E87.5 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of hyperkalemia. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. Hyperkalemia (hyperkalaemia in British English, hyper- high; kalium, potassium; -emia, "in the blood") refers to an elevated concentration of the electrolyte potassium (K+) in the blood.
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code E87.5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM E87.5 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for hypercalcemia?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E83.52. Hypercalcemia. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. E83.52 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM E83.52 became effective on October 1, 2018.
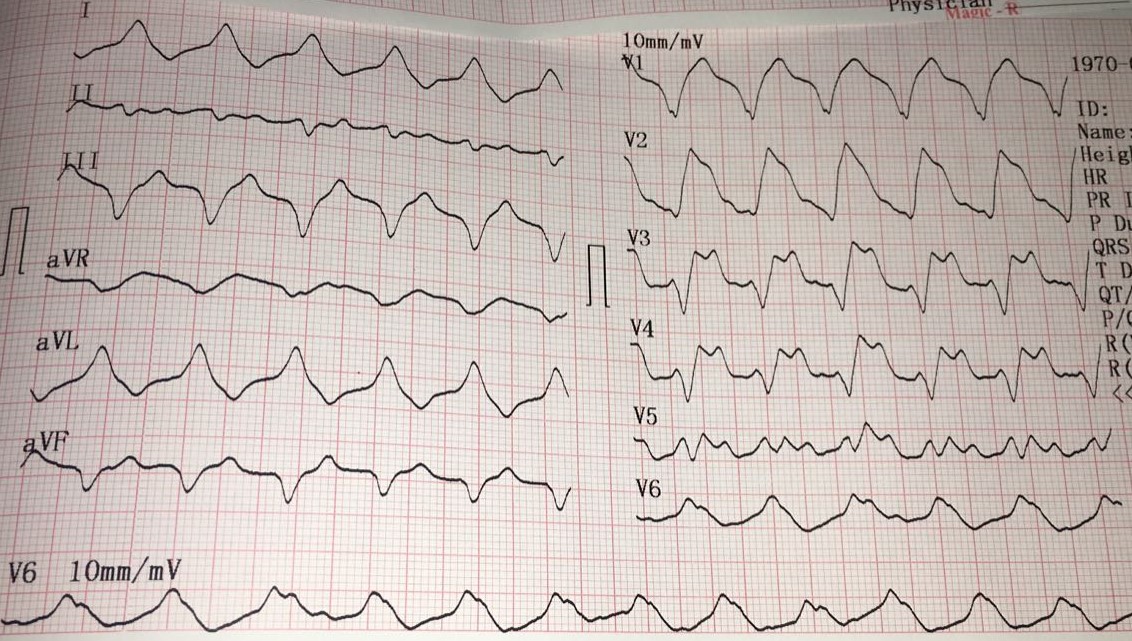
Can hyperkalemia cause EKG changes?
Hyperkalemia can cause a very wide range of EKG changes. The textbook sequence of changes illustrated above often doesn't occur. ( 29244647 ) Instead, hyperkalemia can mimic a wide variety of pathologies (including STEMI and all varieties of bundle/conduction blocks). Severe hyperkalemia (e.g. K>7 mM) can occur without obvious EKG changes.
How is the diagnosis of hyperkalemia confirmed?
If the telemetry/EKG shows features of hyperkalemia, this confirms the diagnosis. If the lab reports severe hyperkalemia but the EKG is normal, repeat the lab. The first step of treatment requires determining whether hyperkalemia is life-threatening (severe). No evidence-based definition for “severe” hyperkalemia exists.
What is the ICD-10-CM code for hyperkalemia?
ICD-10 code E87. 5 for Hyperkalemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for EKG changes?
R94.31ICD-10 code R94. 31 for Abnormal electrocardiogram [ECG] [EKG] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-9 code for hyperkalemia?
Lab-defined hyperkalemia was determined as serum potassium ≥ 6.0 mmol/L, and claims-based hyperkalemia was determined as any coded outpatient or inpatient discharge diagnosis of hyperkalemia (ICD9 267.7).
What is DX code Z51 89?
Encounter for other specified aftercareICD-10 code Z51. 89 for Encounter for other specified aftercare is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What is the difference between 93000 and 93010?
93000 includes the ECG with interpretation and report. 93005 is the tracing only without interpretation and report and 93010 is the interpretation and report only. We would expect providers to bill global if both the test and interpretation was performed by the same physician.
Can 93000 and 93040 be billed together?
The complete testing codes 93000, 93015, 93040 and 93224 may be billed by the same or different providers using the complete test code or respective component test codes, but each set is reimbursable only once per recipient, per day, any provider, per occurrence.
