What are the new ICD 10 codes?
· Z86.59 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z86.59 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z86.59 - other international versions of ICD-10 Z86.59 may differ.
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
· Depression, unspecified. F32.A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F32.A became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of F32.A - other international versions of ICD-10 F32.A may differ.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
agitated F32.2 (single episode) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F32.2. Major depressive disorder, single episode, severe without psychotic features. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. anaclitic - see Disorder, adjustment. anxiety F41.8. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code F41.8. Other specified anxiety disorders.
What is the ICD 10 code for history of depression?
2022 ICD-10-CM Codes F33*: Major depressive disorder, recurrent ICD-10-CM Codes › F01-F99 Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders › F30-F39 Mood [affective] disorders › Major depressive disorder, recurrent F33 Major depressive disorder, recurrent F33- Type 1 Excludes bipolar disorder ( F31.-) manic episode ( F30.-) Includes
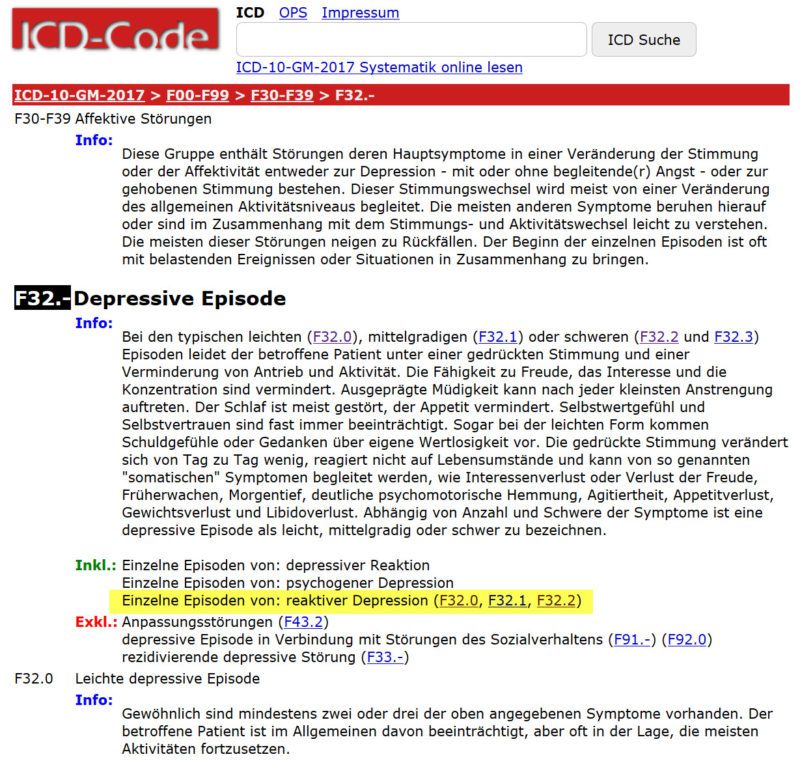
Is F32 9 a valid ICD-10 code?
9 – Major Depressive Disorder, Single Episode, Unspecified. ICD-Code F32. 9 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Major Depressive Disorder, Single Episode, Unspecified.
Is F32 a valid diagnosis code?
Next, we compare the old OUTDATED (FY 2021) Tabular with the new, CURRENT (FY 2022) Tabular. Note that the old OUTDATED code for “Depression” is F32. 9. Note the new, CURRENT code for “Depression” is F32.
What is depression F32 A?
F32. Major depressive disorder, single episode In typical, mild, moderate, or severe depressive episodes the patient suffers from lowering of mood, reduction of energy and decrease in activities.
What is the ICD code for Major depressive disorder?
Major depressive disorder, single episode, unspecified F32. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F32. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is diagnosis code F33 3?
3 Recurrent depressive disorder, current episode severe with psychotic symptoms.
What is the ICD-10 code for depression with anxiety?
2 Mixed anxiety and depressive disorder.
What does F43 23 mean?
23 – Adjustment Disorder with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood. ICD-Code F43. 23 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Adjustment Disorder with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood. Its corresponding ICD-9 code is 309.28.
What is the ICD-10 code for mild depression?
Code F32. 0 is the diagnosis code used for Major depressive disorder, single episode, mild. This falls under the category of mood [affective] disorders.
What does F41 8 mean?
8: Other specified anxiety disorders.
What is the ICD-10 code for severe major depression?
Major depressive disorder, single episode, severe without psychotic features. F32. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for major depressive disorder recurrent severe?
Major depressive disorder, recurrent severe without psychotic features. F33. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F33.
What is the ICD-10 code for major depressive disorder recurrent moderate?
Major depressive disorder, recurrent, moderate F33. 1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the Z86.59 code?
Z86.59 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of personal history of other mental and behavioral disorders. The code Z86.59 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is mental illness?
Mental disorders (or mental illnesses) are conditions that affect your thinking, feeling, mood, and behavior. They may be occasional or long-lasting (chronic). They can affect your ability to relate to others and function each day.
Is Z86.59 a POA?
Z86.59 is exempt from POA reporting - The Present on Admission (POA) indicator is used for diagnosis codes included in claims involving inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals. POA indicators must be reported to CMS on each claim to facilitate the grouping of diagnoses codes into the proper Diagnostic Related Groups (DRG). CMS publishes a listing of specific diagnosis codes that are exempt from the POA reporting requirement. Review other POA exempt codes here.
What are the factors that contribute to mental illness?
A number of factors can contribute to risk for mental illness, such as. Your genes and family history. Your life experiences, such as stress or a history of abuse, especially if they happen in childhood. Biological factors such as chemical imbalances in the brain. A traumatic brain injury.
How to get a diagnosis?
The steps to getting a diagnosis include. A medical history. A physical exam and possibly lab tests, if your provider thinks that other medical conditions could be causing your symptoms. A psychological evaluation. You will answer questions about your thinking, feelings, and behaviors.
What are the factors that affect the brain?
Your life experiences, such as stress or a history of abuse, especially if they happen in childhood. Biological factors such as chemical imbalances in the brain. A traumatic brain injury. A mother's exposure to viruses or toxic chemicals while pregnant.
What are the symptoms of a symtom?
Symptoms may appear at any age and include uncontrolled movements, clumsiness, balance problems, difficulty walking, talking, or swallowing. The disease has a progressive course with a decline in mental abilities, and the development of psychiatric problems.
What is Huntington's disease?
Huntington's disease (hd) is an inherited disease that causes certain nerve cells in the brain to waste away.
How many chances do you have Huntington's disease?
Others are aware of their environment and are able to express emotions.if one of your parents has huntington's disease, you have a 50-50 chance of getting it. A blood test can tell if you have the hd gene and will develop the disease.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for tachy brady syndrome
- 2. icd 10 code for behavioral dysregulation
- 3. icd 10 code for t2dm with hyperglycemia
- 4. icd 10 code for complication breast implant infection
- 5. icd 9 code for liposarcoma
- 6. icd 10 code for j plts
- 7. icd 10 cm code for major depressive disorder
- 8. icd 10 code for dental pre op
- 9. icd 10 code for anatomy
- 10. 2015 icd 10 code for dilation common bile duct