What are symptoms of acute respiratory failure?
Some things you may notice are:
- Bluish color to your fingernails, lips, and skin
- Feeling that you just can't take in enough air
- Confusion
- Heartbeat that's off
- Rapid breathing or extremely slow breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Sleepiness or passing out
What are the clinical indicators of acute respiratory failure?
What are the clinical indicators of acute respiratory failure?
- The signs of symptoms of acute respiratory failure can include:
- ABG (arterial blood gas) values of:
- o PO2 < 60 mm Hg (hypoxemia) (confusion)
- o PCO2 > 50 mm Hg (hypercapnia) (somnolent) o pH < 7.35 (respiratory acidosis)
- o HCO3 < 22 mEq/liter.
- Dyspnea.
- Rapid deep breathing (Respiratory Rate (RR) > 24 per minute)
What are the guidelines for acute respiratory failure?
- Minimise leaks in the circuit.
- Non-vented face mask, or a helmet – with the best fit to the facial contour.
- Secure the mask, prior to turning on the ventilator. ...
- A viral/bacterial filter (to filter particles 0.3 mm in size) at the outlet of the ventilator and also at the expiratory side of the circuit.
What is the criteria for acute respiratory failure?
- pO 2 less than 60 mm Hg (hypoxemia).
- pCO 2 greater than 50 mm Hg (hypercapnia) with pH less than 7.35.
- Signs and symptoms of acute respiratory distress.
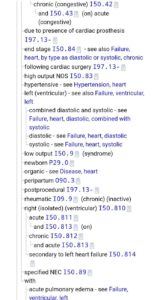
How do you code Acute on chronic respiratory failure?
ICD-10 Code for Acute and chronic respiratory failure- J96. 2- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for Acute on chronic respiratory failure?
J96. 20 - Acute and chronic respiratory failure, unspecified whether with hypoxia or hypercapnia. ICD-10-CM.
What is ICD-10 code for history of respiratory failure?
0 for Personal history of diseases of the respiratory system is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for Acute respiratory?
ICD-10-CM Code for Acute respiratory distress R06. 03.
What is Acute on chronic respiratory failure?
Acute-on-chronic respiratory failure (ACRF) occurs when relatively minor, although often multiple, insults cause acute deterioration in a patient with chronic respiratory insufficiency.
When do you code Acute respiratory failure?
A code from subcategory J96. 0, Acute respiratory failure, or subcategory J96. 2, Acute and chronic respiratory failure, may be assigned as a principal diagnosis when it is the condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for the hospital admission.
Is acute respiratory failure always coded first?
Currently, the direction states that either the acute respiratory failure or the established etiology can be sequenced first; however, we must take the circumstances of the encounter into account. Many cite the coding convention related to etiology/manifestation as dictating that the etiology must be sequenced first.
When do you use Z71 85?
Following the note for Z71, it now states, “Code Z71. 85, Encounter for immunization safety counseling, is to be used for counseling of the patient or caregiver regarding the safety of a vaccine.
What is the diagnosis for ICD 10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
When do you use Z20 828?
Z20. 828, Contact with and (suspected) exposure to other viral communicable diseases. Use this code when you think a patient has been exposed to the novel coronavirus, but you're uncertain about whether to diagnose COVID-19 (i.e., test results are not available).
Is respiratory failure a disease?
Chronic respiratory failure is a serious illness that gets worse over time. As the condition increases in severity, people may develop an abnormal heart rhythm, stop breathing, or slip into a coma. To help meet the challenges of living with COPD, we'll send support and advice for both patients and caregivers.
What is the code for COPD with acute exacerbation?
The Alphabetic Index leads coding professionals to code J44. 1, COPD with (acute) exacerbation, for exacerbation of COPD. However, Coding Clinic Fourth Quarter 2017 advises to assign code J43. 9, Emphysema, unspecified, when a patient with emphysema presents with an acute exacerbation of COPD.
When is acute respiratory failure a principal diagnosis?
OFFICIAL CODING GUIDELINE Acute or acute on chronic respiratory failure may be reported as principal diagnosis when it is the condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for occasioning the admission of the patient to the hospital for care. Refer to Section II of the ICD-10-CM Official Guidelines for Coding and Reporting on “Selection of Principal Diagnosis”.
What are the symptoms of respiratory failure?
Look for documented signs / symptoms of: SOB (shortness of breath) Delirium and/or anxiety. Syncope. Use of accessory muscles / poor air movement.
What to do if documentation is not clear as to whether acute respiratory failure and another condition are equally responsible for occasioning?
If the documentation is not clear as to whether Acute Respiratory Failure and another condition are equally responsible for occasioning the admission, query the provider for clarification.
Is respiratory failure a cut and dry diagnosis?
Very seldom is it a simple cut and dry diagnosis. There always seems to be just enough gray to give coders on any given day some doubt. It’s not only important for a coder to be familiar with the guidelines associated with respiratory failure but they should also be aware of the basic clinical indicators as well.
Does a condition on admission qualify for principal diagnosis?
With any record, keep in mind that because a condition may be present on admission does not necessarily mean it qualifies for principal diagnosis. You have to ask yourself these questions:
Can COPD cause ABG?
A patient with a chronic lung disease such as COPD may have an abnormal ABG level that could actually be considered that particular patient’s baseline.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for chemical pneumonitis
- 2. icd 10 diagnosis code for orthostatic hypotension
- 3. icd 10 code for rearfoot pronation
- 4. 2015 icd 10 code for changes in levels of consciousness
- 5. icd 10 code for history of i bleed
- 6. icd 10 e code for lifting injury
- 7. icd 10 code for resting tremors
- 8. icd 10 code for localized soft tissue swelling of neck
- 9. icd 10 code for high grade b cell lymphoma
- 10. icd-10 code for living-related donor kidney transplant