What are home remedies for burning mouth syndrome?
Mint
- Add a handful of freshly crushed mint leaves to a jug of hot water. Cover and allow it to steep for 1 hour, then strain it. ...
- Chill a cup of strong mint tea in the refrigerator for 30 minutes. Drink this cool tea a few times daily.
- You can even chew a few fresh mint leaves or mint gum daily.
What is the treatment for burning mouth syndrome?
You may have some of the following tests:
- Blood tests. Blood tests can check your complete blood count, glucose level, thyroid function, nutritional factors and immune functioning, all of which may provide clues about the source of your ...
- Oral cultures or biopsies. ...
- Allergy tests. ...
- Salivary measurements. ...
- Gastric reflux tests. ...
- Imaging. ...
- Medication adjustment. ...
- Psychological questionnaires. ...
How do you cure burning mouth?
Seven natural home remedies
- Cold water. Taking immediate action after burning the roof of the mouth can curb the extent of the damage. ...
- Yogurt or milk. Yogurt can ease pain caused by a burn. ...
- Aloe vera. Aloe vera gel is often used on external burns to soothe the skin. ...
- Honey. Honey can help a burn on the roof of the mouth to heal. ...
- Saltwater rinse. ...
- Soft foods. ...
- Look after the skin. ...
What can be done about burning mouth syndrome?
Nine home remedies to help burning mouth syndrome symptoms include capsaicin rinses, vitamin B12, iron-rich foods, zinc, baking soda, mouth rinse, honey, alpha lipoic acid and stress-relieving activities.
What is R68 89 diagnosis code?
ICD-10 code R68. 89 for Other general symptoms and signs is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What K31 89?
ICD-10 code K31. 89 for Other diseases of stomach and duodenum is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is Z51 12 code?
Encounter for antineoplastic immunotherapyICD-10 code Z51. 12 for Encounter for antineoplastic immunotherapy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
Is R13 10 a billable code?
ICD-Code R13. 10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Dysphagia, Unspecified. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 787.2.
What is focal foveolar hyperplasia?
Foveolar hyperplasia is a rare disorder characterized by an overgrowth of mucous cells in the stomach. In children, it may present as a localized lesion that affects the antrum primarily, called focal foveolar hyperplasia (FFH), or as a diffuse lesion, known as Ménétrier disease.
What is Patulous pylorus?
(pī-lōrik in-kompĕ-tĕns) Patulous state or want of tone of pylorus that allows passage of food into intestine before gastric digestion is completed.
What is the difference between Z51 11 and Z51 12?
0, Encounter for antineoplastic radiation therapy, or Z51. 11, Encounter for antineoplastic chemotherapy, or Z51. 12, Encounter for antineoplastic immunotherapy followed by any codes for the complications.
What is diagnosis code Z51 11?
ICD-10 code Z51. 11 for Encounter for antineoplastic chemotherapy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
Can Z51 11 be a primary diagnosis?
11 or Z51. 12 is the only diagnosis on the line, then the procedure or service will be denied because this diagnosis should be assigned as a secondary diagnosis. When the Primary, First-Listed, Principal or Only diagnosis code is a Sequela diagnosis code, then the claim line will be denied.
What does code Z12 11 mean?
Z12. 11: Encounter for screening for malignant neoplasm of the colon.
What is R13 12?
ICD-10 code R13. 12 for Dysphagia, oropharyngeal phase is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is diagnosis code Z86 010?
“Code Z86. 010, Personal history of colonic polyps, should be assigned when 'history of colon polyps' is documented by the provider. History of colon polyp specifically indexes to code Z86.
The Clinical Syndrome
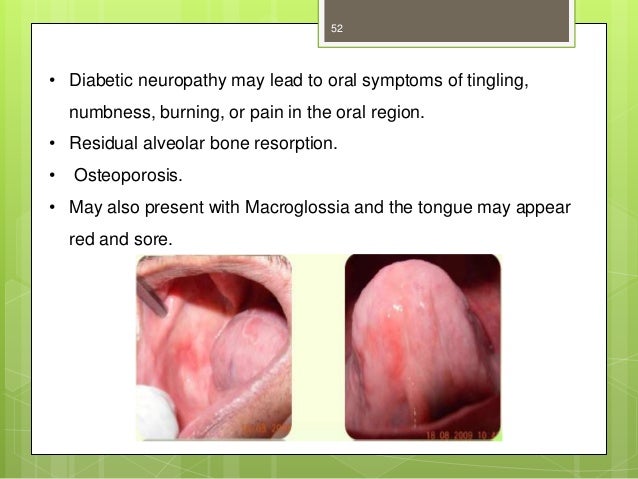
Burning mouth syndrome is an infrequent but serious cause of oral pain.
