that involve more than 40% of the humeral head almost always require treatment. In situations where the Hill-Sachs defect involves between 20% and 40% of the humeral head, your surgeon will determine if the defect is contributing to shoulder instability. 1 . A Hill-Sachs defect that causes the ball to move abnormally within ...
What is Hill Sachs injury?
Updated on January 28, 2021. A Hill-Sachs injury to the shoulder can occur due to a shoulder dislocation, resulting in a Hill-Sachs lesion or a Hill-Sachs deformity of the head of the humerus bone (the upper arm bone) As the bones in the shoulder joint dislocate, the round humeral head (the ball on the top of the arm bone) can strike the edge ...
What happens if you have a Hill-Sachs defect?
If the Hill-Sachs defect is large and left untreated, recurrent shoulder instability could occur.
What is shoulder damage?
Damage to the shoulder is mostly dependent on the age of the person who sustained the injury. The usual damage is either to the shoulder ligaments, called a Bankart tear, which occurs in younger people, or to the rotator cuff tendons, which usually occur in older people. 2 . In addition to ligament or tendon damage, ...
What is the most common type of damage from a dislocation?
In addition to ligament or tendon damage, the bone and cartilage can also be damaged; the most common type of damage from a shoulder dislocation is a Hill-Sachs defect. A shoulder dislocation is often confused with a separated shoulder, but these are very different injuries. Understanding Bone Fracture X-Rays.
How long does it take to recover from arthroscopic surgery?
Arthroscopic surgery often has a shorter recovery time than open surgery. If you have surgery for a dislocated shoulder and Hill-Sachs lesion repair, you may have pain and discomfort for a week or more. Your shoulder will be immobilized in a sling for three to six weeks.
How to tell if your shoulder is dislocated?
Also, more than one part of your shoulder may be damaged in an injury. A dislocated shoulder requires emergency care. The symptoms of a dislocated shoulder are: intense pain. difficulty moving the joint. visible deformation of the shoulder, often with a bulge in the front of the joint. swelling or bruising.
What is Hill Sachs procedure?
The procedure is usually done on Hill-Sachs lesions that are moderate in size and also have some amount of glenoid defect. Disimpaction: This involves a bone graft under the lesion to lift the humerus up to the pre-injury position.
How to tell if you have a Hill-Sachs lesion?
A Hill-Sachs lesion or fracture occurs when the humerus bone pops out of the socket, scraping the head of the bone against the edge of the socket. You won’t be able to tell right away if you have a Hill-Sachs lesion. But you’ll feel the pain of your shoulder dislocation. Also, more than one part of your shoulder may be damaged in an injury.
How to diagnose a dislocated shoulder?
A doctor can diagnose a dislocated shoulder during a physical examination, but determining whether you have a Hill-Sachs lesion or other damage will require further testing. The doctor will ask how your shoulder injury occurred, whether it’s happened before, and what your symptoms are.
What percentage of dislocations result from a fall?
Common causes for a dislocated shoulder include: of 8,940 people with shoulder dislocations found that 58.8 percent of dislocations resulted from a fall. Of these cases, 47.7 percent occurred at home.
What is the procedure to replace the humeral head?
Resurfacing: This can be done with a metal implant or a complete replacement of the humeral head. The complete replacement is called a hemiarthroplasty. It’s done on people who have recurrent problems that involve more than 40 percent of the humerus bone. It’s not recommended for younger people.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 data code for b12 deficiency
- 2. icd-10 code for left eye pain
- 3. icd 9 code for diabetic polyneuropathy
- 4. icd 9 code for screening labs
- 5. icd 10 code for nerve pain in left thigh injury
- 6. icd 10 code for arthritis lower lumbar spine
- 7. icd 10 code for gastroc contracture
- 8. icd 10 code for nash cirrhosis of liver with ascites
- 9. icd 9 code for mixed receptive expressive language disorder
- 10. icd-10 code for hydroxyurea