What drugs are used for UTI?
Oct 01, 2021 · Z87.440 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z87.440 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z87.440 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z87.440 may differ.
How do you code recurrent UTI?
4 rows · May 22, 2021 · E.Coli sepsis due to UTI, E.Coli UTI due to indwelling catheter. UTI ICD 10 ...
What is the ICD 10 code for UTI?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B96.20 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified Escherichia coli [E. coli] as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. Unsp Escherichia coli as the cause of diseases classd elswhr; E coli infection; Escherichia coli urinary tract infection; Infection due to escherichia coli; Escherichia coli [E. coli] NOS.
What is the diagnosis code for UTI?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B96.20 Unspecified Escherichia coli [E. coli] as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code B96.20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.

What is the ICD-10 code for UTI with E. coli?
A04. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM A04. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do you code UTI history?
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary tract infection?
What is the ICD-10 code for bacteremia due to Escherichia coli?
When was urinary tract infection first discovered?
What is the ICD-10 code for urinary retention?
What is the ICD 10 code for UTI site not specified?
What is the CPT code for urinary tract infection?
What class is Macrobid?
What is the ICD 10 code for sepsis due to urinary tract infection?
A41.
How do you code UTI with sepsis?
What is ESBL E. coli?
Can E. coli cause diarrhea?
e. Coli is the name of a type of bacteria that lives in your intestines. Most types of e. Coli are har mless. However, some types can make you sick and cause diarrhea. One type causes travel ers' diarrhea. The worst type of e. Coli causes bloody diarrhea, and can sometimes cause kidney failure and even death.
Can E. coli make you sick?
Coli is the name of a type of bacteria that lives in your intestines. Most types of e. Coli are harmless. However, some types can make you sick and cause diarrhea. One type causes travelers' diarrhea. The worst type of e.
What is the code for urosepsis?
Urosepsis is a general term, and there is no code for it. If the documentation indicates “urosepsis,” query the physician for more information.
Can E. coli enter the urinary tract?
Typically, urinary tract infections occur when bacteria, such as E. coli, enter the urinary tract by way of the urethra and start to multiply in the bladder. If the infection goes untreated, it can progress into the kidneys. Females have an increased risk of UTIs compared to males because of their anatomy.
What is the most common bacterial infection in women?
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are one of the most common, recurrent bacterial infections in individuals, mostly women. Bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), enters the urethra and infects one or several parts of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, or kidneys. UTIs can be mild to serious and even result in death.
What is the most common type of urinary tract infection?
The most common type of urinary tract infection is a bladder infection, called cystitis. It affects the bladder and urethra in the lower urinary tract. A UTI that occurs in the urethra only is called urethritis.
Can a urinary tract infection cause a burning sensation?
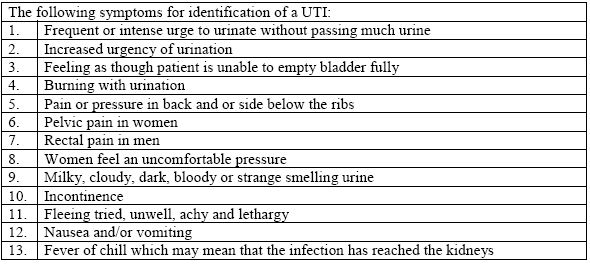
Urinary tract infections do not always cause signs and symptoms. When they do, however, they may include: Frequent urges to urinate (polyuria) Burning feeling while urinating (dysuria) Feeling the need to urinate even when the bladder is empty. Cloudy and strong-smelling urine.
What happens if you get an infection in the urinary tract?
coli, enter the urinary tract by way of the urethra and start to multiply in the bladder. If the infection goes untreated, it can progress into the kidneys.
Why are diaphragms at risk for urinary tract infections?
This is due to a decline in circulating estrogen.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hepatic hypodensities
- 2. icd 10 code for trapezius muscle atrophy
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for contusion left ribs
- 4. icd 10 code for leg weakiness
- 5. icd 10 z code for preventivie labs
- 6. icd 10 code for personal history of vocal cord cancer
- 7. icd 10 code for anterior calcaneous
- 8. icd-10 code for altered level of consciousness for hypoglycemia
- 9. icd 10 code for closed nondisplaced spiral fracture of shaft of left femur
- 10. icd 10 code for anteroseptal myocardial infarct