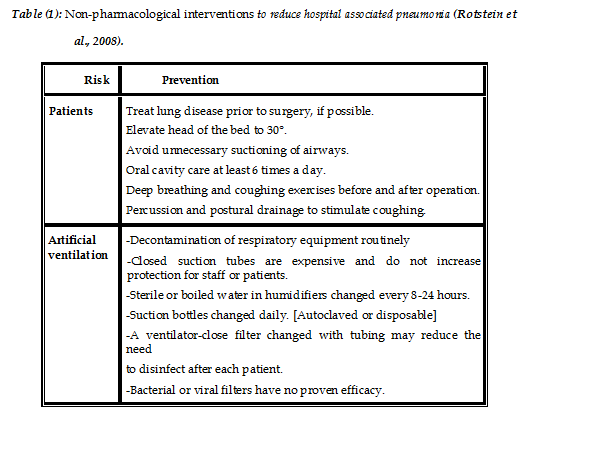
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z87.01. Personal history of pneumonia (recurrent) 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O89.01 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Aspiration pneumonitis due to anesthesia during the puerperium. Aspiration pneumonitis due to anesth during the puerperium; Aspiration pneumonitis …
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · History of aspiration pneumonia History of pneumonia History of pneumonia due to inhaled materiel History of recurrent pneumonia Present On Admission Z87.01 is considered exempt from POA reporting. ICD-10-CM Z87.01 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 951 Other factors influencing health status Convert Z87.01 to ICD-9-CM
What is the history of ICD - 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · J69.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J69.0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J69.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 J69.0 may differ. Applicable To Aspiration pneumonia NOS
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM code Z87.01 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like h/o: pneumonia, history of aspiration pneumonia, history of chronic lung disease, history of pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia or history of recurrent pneumonia. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.
What is the ICD-10 code for History of aspiration?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code P24 P24. 1 Neonatal aspiration of (clear) amniotic fluid...
How do you code aspiration pneumonia?
J69. 0 - Pneumonitis due to inhalation of food and vomit | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for aspiration?
ICD-10-CM Code for Aspiration of fluid as the cause of abnormal reaction of the patient, or of later complication, without mention of misadventure at the time of the procedure Y84. 4.
What is aspiration pneumonia?
Pneumonia is a breathing condition in which there is inflammation (swelling) or an infection of the lungs or large airways. Aspiration pneumonia occurs when food, saliva, liquids, or vomit is breathed into the lungs or airways leading to the lungs, instead of being swallowed into the esophagus and stomach.
What is the ICD-10 code for aspiration of food?
J69.0ICD-10 code J69. 0 for Pneumonitis due to inhalation of food and vomit is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
Is aspiration pneumonia the same as aspiration pneumonitis?
Aspiration pneumonitis (Mendelson's syndrome) is a chemical injury caused by the inhalation of sterile gastric contents, whereas aspiration pneumonia is an infectious process caused by the inhalation of oropharyngeal secretions that are colonized by pathogenic bacteria.Mar 1, 2001
How can you tell if someone aspirated?
What are the symptoms of aspiration from dysphagia?Feeling that food is sticking in your throat or coming back into your mouth.Pain when swallowing.Trouble starting a swallow.Coughing or wheezing after eating.Coughing while drinking liquids or eating solids.Chest discomfort or heartburn.More items...
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral pneumonia?
ICD-10 codeICD-10 termRead termBilateral pneumoniaJ220Unspecified acute lower respiratory tract infectionAcute respiratory infectionsAcute low respitract infectionAcute resp. infection NOS56 more rows
What is the ICD-10-CM code for organic pneumonia?
J84.116ICD-10 code J84. 116 for Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is the most common form of aspiration pneumonia?
Nosocomial bacterial pneumonia caused by aspiration is common, and the major pathogens involved are hospital-acquired florae through oropharyngeal colonization (eg, enteric gram-negative bacteria, staphylococci).Oct 12, 2021
What is the pathophysiology of aspiration pneumonia?
The pathological process of aspiration pneumonia occurs when the normal defense mechanisms fail in a predisposed individual. The entry of fluid into the bronchi and alveolar space triggers an anti-inflammatory reaction with the release of proinflammatory cytokines, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukins.
