What is the ICD 10 code for Ewing's sarcoma?
C41.9 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of malignant neoplasm of bone and articular cartilage, unspecified. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Ewing's sarcoma or Ewing sarcoma (/ˈjuːɪŋ/) is a malignant small, round, blue cell tumor.
What is the ICD 10 code for Kaposi sarcoma?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C96.A ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C96.4 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C46.4 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C46.1 Kaposi's sarcoma of lymph glands and nodes ( C46.3) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C46.4 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C46.5- ICD-10-CM...
What is the history of Ewing's sarcoma?
Ewing's sarcoma. Although usually classified as a bone tumor, Ewing's sarcoma can have characteristics of both mesodermal and ectodermal origin, making it difficult to classify. James Ewing (1866–1943) first described the tumour, establishing that the disease was separate from lymphoma and other types of cancer known at that time.
What are the symptoms of Ewing sarcoma?
Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that may be a bone sarcoma or a soft-tissue sarcoma. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture.
What is the ICD-10 for Ewing's sarcoma?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C41. 9: Malignant neoplasm of bone and articular cartilage, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for history of sarcoma?
Personal history of malignant neoplasm of soft tissue Z85. 831 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for bone metastasis?
Patients diagnosed with bone metastases were identified using a diagnostic code (ICD-10 code for bone metastasis: C795).
What is the ICD-10 code for liver cancer?
C22. 0 - Liver cell carcinoma | ICD-10-CM.
What is code Z85?
ICD-10 code Z85 for Personal history of malignant neoplasm is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
When is it appropriate to use history of malignancy?
When a primary malignancy has been excised or eradicated from its site, there is no further treatment (of the malignancy) directed to that site, and there is no evidence of any existing primary malignancy, a code from category Z85, Personal history of malignant neoplasm, should be used to indicate the former site of ...
What is diagnosis code Z51 11?
ICD-10 code Z51. 11 for Encounter for antineoplastic chemotherapy is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the ICD-10 code for metastatic unknown primary?
C80. 1 - Malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified | ICD-10-CM.
How do you code metastasis?
If the site of the primary cancer is not documented, the coder will assign a code for the metastasis first, followed by C80. 1 malignant (primary) neoplasm, unspecified. For example, if the patient was being treated for metastatic bone cancer, but the primary malignancy site is not documented, assign C79. 51, C80.
What is the ICD-10 code for secondary liver cancer?
ICD-10 code: C78. 7 Secondary malignant neoplasm of liver and intrahepatic bile duct.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for secondary liver cancer?
7 for Secondary malignant neoplasm of liver and intrahepatic bile duct is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Malignant neoplasms .
What is the ICD-10 code for chronic liver disease?
ICD-10-CM Code for Liver disease, unspecified K76. 9.
Where is Ewing's sarcoma found?
The most common areas in which it occurs are the pelvis, the femur, the humerus, the ribs and clavicle (collar bone).
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code C41.9 and a single ICD9 code, 170.9 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
Where is Ewing sarcoma found?
Ewing Sarcoma is part of a group of four different types of cancer, known collectively as the Ewing Family of Tumors (EFT): Ewing bone sarcoma, which accounts for about 85% of all cases, is usually found in the long bones in the arm or leg, although it sometimes occurs in the pelvis or ribcage;
What is the treatment for ewing sarcoma?
The main treatments for Ewing Sarcoma are chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation, virtually always used in combination. In the past, surgery on tumors in the arm or leg bones usually required amputation.
How much of a tumor is metastatic?
The prognosis depends on the location of the tumor and whether or not the cancer has spread. Approximately 30% are metastatic at presentation. Diagnostic staging procedures attempt to distinguish individuals with localized disease from those with metastatic disease.
What is the Ewing's sarcoma?
PAS stain. Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that may be a bone sarcoma or a soft-tissue sarcoma. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture.
What is the prognostic factor for Ewing's Sarcoma?
The most common areas of metastasis are the lungs, bone and bone marrow with less common areas of metastasis being the lymph nodes liver and brain. The presence of metastatic disease is the most important prognostic factor in Ewing's Sarcoma with the 5 year survival rate being only 30% when metastasis is present at the time of diagnosis as compared to a 70% 5 year survival rate with no metastasis present. Another important prognostic factor is the location of the primary tumor; proximal tumors (located in the pelvis and sacrum) are worse prognostic indicators as compared to more distal tumors. Other factors associated with a poor prognosis include a large primary neoplasm, older age at diagnosis (older than 18 years of age) and increased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels.
