Endometrial hyperplasia, unspecified. N85.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N85.0 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N85.0 Endometrial hyperplasia 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code N85.0 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail.
What are ICD 10 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Endometrial hyperplasia, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code N85.00 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM N85.00 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · History of atypical hyperplasia of breast History of endometrial hyperplasia History of endometriosis History of ovarian tumor, low malignant potential Present On Admission Z87.42 is considered exempt from POA reporting. ICD-10-CM Z87.42 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 951 Other factors influencing health status
What is the ICD 10 code for uterine mass?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N85.00 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Endometrial hyperplasia, unspecified. Benign (not cancer)endometrial hyperplasia; Benign endometrial hyperplasia; Endometrial hyperplasia; Hyperplasia (adenomatous) (cystic) (glandular) of endometrium; Hyperplastic endometritis. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N85.00.
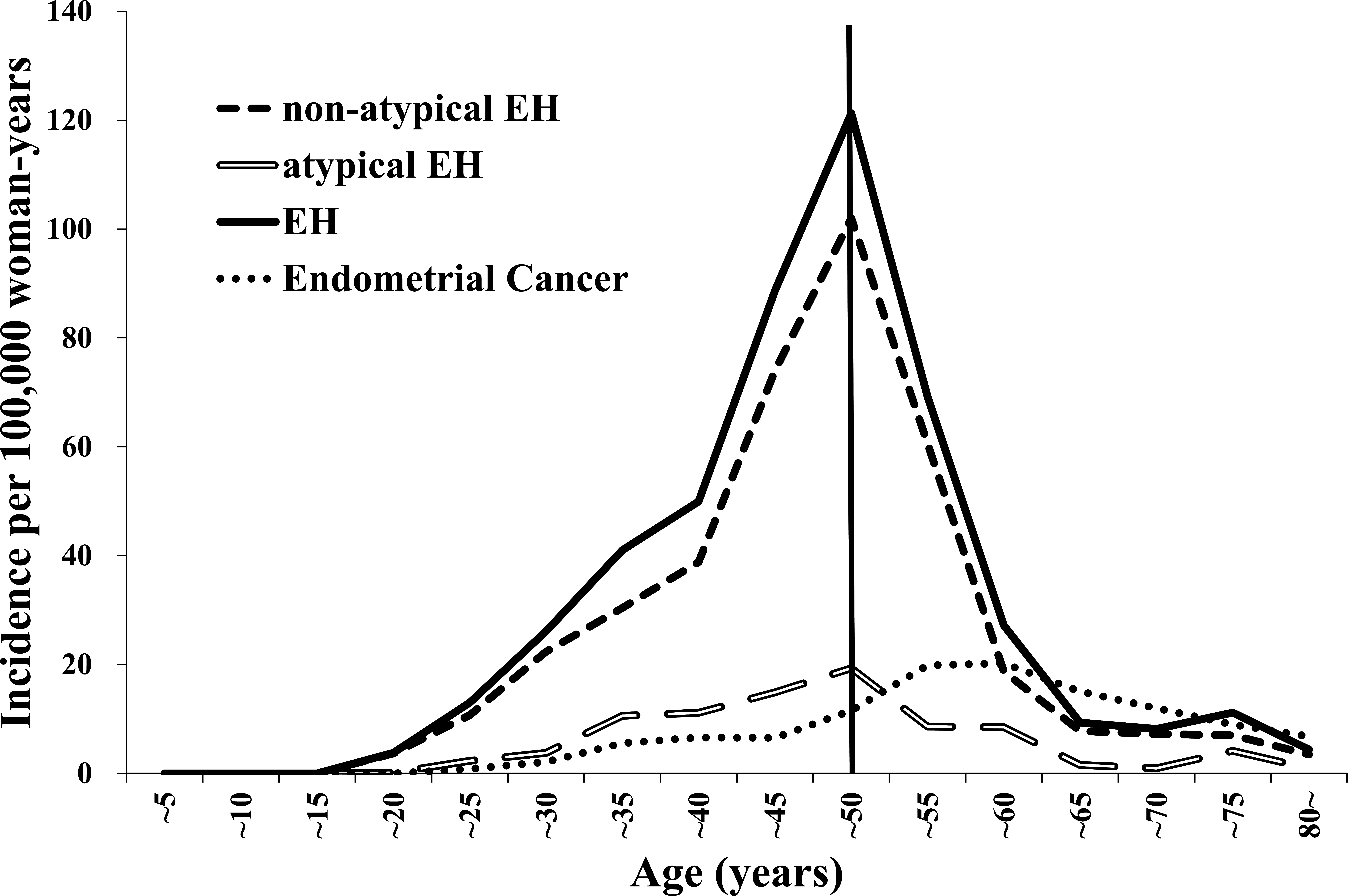
What is the ICD-10 code for endometrial hyperplasia without atypia?
What is the ICD-10 code for endometrial thickening?
What is endometrial hyperplasia unspecified?
What is the ICD-10 code for endometrial hyperplasia with atypia?
What is diagnosis code R93 89?
What is cystic endometrial hyperplasia?
Is endometrial hyperplasia the same as endometriosis?
What is atypical endometrial hyperplasia?
What are the types of hyperplasia?
What is hyperplastic growth?
What is the ICD-10 code for complex atypical hyperplasia?
What does a thickened endometrium mean?
What is the ICd 10 code for endometrial hyperplasia?
N85.00 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of endometrial hyperplasia, unspecified. The code N85.00 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code N85.00 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like abnormal uterine bleeding due to endometrial disorder, abnormal uterine bleeding due to endometrial hyperplasia, endometrial cystic hyperplasia, endometrial hyperplasia or hypoplasia of endometrium.#N#The code N85.00 is applicable to female patients only. It is clinically and virtually impossible to use this code on a non-female patient.#N#Unspecified diagnosis codes like N85.00 are acceptable when clinical information is unknown or not available about a particular condition. Although a more specific code is preferable, unspecified codes should be used when such codes most accurately reflect what is known about a patient's condition. Specific diagnosis codes should not be used if not supported by the patient's medical record.
What causes a baby to grow in the womb?
Causes can include hormones, thyroid problems, fibroids, polyps, cancer, infection, or pregnancy.
Can birth control stop bleeding?
Treatment depends on the cause. Sometimes birth control pills treat hormonal imbalances. If a thyroid problem is the cause, treating it may also stop the bleeding. If you have cancer or hyperplasia, an overgrowth of normal cells in the uterus, you may need surgery.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for metastatic cholangiocarcinoma
- 2. icd-10 code for medication education
- 3. icd 10 code for subdermal contraceptive implant
- 4. icd 10 code for carotid endarterectomy
- 5. icd 10 code for r leg cellulitis
- 6. icd 10 code for local pain over the anterior chest wall -
- 7. icd 10 code for suicide attempt by acetaminophen overdose
- 8. icd 10 code for uncontrolled hypertension
- 9. icd 10 cm code for right hilar abnormality
- 10. icd 10 cm code for aftercare after ventrical emphema surgery