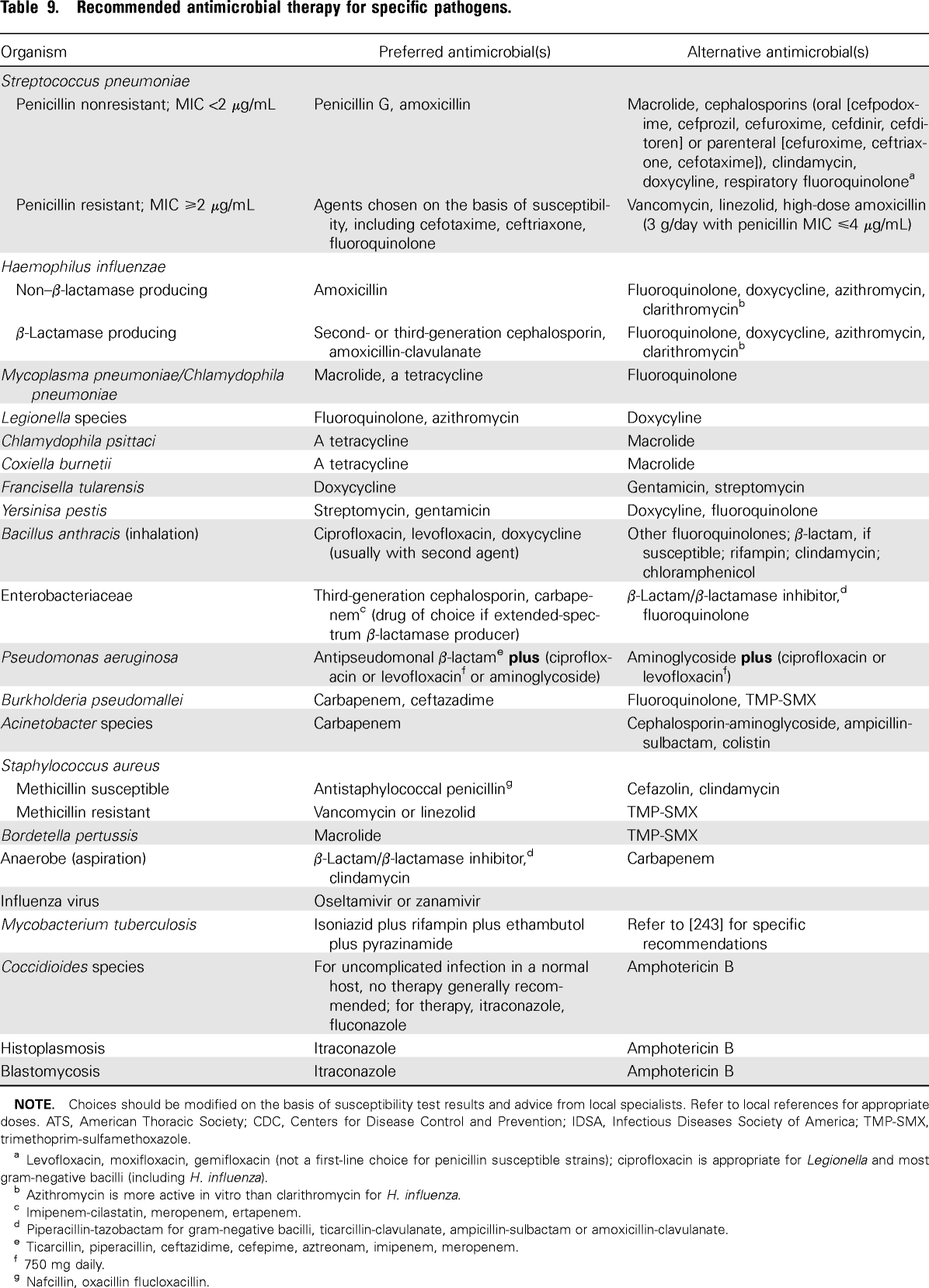
What organism causes aspiration pneumonia?
The causative microorganisms in aspiration pneumonia, similar to community-acquired pneumonia, are basically thought to be bacteria residing in the oral cavity, such as pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus and anaerobes.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, fevers, chills, chest pain, headache, sweating, and weakness. Inflammation of any part, segment or lobe, of the lung parenchyma. Inflammation of the lungs with consolidation and exudation. Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection.
How old do you have to be to get pneumonia?
People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age , or already have health problems. If you have pneumonia, you may have difficulty breathing and have a cough and a fever. A physical exam and history can help determine if you have pneumonia.
What causes pneumonia in the lung?
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection. Three common causes are bacteria, viruses and fungi. You can also get pneumonia by accidentally inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems.
What is lung parenchyma?
An acute, acute and chronic, or chronic inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma, due to infections (viruses, fungi, mycoplasma, or bacteria), treatment (e.g. Radiation), or exposure (inhalation) to chemicals.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for leg swelling
- 2. icd 10 code for hbp
- 3. icd 10 code for hypertension associated with diabetes
- 4. icd 10 code for c5 to c7 spondylosis
- 5. icd 10 code for leg cramps
- 6. icd 10 code for midepigastric pain
- 7. icd 10 code for pap smer
- 8. icd 10 code for peripheral vision loss due to cva
- 9. icd code for scaphoid proximal pole fracture
- 10. icd 10 code for mitral annulus calcifications