What causes Ewing sarcoma?
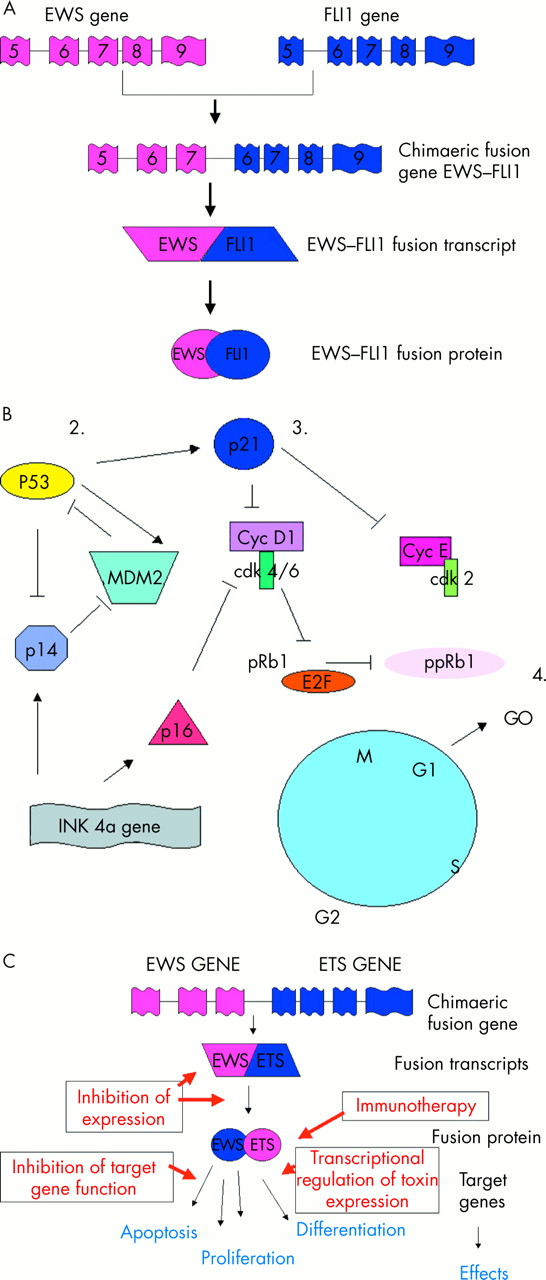
The cause of Ewing sarcoma is unknown. Most cases appear to occur randomly. It is sometimes grouped together with primitive neuroectodermal tumors, in a category known as the Ewing family of tumors. The underlying mechanism often involves a genetic change known as a reciprocal translocation.
How many people are affected by ewing sarcoma?
It affects about one in a million people per year in the United States. Ewing sarcoma occurs most often in teenagers and young adults and represents 2% of childhood cancers. Caucasians are affected more often than African Americans or Asians. Males are affected more often than females.
Where does ewing sarcoma occur?
It can occur anywhere in the body but most commonly in the pelvis and proximal long tubular bones, especially around the growth plates.
How common is ewing sarcoma?
In the United States, they are most common in the second decade of life, with a rate of 0.3 cases per million in children under 3 years of age, and as high as 4.6 cases per million in adolescents aged 15–19 years. Internationally, the annual incidence rate averages less than 2 cases per million children.
What is the name of the cancer that starts in the legs and pelvis?
Ewing sarcoma is a type of cancer that may be a bone sarcoma or a soft-tissue sarcoma. Symptoms may include swelling and pain at the site of the tumor, fever, and a bone fracture. The most common areas where it begins are the legs, pelvis, and chest wall.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for gram neg bacteremia
- 2. icd 10 code for right partial foot amputation
- 3. icd 10 code for portal htn gastropathy
- 4. chiropractic icd 10 code for 97110
- 5. icd-10 code for squamous cell carcinoma involving cervical lymph nodes
- 6. icd-10 code for chronic osteoarthritisd of the knee
- 7. icd 10 code for history pe
- 8. icd-10 code for history of pneumonia
- 9. what is the icd 10 code for torn meniscusbilateral knee
- 10. icd code for pt