What is the ICD-10 code for hindfoot valgus?
Other congenital valgus deformities of feet Q66. 6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q66. 6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for left valgus?
M20.12ICD-10 code M20. 12 for Hallux valgus (acquired), left foot is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Arthropathies .
What is congenital valgus deformity of foot?
Congenital convex pes valgus is a severe condition that presents an appearance at birth similar to talipes calcaneovalgus. Accordingly, podiatrists must differentiate between the two. With both deformities, the forepart of the foot is dorsiflexed and everted, and there is a limitation of plantarflexion and inversion.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for right foot pain?
671 Pain in right foot.
What is the ICD-10 code for foot pain?
ICD-10 code M79. 67 for Pain in foot and toes is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Soft tissue disorders .
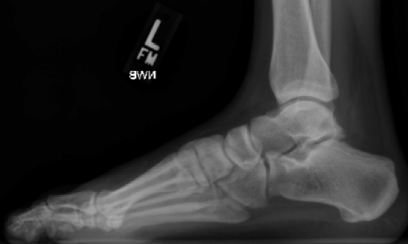
What is hindfoot valgus deformity?
Hindfoot valgus refers to malalignment of the hindfoot in which the mid-calcaneal axis is deviated away from the midline of the body. On the DP view, this results in an increase in the angle between the mid-calcaneal axis and the mid-talar axis (talocalcaneal angle) 1.
What is a valgus deformity?
What is Valgus Deformity? Valgus knee is a lower leg deformity that exists when the bone at the knee joint is angled out and away from the body's midline. This causes the inability for a person to touch his or her ankles while the knees touch together.
What is ankle valgus?
Ankle valgus is an insidious deformity that results in pronation of the foot and medial malleolar prominence. The causes are varied and include neuromuscular disorders, skeletal dysplasia, and clubfoot. [4, 5, 6, 7, 8] The indications for treatment of ankle valgus are as follows: Presence of related discomfort.
What is R53 83?
ICD-9 Code Transition: 780.79 Code R53. 83 is the diagnosis code used for Other Fatigue. It is a condition marked by drowsiness and an unusual lack of energy and mental alertness. It can be caused by many things, including illness, injury, or drugs.
Is R51 a billable code?
R51. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R51. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for back pain?
5 – Low Back Pain. ICD-Code M54. 5 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of chronic low back pain.
How do you fix valgus deformity?
Abstract. Valgus deformities at the knee can be successfully corrected with V-shaped supracondylar osteotomy. The advantages of this relatively simple technique are low morbidity, good stability with early weight-bearing, no need for internal fixation, and ability to adjust alignment with postoperative cast.
What causes valgus feet?
This foot deformity occurs from years of pressure on the big toe joint (the metatarsophalangeal, or MTP, joint). Eventually, the toe joint gets out of alignment, and a bony bump forms. The medical term for bunions is hallux abducto valgus.
How do you fix ankle valgus?
No medical treatment is effective and the only option is surgical correction of the deformity. Two main options are available: supramalleolar osteotomy and medial malleolar epiphysiodesis.
How do you fix heel valgus?
In order to correct the calcaneal valgus, reduce the tendency of your arch of the foot to sag and fight against the premature wear of your shoes; Place the Supinator Heels inside all your shoes to straighten up the heel. - If the wear of the shoes is too pronounced repair them or replace them.
What is flat foot?
The clinical finding of flatfoot is characterized by a flattening of the medial longitudinal arch and valgus deformity of the hindfoot. The differential diagnosis of flatfoot is the physiological, flexible, contracted flatfoot, which occurs as a congenital or acquired deformity. Congenital flatfoot deformity requires early intensive therapy, while a flexible flatfoot in children has a good prognosis and conservative treatment usually leads to a stable and sufficient load-bearing foot. Severe flatfoot in children can be corrected successfully by simple, minimally invasive procedures. In adults with symptomatic flatfoot, which usually occurs due to an insufficiency of the tendon of the tibialis posterior, conservative therapy with insoles, shoe modifications and physiotherapeutic measures can lead to significant improvement, otherwise surgical correction is recommended. Early, stage-appropriate therapy helps to prevent an impending decompensation of the hindfoot.
What is the treatment for flat foot?
In adults with symptomatic flatfoot, which usually occurs due to an insufficiency of the tendon of the tibialis posterior, conservative therapy with insoles, shoe modifications and physiotherapeutic measures can lead to significant improvement, otherwise surgical correction is recommended.
Can flat feet be corrected?
Congenital flatfoot deformity requires early intensive therapy, while a flexible flatfoot in children has a good prognosis and conservative treatment usually leads to a stable and sufficient load-bearing foot. Severe flatfoot in children can be corrected successfully by simple, minimally invasive procedures.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for family history of abdominal aortic aneurysm
- 2. icd code for brain tumor
- 3. icd 10 code for malignant melanoma in situ
- 4. icd 10 code for 211.3
- 5. icd 10 code for esophageal/gastric anastomosis stricture status
- 6. icd 9 code for blood loss
- 7. icd 10 code for limb weakness
- 8. icd 10 code for m19.90
- 9. icd 10 code for pulm fibrosis
- 10. icd 10 cm code for fatty liver