The Clinical Syndrome
Burning mouth syndrome is an infrequent but serious cause of oral pain.
Signs and Symptoms
The hallmark of burning mouth syndrome is mouth and tongue burning pain in the absence of clinically demonstrable oral pathology. Depressive affect or a phobic preoccupation with occult cancer is often present, as is xerostomia.
Testing
No specific test exists for burning mouth syndrome, and a presumptive diagnosis can be made only if (1) the clinical examination is normal and (2) a workup for all underlying pathological findings fails to identify a specific cause for the patient’s pain symptomatology.
How do you know if you have burning mouth syndrome?
Symptoms of burning mouth syndrome may include severe burning or tingling in the mouth which may persist or come and go over the course of months to years. The tongue is usually affected, but the pain may also be in the lips, gums, palate, throat or whole mouth. The burning sensation may be absent in the morning and increase over the course ...
What is the cause of burning sensation in the mouth?
Burning mouth syndrome may be primary or secondary. Experts believe that the primary form may be caused by damage to the nerves that control pain and taste.
What causes mouth irritation?
Endocrine disorders, such as diabetes or hypothyroidism. Excessive mouth irritation which may result from over-brushing, use of abrasive toothpastes, over use of mouthwashes, or drinking too many acidic drinks. Psychological factors, such as anxiety, depression, or stress.
How to stop a swollen mouth from sneezing?
Sip water frequently. Suck on ice chips. Chew sugarless gum. Avoid irritating substances like tobacco, hot or spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, mouthwashes that contain alcohol, and products high in acid, like citrus fruits and juices, as well as cinnamon or mint.
Why does my mouth dry out?
Dry mouth, which can be caused by various medications or underlying health problems. Other oral conditions, such as fungal infections, oral lichen planus, or geographic tongue. Nutritional deficiencies, such as l ack of iron, zinc, folic acid, thiamin, riboflavin, pyridoxine, and cobalamin.
Does burning sensation come and go?
The burning sensation may be absent in the morning and increase over the course of the day, start first thing in the morning and last all day, or come and go all day long. For many, the pain is reduced when eating or drinking. Other symptoms may include a sensation of dry mouth with increased thirst, a bitter or metallic taste, or loss of taste.
What are the symptoms of burning mouth syndrome?
The three key symptoms of burning mouth syndrome are: Oral pain. Abnormal taste. Dry mouth feeling. Oral pain. Oral pain is the major symptom and is most commonly described as a burning sensation in the mouth like a scald from a hot drink, or as tingling or numbness. The tongue is the most common site involved, ...
What does it mean when you have a burning mouth?
Burning mouth syndrome may be associated with personality or mood disturbances, particularly anxiety and depression. It is not clear if these are due to the mouth symptoms or if they contribute to the development of the problem.
What does it mean when your mouth is frothy?
Frothy saliva pooling in the floor of the mouth indicating excessive mucoid submandibular saliva that does not clear easily with swallowing. Mild redness on the symptomatic areas such as the tongue, hard palate, inside lower lip near the incisors.
What is the examination of the mouth?
The examination of the mouth. A thorough clinical examination should be performed, including the oral cavity where local organic causes, such as oral candidiasis (thrush) and oral cancer, must be excluded. The top of the tongue should have a complex architecture (i.e. it should not be smooth as is seen in anaemia ).
How long does burning mouth last?
Symptoms of burning mouth. In burning mouth syndrome, symptoms persist for many months and often years. Not everyone with this condition describes all three key symptoms and the absence of any of these does not exclude the diagnosis. Many other symptoms may also be described and may include:
Is there a cure for burning mouth syndrome?
There is no definitive cure. A list of symptoms and signs of burning mouth syndrome may help the patient accept the diagnosis as this is an important step in order to make progress. For some, recognition and explanation only is required. For many, the condition is disabling and active treatment is required.
Is burning mouth syndrome normal?
Tests may be required based on the findings of history and examination. However, in burning mouth syndrome these are all normal/negative.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for displaced fracture of distal left femur
- 2. icd 9 code for biliary drain insertion
- 3. icd 10 code for intraparenchymal hemorrhage of brain
- 4. icd 10 code for anxity
- 5. icd 10 code for congenital flat feet
- 6. icd 10 code for bipolar type 1 with schizophrenia
- 7. what is the icd 10 code for acute on chronic kidney disease?
- 8. icd 10 code for screening for ovarian cancer
- 9. icd 10 code screening for arm pain
- 10. icd code for bug bites