What is the ICD 10 code for left eyelid hordeolum externum?
ICD-10-CM Code H00.015 Hordeolum externum left lower eyelid Billable Code H00.015 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Hordeolum externum left lower eyelid. It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for hordeolum internum?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H00.029. Hordeolum internum unspecified eye, unspecified eyelid. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. H00.029 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for unspecified eye disease?
Hordeolum internum unspecified eye, unspecified eyelid 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code H00.029 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H00.029 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for right lower eyelid?
Hordeolum externum right lower eyelid 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code H00.012 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H00.012 became effective on October 1, 2020.
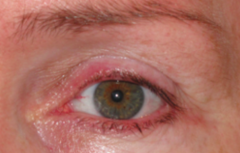
What is the ICD-10 code for hordeolum?
Hordeolum externum unspecified eye, unspecified eyelid H00. 019 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H00. 019 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the correct code for a Hordeolum Externum right upper eyelid?
ICD-10-CM Code for Hordeolum externum right upper eyelid H00. 011.
What is the difference between a hordeolum and chalazion?
Chalazia and hordeola (styes) are sudden-onset localized swellings of the eyelid. A chalazion is caused by noninfectious meibomian gland occlusion, whereas a hordeolum usually is caused by infection. Both conditions initially cause eyelid hyperemia and edema, swelling, and pain.
What is internal Hordeolum?
A stye happens when a gland on the edge of your eyelid gets infected. When it occurs inside or under the eyelid, it is called an internal hordeolum. The infection is most often caused by a bacteria or germ called staph (Staphylococcus aureus).
Can F07 81 be used as a primary diagnosis?
Our physicians have used IDC-10 code F07. 81 as the primary diagnosis for patients presenting with post concussion syndrome.
Can B96 81 be used as a primary diagnosis?
The note in ICD-10 under codes B95-B97 states that 'these categories are provided for use as supplementary or additional codes to identify the infectious agent(s) in disease classified elsewhere', so you would not use B96. 81 as a primary diagnosis, but as an additional code with the disease listed first.
What is external hordeolum?
A hordeolum (ie, stye) is a localized infection or inflammation of the eyelid margin involving hair follicles of the eyelashes (ie, external hordeolum) or meibomian glands (ie, internal hordeolum). A hordeolum usually is painful, erythematous, and localized. It may produce edema of the entire lid.
How do you get hordeolum?
A hordeolum is usually caused by a bacterial staph infection and results in pain, swelling, and redness. A hordeolum looks like a pus-filled lump or pimple at the edge of the eyelid. Treatment includes warm compresses and antibiotic eye drops or ointments.
Can chalazion become hordeolum?
A chalazion is a large, non-infectious cyst in the eyelid that often takes several weeks to develop. It can be caused by either inflammation of the meibomian glands or it can start as a hordeolum. A chalazion is not painful and usually occurs on the upper eyelid.
What is the difference between a stye and a hordeolum?
Stye is a term used often by the general public to denote a small localized swelling/inflammation of the eyelid. A hordeolum (or a stye) is term used by the medical profession to denote a localized inflammation and/or infection of the hair follicles of the eyelid or the meibomian glands.
What is the difference between internal and external hordeolum?
An internal hordeolum affects the Meibomian (oil) glands within the eyelids whereas an external hordeolum (stye) affects the glands associated with the eyelashes. Both conditions cause red and tender swellings of the eyelid. Traditional remedies such as hot spoon bathing and/or warm compresses may relieve symptoms.
What is the difference between hordeolum Internum and Externum?
An internal hordeolum (stye) is a bacterial infection of the meibomian glands inside the eyelids. Internal styes tend to be more severe and occur a little less often than an external hordeolum. An external hordeolum (stye) is a bacterial infection of the Glands of Zeis and/or Glands of Moll inside the eyelids.
What is the approximate match between ICd9 and ICd10?
This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code H00.014 and a single ICD9 code, 373.11 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is a stye on the outside of the eye?
An external stye or sty /ˈstaɪ/, also hordeolum /hɔːrˈdiːələm/, is an infection of the sebaceous glands of Zeis at the base of the eyelashes, or an infection of the apocrine sweat glands of Moll. External styes form on the outside of the lids and can be seen as small red bumps. Internal styes are infections of the meibomian sebaceous glands lining the inside of the eyelids. They also cause a red bump underneath the lid with only generalized redness and swelling visible on the outside. Styes are similar to chalazia, but they tend to be smaller and more painful, and they usually don't cause any lasting damage. They contain water and pus, and the bacteria will spread if the stye is forcefully ruptured. Styes are characterized by an acute onset and usually short in duration (7–10 days without treatment) compared to chalazia, which are chronic and usually do not resolve without intervention. Styes are usually caused by the Staphylococcus aureus bacterium.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for cough and wheezing
- 2. icd 10 code for severe involvement of left hip
- 3. icd 10 code for history of esbl
- 4. icd-10 code for lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy
- 5. 2016 icd 10 code for partial seizure disorder
- 6. icd 10 code for sprain, back:
- 7. icd 10 code for contraction alkalosis
- 8. icd-10 code for emphysema with copd
- 9. whats the icd-10 dx code for hepatorenal syndrome
- 10. icd 9 code for missing steps