What does hyperkalemia mean?
Hyperkalemia is the medical term that describes a potassium level in your blood that's higher than normal. Potassium is a chemical that is critical to the function of nerve and muscle cells, including those in your heart. Your blood potassium level is normally 3.6 to 5.2 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
What is the medical code for potassium?
001180: Potassium | Labcorp.
Are there ICD-10 procedure codes?
ICD-10-PCS will be the official system of assigning codes to procedures associated with hospital utilization in the United States. ICD-10-PCS codes will support data collection, payment and electronic health records. ICD-10-PCS is a medical classification coding system for procedural codes.
What is the ICD-10 code for CVA?
ICD-10 Code for Cerebral infarction, unspecified- I63. 9- Codify by AAPC.
What is the ICD-10 code for rapid heart rate?
ICD-10 code R00. 0 for Tachycardia, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for multiple sclerosis?
What is the ICD-10 Code for Multiple Sclerosis? The ICD-10 Code for multiple sclerosis is G35.
What is the ICD-10 CM code for acute contact urticaria?
ICD-10 code L50. 6 for Contact urticaria is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is Encounter for other aftercare?
Encounter for other specified aftercare 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z51. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Z51.
What is the treatment for hyperkalemia?
Moderate hyperkalemia can generally be treated with a single diuretic (e.g. IV furosemide), followed by volume replacement with Lactated Ringer's to maintain a net even fluid balance. If this regimen fails, more aggressive therapies may be utilized with additional medications discussed below.
What is the best fluid for resuscitative fluid?
Isotonic bicarbonate is the preferred resuscitative fluid in metabolic acidosis (excluding lactic acidosis or ketoacidosis). The isotonic bicarbonate should be dosed with the goal of bringing the patient's serum bicarbonate level back to a high-normal level (e.g. bicarbonate 24-28 mM).
What is the backbone of kaliuresis?
The backbone of kaliuresis is a combination of potassium-wasting diuretics, which synergize to cause potassium excretion in the urine. #N#Diuretic dose should be adjusted based on the severity of the hyperkalemia and the degree of the renal dysfunction (renal dysfunction generally causes diuretic resistance).#N#In emergent hyperkalemia, it's better to err on the side of giving excessive diuretic. If the patient experiences a large-volume diuresis, this can be easily corrected by giving back IV fluid. Alternatively, if in inadequate diuretic dose is given, this may cause the patient to be dialyzed unnecessarily.
How much albuterol is needed for potassium?
Albuterol#N#Causes a small shift of potassium into cells.#N#Requires a lot of albuterol (10-20 mg, equal to about 4-8 nebulized treatments back-to-back). Logistically, the best way to achieve this dose is to provide albuterol as a continuous nebulized therapy.
Does isotonic bicarbonate work?
Isotonic bicarbonate infusions have been demonstrated to work, but only for patients with metabolic acidosis. ( 1552710, 24132, 1668124) This requires giving 1-2 liters of fluid, so it is not a viable treatment for patients with volume overload.
Does isotonic bicarbonate work in metabolic acidosis?
( 2402122) This counteracts the effect of increasing the pH, with an overall neutral effect on the potassium. Isotonic bicarbonate does work in metabolic acidosis.
How long does calcium chloride last?
ongoing bradycardia with hypoperfusion). Additionally, calcium only lasts for about 30-60 minutes, so the dose may need to be repeated.
What is the earliest manifestation of hyperkalaemia?
The earliest manifestation of hyperkalaemia is an increase in T wave amplitude.
What is the T wave in hyperkalaemia?
In hyperkalaemia, the T wave is “pulled upwards”, creating tall “tented” T waves, and stretching the remainder of the ECG to cause P wave flattening, PR prolongation, and QRS widening.
Where is Rob from UWA?
MBBS (UWA) CCPU Rob is an Emergency Medicine Advanced Trainee currently based at The Alfred Emergency & Trauma Centre in Melbourne, Australia. He has special interests in medical education, ECG interpretation, and the use of diagnostic and procedural ultrasound in the undifferentiated and unwell patient.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for chiroproc
- 2. icd 10 cm code for family hx migraine
- 3. icd 10 code for s93.401a
- 4. icd 10 code for abnormal imaging
- 5. icd 10 code for infected common femoral graft
- 6. icd 10 code for periapical abscess
- 7. icd 10 code for left eye stye
- 8. icd 10 code for contracture right hand
- 9. icd 10 code for status post tka
- 10. icd 10 code for premature infant 25 weeks