How many codes in ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · Hypercalcemia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. E83.52 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM …
What are common ICD 10 codes?
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R82.994 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Hypercalciuria. Idiopathic hypercalciuria. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R82.994. Hypercalciuria. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. …
What is the ICD 10 code for hypokalemia?
E83.59 ICD-10-CM Code for Hypercalcemia E83.52 ICD-10 code E83.52 for Hypercalcemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash. Request a Demo 14 Day Free Trial Buy Now Official Long Descriptor Hypercalcemia
What is diagnosis code k08.121 in the ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · ICD-10-CM Code E83.52 Hypercalcemia Billable Code E83.52 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Hypercalcemia . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . ↓ See below for any exclusions, inclusions or special notations
What causes hypercalcemia?
Hypercalcemia complications can include:Osteoporosis. ... Kidney stones. ... Kidney failure. ... Nervous system problems. ... Abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
What is E83 52?
ICD-10 code E83. 52 for Hypercalcemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is ICD-10 for hypocalcemia?
E83.51ICD-10 | Hypocalcemia (E83. 51)
What is E83 51?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E83. 51: Hypocalcemia.
What is the ICD-10 code for Macrocytic anemia?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D50 D50.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypokalemia?
ICD-10 | Hypokalemia (E87. 6)
What is the ICD-10 code for hyperkalemia?
ICD-10 | Hyperkalemia (E87. 5)
What is the correct ICD-10 code for leukocytosis?
288.60 - Leukocytosis, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for hyperlipidemia?
E78.5ICD-10 | Hyperlipidemia, unspecified (E78. 5)
What is ICD-10 code for osteoporosis?
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM CodesOsteoporosis ICD-9-CM & ICD-10-CM CodesOSTEOPOROSISOsteoporosis unspecified: 733.00M81.0Senile osteoporosis: 733.01M81.0Idiopathic osteoporosis: 733.02M81.812 more rows
What is the ICd 10 code for hypercalcemia?
E83.52 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Hypercalcemia . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Burnett's syndrome E83.52.
What foods are rich in calcium?
Foods rich in calcium include. Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt. Leafy, green vegetables. Fish with soft bones that you eat, such as canned sardines and salmon. Calcium-enriched foods such as breakfast cereals, fruit juices, soy and rice drinks, and tofu.
Why is calcium important for the body?
Your body needs calcium to help muscles and blood vessels contract and expand, to secrete hormones and enzymes and to send messages through the nervous system. It is important to get plenty of calcium in the foods you eat. Foods rich in calcium include. Dairy products such as milk, cheese, and yogurt.
What is the most important mineral in the body?
Calcium. You have more calcium in your body than any other mineral. Calcium has many important jobs. The body stores more than 99 percent of its calcium in the bones and teeth to help make and keep them strong. The rest is throughout the body in blood, muscle and the fluid between cells.
Do teenagers need calcium?
Growing children and teenagers need more calcium than young adults. Older women need plenty of calcium to prevent osteoporosis. People who do not eat enough high-calcium foods should take a calcium supplement. NIH: National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements.
What is the ICd code for nephrocalcinosis?
The ICD code E835 is used to code Nephrocalcinosis. Nephrocalcinosis, once known as Albright's calcinosis after Fuller Albright, or "Anderson-Carr" Kidneys, is a term originally used to describe deposition of calcium salts in the renal parenchyma due to hyperparathyroidism. It is now more commonly used to describe diffuse, fine, ...
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
Is nephrocalcinosis a mottling disease?
During its early stages, nephrocalcinosis is visible on x-ray, and appears as a fine granular mottling over the renal outlines. These outlines eventually come together to form a dense mass. It is most commonly seen as an incidental finding with medullary sponge kidney on an abdominal x-ray.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for positive quantiferon gold test
- 2. icd 10 code for bladder mas versus pseudomass
- 3. icd 10 code for men's annual physical exam age 42
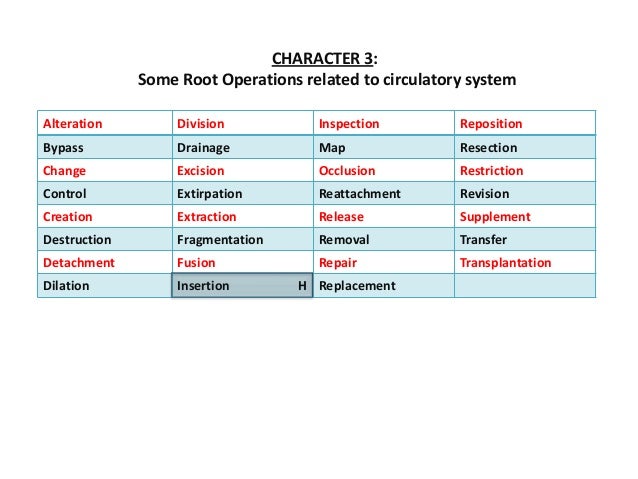
- 4. code for mri brain in icd-10-pcs
- 5. icd 10 code for upper sinusitis frontal
- 6. icd code for psa test
- 7. icd-10-cm 2018 offical code set in optum professional for physicians
- 8. icd 10 code for talipes equinovarus
- 9. icd 10 code for posterior capsular opacity
- 10. icd 10 code for lumbar spondylosis