What are the common ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM CATEGORY CODE RANGE SPECIFIC CONDITION ICD-10 CODE Diseases of the Circulatory System I00 –I99 Essential hypertension I10 Unspecified atrial fibrillation I48.91 Diseases of the Respiratory System J00 –J99 Acute pharyngitis, NOS J02.9 Acute upper respiratory infection J06._ Acute bronchitis, *,unspecified J20.9 Vasomotor rhinitis J30.0
What is the longest ICD 10 code?
What is the ICD 10 code for long term use of anticoagulants? Z79.01. What is the ICD 10 code for medication monitoring? Z51.81. How do you code an eye exam with Plaquenil? Here’s the coding for a patient taking Plaquenil for RA:Report M06. 08 for RA, other, or M06. Report Z79. 899 for Plaquenil use for RA.Always report both.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Search the full ICD-10 catalog by:
- Code
- Code Descriptions
- Clinical Terms or Synonyms
How many ICD 10 codes are there?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...
What diagnosis will covers homocysteine?
Homocysteine levels will be covered by Medicare to confirm Vitamin B12 or folate deficiency. known vascular disease or risk thereof (based upon abnormal lipid metabolism, high blood pressure (BP) or diabetes mellitus (DM)) for the purpose of risk stratification.
What is a homocysteine level?
A homocysteine test measures the amount of homocysteine in your blood. Homocysteine is a type of amino acid, a chemical your body uses to make proteins. Normally, vitamin B12, vitamin B6, and folic acid break down homocysteine and change it into other substances your body needs.
What is the lab code for homocysteine?
ComponentsComponent Test Code*Component Chart NameLOINC0099869Homocysteine, Total13965-9
Does Medicare cover homocysteine blood test?
Homocysteine levels will be covered by Medicare to confirm vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
Is cholesterol and homocysteine related?
In general, there is a fairly high correlation between homocysteine levels in populations and elevated LDL cholesterol.
What causes elevated homocysteine levels?
Most people who have a high homocysteine level don't get enough folate (also called folic acid), vitamin B6, or vitamin B12 in their diet. Replacing these vitamins often helps return the homocysteine level to normal. Other possible causes of a high homocysteine level include: Low levels of thyroid hormone.
What happens when homocysteine levels are high?
High, or elevated, homocysteine levels are known as hyperhomocysteinemia. This could indicate a person has a vitamin deficiency, as the body needs certain nutrients to break it down. Less commonly, hyperhomocysteinemia can occur due to homocystinuria, which is a genetic disease.
What does CPT code 83090 mean?
CPT® Code 83090 - Chemistry Procedures - Codify by AAPC. CPT. Pathology and Laboratory Procedures. Chemistry Procedures.
What is methylmalonic acid and homocysteine?
Serum homocysteine and methylmalonic acid (MMA) levels are helpful confirmatory tests for cobalamin and folate deficiencies. Both are increased in cobalamine deficiency. Homocysteine but not MMA is increased in folate deficiency.
What diagnosis covers vitamin B12 testing?
There is agreement within the literature that serum vitamin B12 testing should be used to diagnose vitamin B12 deficiency in symptomatic and high-risk populations. One of the leading causes of vitamin B12 deficiency is pernicious anemia, an autoimmune disease that results in the failure to produce intrinsic factor.
What blood tests are not covered by Medicare?
Medicare does not cover the costs of some tests done for cosmetic surgery, insurance testing, and several genetic tests. There are also limits on the number of times you can receive a Medicare rebate for some tests. Your private health insurance may pay for diagnostic tests done while you are a patient in hospital.
When do you check homocysteine?
You may need a homocysteine test if you have a high risk of heart disease. You may also need a homocysteine blood test if you have symptoms of a vitamin B deficiency. Common symptoms of vitamin B deficiencies include: Dizziness.
General Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2021 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
CMS National Coverage Policy
Title XVIII of the Social Security Act §1833 (e) prohibits Medicare payment for any claim which lacks the necessary information to process the claim.
Article Guidance
The information in this article contains billing, coding or other guidelines that complement the Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Homocysteine Level, Serum L34419.
ICD-10-CM Codes that Support Medical Necessity
The correct use of an ICD-10 code listed below does not assure coverage of a service. The service must be reasonable and necessary in the specific case and must meet the criteria specified in the Homocysteine Level, Serum L34419 LCD.
Bill Type Codes
Contractors may specify Bill Types to help providers identify those Bill Types typically used to report this service. Absence of a Bill Type does not guarantee that the article does not apply to that Bill Type.
Revenue Codes
Contractors may specify Revenue Codes to help providers identify those Revenue Codes typically used to report this service. In most instances Revenue Codes are purely advisory. Unless specified in the article, services reported under other Revenue Codes are equally subject to this coverage determination.
What is the code for alcohol or drugs in blood?
code for findings of alcohol or drugs in blood (R78.-)
What is the code for a neonatal aspiration?
