What is the ICD 10 code for hemianopia with bilateral field defects?
Hemianopia, hemianopsia (heteronymous) H53.47ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H53.47Heteronymous bilateral field defects2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific CodeApplicable ToHeteronymous hemianop (s)ia. homonymous H53.46-. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H53.46-. Homonymous bilateral field defects.
What is the ICD 10 code for bilateral bilateral field defects?
Homonymous bilateral field defects, left side. H53.462 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H53.462 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is a billable code for bitemporal hemianopsia?
A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Bitemporal hemianopsia (aka bitemporal heteronymous hemianopsia or bitemporal hemianopia) is the medical description of a type of partial blindness where vision is missing in the outer half of both the right and left visual field.
What is the ICD 10 for right sided homonymous bilateral visual field defects?
Right sided homonymous bilateral visual field defects ICD-10-CM H53.461 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 123 Neurological eye disorders Convert H53.461 to ICD-9-CM
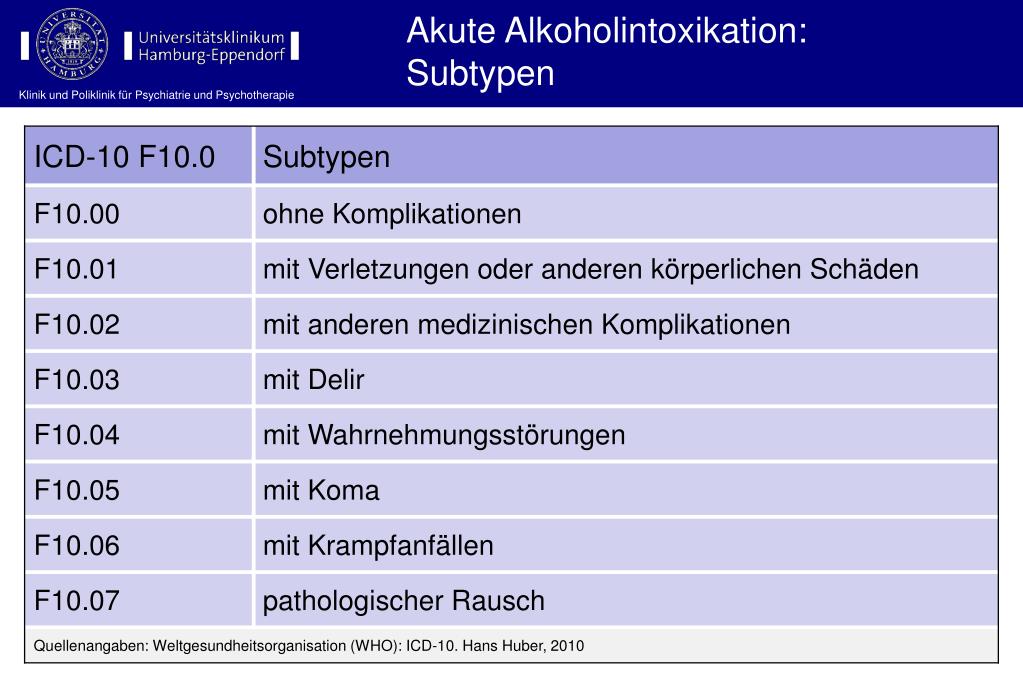
What is the ICD-10 code for left homonymous hemianopsia?
H53. 46 - Homonymous bilateral field defects. ICD-10-CM.
What is homonymous hemianopsia?
INTRODUCTION. Homonymous hemianopia is a visual field defect involving either the two right or the two left halves of the visual fields of both eyes.
What causes homonymous hemianopia?
What causes homonymous hemianopsia? The most common cause of this type of vision loss is stroke. However, any disorder that affects the brain — including tumors, inflammation and injuries — can be a cause.
What is the ICD-10 code for blindness both eyes?
ICD-10 code H54. 0 for Blindness, both eyes is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
What is the difference between hemianopia and hemianopsia?
Hemianopia, sometimes called hemianopsia, is partial blindness or a loss of sight in half of your visual field. It's caused by brain damage, rather than a problem with your eyes. Depending on the cause, hemianopia may be permanent or temporary.
Which strokes cause homonymous hemianopia?
3 Homonymous hemianopia is a loss of the right or left halves of the visual field of both eyes (Figure 1a, 1b) and usually occurs as a result of a middle cerebral or posterior cerebral artery stroke affecting either the optic radiation or visual cortex of the occipital lobe (Figure 2).
Is homonymous hemianopia blindness?
Homonymous hemianopia (HH) involves vision loss on the same side of the visual field in both eyes. This type of visual field loss is indicative of a lesion involving the visual pathway posterior to the chiasm.
WHO ICD-10 visual impairment?
1 Severe visual impairment, binocular. Visual impairment category 2.
What does unqualified visual loss both eyes mean?
If “blindness” or “low vision” of both eyes is documented but the visual impairment category is not documented, assign code H54. 3, Unqualified visual loss, both eyes. If “blindness” or “low vision” in one eye is documented but the visual impairment category is not documented, assign a code from H54.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for legally blind?
ICD-10 code H54. 8 for Legal blindness, as defined in USA is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
What is the meaning of homonymous?
Definition of homonymous 1 : ambiguous. 2 : having the same designation. 3 : of, relating to, or being homonyms.
What causes left homonymous hemianopsia?
Stroke is the most common cause of homonymous hemianopia (HH) in adults, followed by trauma and tumors. Associated signs and symptoms, as well as visual field characteristics such as location and congruity, can help determine the location of the causative brain lesion.
Can someone with homonymous hemianopia drive?
“It is clear that not all people with hemianopia function at the same level and many probably could not drive safely. However, a fair percentage of these patients may compensate for their visual loss to such an extent that they can drive as safely as any driver.”
Can you recover from homonymous hemianopia?
Patients can spontaneously recover from HH, but the probability of such recovery is proportional to the time that has elapsed since the lesion occurred. Reported recovery rates range from 7% to 86% (for a review, see: Sabel and Kasten, 2000).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for right adrenal mass
- 2. icd 10 code for chronic bilateral upper extremity rest tremors
- 3. icd 10 code for family history skin cancer
- 4. 2016 icd 10 code for nondisplaced fracture right proximal pinky finger
- 5. icd 10 code for sprain, left ankle
- 6. icd-10-pcs code for collection of csf from a vp shunt
- 7. icd 10 code for pressure ulcer left shoulder and sacral stage 2
- 8. what is the correct icd 10 code for c23
- 9. icd 10 code for full thickness burn left wrist 2nd degree
- 10. icd 10 code for cervical spine pain with radiculopathy