What is the ICD 10 code for bilateral Hollenhorst plaque?
Bilateral hollenhorst plaque; Bilateral partial retinal artery occlusion; Hollenhorst plaque of bilateral eyes; Partial retinal artery occlusion, both eyes ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K05.10 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Chronic gingivitis, plaque induced
What is the pathophysiology of Hollenhorst plaques?
Four months following CEA, FA revealed significantly normalized vascular filling of his left retinal circulation (Figure 3). Hollenhorst plaques were first described in 1961 by Robert Hollenhorst, MD, who aptly inferred their intraarterial location as indicative of embolic disease, classically related to carotid arterial disease. 1,2
What is the prevalence of Hollenhorst plaques in retinal embolism?
Hollenhorst plaques make up the majority of the retinal emboli at 80%. An estimated 10% of carotid emboli reach the retinal arteries. [5] Pathophysiology
What are the signs and symptoms of Hollenhorst disease?
The presence of a Hollenhorst plaque is a confirming diagnosis; however, the absence of a plaque does not rule out the possibility of embolic occlusion. If an RAO takes place, the most common symptom is sudden, painless vision loss. The fundus will display typical ischemic signs such as retinal whitening around the occluded vessel.
What is the ICD-10 code for hollenhorst plaque?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H34. 212 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is hollenhorst plaque?
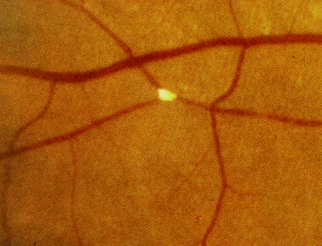
Cholesterol emboli aka Hollenhorst plaque: Yellow, refractile, typically located at the carotid artery bifurcation. They tend to originate from carotid arteries or the aorta. This finding is consistent with carotid disease originating from atherosclerotic lesions.
What is the diagnosis code for cataract left eye?
ICD-10 Code for Combined forms of age-related cataract, left eye- H25. 812- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for iridocorneal endothelial syndrome?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H18. 892 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H18.
Is Hollenhorst plaque an emergency?
The general consensus among these is that, in asymptomatic patients, findings of Hollenhorst plaques do not correlate with significant carotid artery disease or subsequent cerebrovascular events. Therefore, no urgent workup is necessary.
How common is Hollenhorst plaque?
A Hollenhorst plaque is a relatively common retinal finding in the geriatric population. Patients often are visually asymptomatic and present with retinal emboli from plaque ulceration in the internal carotid artery.
What is the ICD-10 code for cataracts of both eyes?
Combined forms of age-related cataract, bilateral H25. 813 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H25. 813 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for combined age-related cataract left eye?
H25. 812 Combined forms of age-related cataract, left eye - ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes.
What is the ICD-10 code for right cataract?
ICD-10 Code for Cortical age-related cataract, right eye- H25. 011- Codify by AAPC.
What are Guttata?
Definition. Corneal guttata are droplet-like accumulations of non-banded collagen on the posterior surface of Descemet's membrane. The presence of focal thickenings of Descemet's membrane histologically named guttae.
What is Cogan Reese syndrome?
Cogan-Reese syndrome is an extremely rare eye disorder characterized by a matted or smudged appearance to the surface of the iris; the development of small colored lumps on the iris (nodular iris nevi); the attachment of portions of the iris to the cornea (peripheral anterior synechiae); and/or increased pressure in ...
What is the ICD-10 code for neurotrophic Keratopathy?
Neurotrophic keratoconjunctivitis, unspecified eye H16. 239 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H16. 239 became effective on October 1, 2021.
When were Hollenhorst plaques first described?
Hollenhorst plaques were first described in 1961 by Robert Hollenhorst, MD, who aptly inferred their intraarterial location as indicative of embolic disease, classically related to carotid arterial disease. 1,2.
Is Hollenhorst a symptomatic or asymptomatic?
Evidence suggests that both symptomatic and asymptomatic Hollenhorst plaques may be markers for significant carotid artery disease, and their presence indicates risk factor analysis and carotid ultrasonography.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for metastisis unspecified primary or secondary
- 2. icd 10 code for renal transplant status
- 3. icd 10 code for psychological counseling
- 4. icd 10 code for shoulder abscess
- 5. icd 10 code for cvd
- 6. icd 10 code for supratherapeutic inr
- 7. icd-10 code for exostosis of wrist
- 8. icd 10 code for thigh mass
- 9. icd 10 code for follicular hyperkeratosis
- 10. 2016 icd 10 code for loss of consciousness