Neonatal aspiration of blood co-occurrent with respiratory symptoms; Neonatal aspiration of blood with pneumonia; Neonatal aspiration of blood with pneumonitis; code to identify any secondary pulmonary hypertension, if applicable (I27.2-)
What is the CMS 410.32?
Under CMS National Coverage Policy - revised title for 42 CFR §410.32 ‘Indicates that diagnostic tests may only be ordered by the treating physician (or other treating practitioner acting within the scope of his or her license and Medicare requirements). Added title ‘Diagnostic Services Defined’ to CMS internet-only manual, Publication 100-02 Chapter 6 Section 20.4.1. Added title ‘Diagnosis Code Requirements’ to CMS internet-only manual Publication 100-08 Chapter 3 Section 3.4.1.3. Under Sources of Information and Basis for Decision – revised title of the eleventh article listed.
What is a local coverage determination?
A Local Coverage Determination (LCD) is a decision made by a Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) on whether a particular service or item is reasonable and necessary, and therefore covered by Medicare within the specific jurisdiction that the MAC oversees.
Does Medicare cover homocysteine?
Homocysteine levels will be covered by Medicare to confirm vitamin B12 or folate deficiency.
Is homocysteine level necessary for CV?
Serum homocysteine levels for the evaluation of treatment of hyperhomocysteinemia in patients with CV risk factors will be denied as not medically necessary.
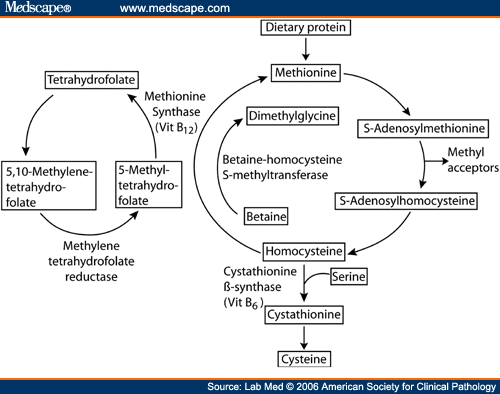
How is homocysteine formed?
Homocysteine (Hcy), a sulphur-containing amino acid, is formed from the conversion of methionine into cysteine. It is usually rapidly metabolized via 1 of 2 pathways:
What is the cause of homocystinuria?
The most common form of homocystinuria is caused by the lack of cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), a vitamin B6-dependent enzyme. Homocystinuria caused by CBS deficiency affects at least 1 in 200,000 to 335,000 people worldwide. Other forms of homocystinuria are much rarer. Moreover, the hallmarks of homocystinuria caused by CBS deficiency are developmental delay/mental retardation, ectopia lentis (dislocation of the ocular lens) and/or severe myopia, skeletal abnormalities as well as thrombo-embolism. There are two phenotypic variants of homocystinuria:
What is the name of the amino acid that is formed from the conversion of methionine into cysteine?
Excess levels in the blood are purported to increase the risk of stroke, certain types of heart disease or peripheral artery disease (PAD). Homocysteine (Hcy), a sulphur-containing amino acid, is formed from the conversion of methionine into cysteine. It is usually rapidly metabolized via 1 of 2 pathways:
Which pathway converts HCY to cysteine?
a vitamin B6-dependent trans-sulphuration pathway that converts Hcy to cysteine.
What is CPB 0536?
Assessment of borderline vitamin B12 deficiency, where the results will impact the member's management (see CPB 0536 - Vitamin B-12 Therapy ); or
Is homocysteine testing experimental?
Aetna considers homocysteine testing experimental and investigational for all other indications, including the following (not an all inclusive list) because its effectiveness for these indications has not been established: As a biomarker for the development and/or progression of erectile dysfunction.
Does HCY cause stroke?
While Hcy has been reported to exhibit atherogenic and prothrombotic properties, and histopathological hallmarks of Hcy-induced vascular injury include intimal thickening, elastic lamina disruption, smooth muscle hypertrophy, marked platelet accumulation, and the formation of platelet-enriched occlusive thrombi, its role in coronary heart disease and stroke is unclear. In randomized trials, reduction in Hcy levels has failed to lower overall risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD).
What is homocysteine test?
Homocysteine - An elevated concentration of homocysteine is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease. When used in conjunction with methylmalonic acid (MMA), these tests are useful to diagnose and monitor vitamin B12 (cobalamin) and folic acid deficiency and are often useful in evaluating macrocytosis (an elevated MCV, ...
What is CPT code 83090?
CPT Code is subject to a Medicare Limited Coverage Policy and may require a signed ABN when ordering. CPT Code is subject to a Medicare Limited Coverage Policy and may require a signed ABN when ordering. Ordering Restrictions may apply.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for reaction to immunization
- 2. icd--10 code for psoriasis
- 3. icd 9 code for urosepsis
- 4. icd 10 code for left wrist ganglion cyst
- 5. icd 10 cm code for boil on nose
- 6. icd 10 code for postural instability
- 7. icd-10 code for post covid vaccination reaction
- 8. icd 10 code for activity gymnastics
- 9. 2018 icd 10 code for compression t12
- 10. icd-10 code for right breast with mets to the left lung